These sunny fruits related to apples and pears came to us from the imperial gardens of Japan. Juicy, bright, tart ... But what is known about the beneficial properties and contraindications of Japanese quince?
Material Content:
The chemical composition and calorie content of Japanese quince
In our climate, the shrubs of genomeles (the second name of Japanese quince) have taken root perfectly. They are often used for decoration, because their leaves have a bright yellow color. The plants are unpretentious, abundantly bear fruit and mature quickly.
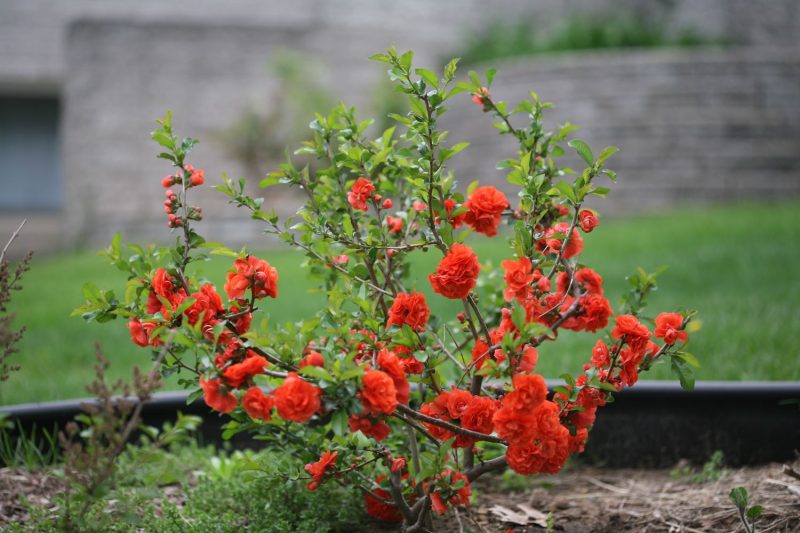

Although the fruits are not too palatable, hard, tart, with a weak aroma, they are not inferior to other fruits in their useful properties.
The composition of the Japanese quince includes:
- ascorbic acid (more than in currants and lemon);
- vitamins of group B, E, K, PP;
- carotene;
- organic acids (malic, tartronic, citric);
- minerals (iron, calcium, zinc, copper, silicon, boron, phosphorus);
- antioxidants;
- tannins;
- cellulose;
- fructose;
- essential oils.
According to the amount of iron, henomeles is a champion among other fruits.
In 100 g of quince - 30 mg of this element that is beneficial for the body. Therefore, eating fruit is a good prophylaxis of anemia.
The calorie content of the sun fruit is low: 40 - 45 kcal per 100 g of product. But in dishes prepared from quince, the number of calories grows. Compote has 75 kcal, and jam or jam - about 170 kcal.
Japanese quince: useful properties

The composition rich in valuable substances determines the properties of the genomeles:
- restorative;
- immunostimulating;
- atherosclerotic;
- antispasmodic;
- diuretic;
- fastening;
- hemostatic;
- antioxidant;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antivirus;
- wound healing;
- antiemetic.
Such an impressive characteristic of Japanese quince allows the use of fruit for the prevention and treatment of various diseases.
How do fruits affect the body?
- Strengthen the immune system, accelerate recovery during colds.
- Remove toxins and salts of heavy metals.
- Normalize the work of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Eliminate diseases of the respiratory system and oral cavity.
- Lower cholesterol.
- Strengthen blood vessels.
- Normalize blood flow.
- Improve vision, relieve eye fatigue.
- Prevent liver disease.
- Strengthen teeth, bones, joints.
- Improve digestion.
- Reduce exposure to radiation, radiation.
- Normalize blood pressure.
- Improve skin condition.
For men
Quince is especially beneficial for men's health. Eating fruits normalizes the blood supply to the pelvic organs, which positively affects potency. In men, libido rises, erectile function is restored.
For women

The fruits of Japanese quince have a positive effect on the female body:
- stop uterine bleeding;
- reduce discharge during heavy menstruation;
- normalize the microflora of the genital organs;
- improve hair condition;
- rejuvenate the skin, eliminate small wrinkles.
Separately, it should be noted the effect of genomeles during pregnancy.
Doctors recommend that women, expecting a baby three times a week, to consume solar fruits.
The benefits of quince during pregnancy:
- supplies nutrients without harming the figure;
- eliminates the symptoms of toxicosis;
- interferes with swelling;
- struggling with anemia.
Nursing mothers compotes, decoctions or jams of sunny fruits should be used with caution because of the possible development of allergies in children. It is necessary to introduce fruits into your diet little by little, observing the reaction of the baby.
The healing properties of henomeles

Quince is used to prevent and treat such diseases:
- atherosclerosis, high cholesterol;
- nervous exhaustion, stress;
- disturbances in the endocrine system, diabetes mellitus;
- enterocolitis, bloating;
- obesity, metabolic disorder;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- hemorrhoids;
- liver pathology;
- flu, a cold;
- tracheitis, bronchitis;
- asthma, pulmonary tuberculosis;
- ear diseases.
Application in traditional medicine
The medicinal properties of henomeles have been used by healers for many years to prepare effective traditional medicine.
For the prevention and treatment of diseases, the pulp of the fruit, the leaves of the plant, as well as the seeds of Japanese quince, are used. Since the latter have hazardous substances inside, preparing preparations based on them should be especially careful without opening the bones.
Decoctions and compotes with Japanese quince

Popular recipes for traditional medicine:
- A decoction of dried fruits will effectively eliminate uterine bleeding in women. The drug should be drunk half a cup 2 to 3 times a day. Also, the decoction relieves pain during menstruation, if you start taking it 7 days before they start.
- Henomeles leaf tincture lowers hypertensive blood pressure. To prepare the product, 100 g of leaves should be filled with 100 ml of alcohol or vodka. Close the container tightly and place for 7 days in a dark, cool place, then strain. Use tincture should be 20 drops 2 times a day before meals.
- Quince juice is used as lotions for the treatment of hemorrhoids and anal fissures.
- A decoction of seeds improves the digestive system. For its preparation, it is necessary to pour dried seeds (1 g) with water (200 ml), cook for 15 - 20 minutes on low heat. Drink a decoction should be 1 tbsp. l3 times a day after meals. Also, this tool effectively eliminates the symptoms of a cold, fights cough and fever.
- Stewed fruit from sunny fruits nourishes the body with iron, increases hemoglobin in case of anemia. To do this, peel the fruits, and carefully remove the seeds. Cut the pulp into pieces, boil for 10 - 15 minutes and squeeze. Then cook the broth until it reaches the consistency of the syrup. Means to use 50 g 3 times a day. Compote also eliminates indigestion.
- For quick healing of wounds and burns on the skin lotions from an aqueous infusion of seeds (1 tsp) are used.
- Tincture from the leaves of the plant normalizes the sugar level in patients with diabetes. To cook it, you need to fill in the leaves (1 tbsp. L.) With boiling water (20 ml). After cooling, the tincture should be filtered. Use the tool for 2 tbsp. l 3 times a day.
- Infusion of quince fruits relieves inflammation of the eyes. To do this, it is used in the form of lotions.
Decoctions, tinctures and syrups can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 4 days.
Japanese quince jam: benefits and harms
Jam made from the pulp of peeled ripe fruit is a delicious treat. The healing properties of quince do not disappear during heat treatment, so jam has a lot of useful properties.

Among them:
- heart disease prevention;
- stress relief, fatigue;
- increase immunity;
- preventing the development of oncology;
- the fight against anemia;
- normalization of the digestive tract;
- prevention of seasonal colds;
- lower fever;
- cystitis treatment (due to diuretic effect);
- elimination of toxicosis in pregnant women.
Due to the sugar present in quince jam, do not abuse the treat. Otherwise, there may be problems with teeth and extra pounds.
To maximize the effectiveness of treatment, you must listen to the advice and recommendations of a doctor in order to avoid unpleasant side effects.
Contraindications and possible harm
Although Japanese quince is a healthy fruit, it, like all products, has contraindications for consumption.

You can not enjoy the fruits:
- with a stomach ulcer and duodenal ulcer;
- with a tendency to constipation (provokes complications);
- with enterocolitis;
- with thrombosis (the fruit thickens the blood);
- with pleurisy;
- people whose work is associated with increased tension of the vocal cords (speakers, singers, actors);
- with individual intolerance to the product;
- children under 3 years of age, due to the high probability of allergies.
Care should be taken in nursing mothers.
Raw quince can cause harm to the body due to the high concentration of toxins in the fruits. Eating too much fruit (more than 2 per day) can cause digestive upsets. It is safer to eat already processed sun fruits: after baking or boiling.
Of particular danger are quince seeds, in which amygdalin accumulates. This substance can be converted into cyanide during digestion - a dangerous poison that causes poisoning. Therefore, before preparing quince dishes, it must be thoroughly peeled.
If you follow the tips for use and include quince in the diet several times a week, the fruits will bring only benefits to the body.