The primary stage of syphilis, when the formation of chancres occurred, in the absence of proper therapy is followed by secondary syphilis. It develops 2 to 3 months after the pale treponemas enter the body fluids.
Material Content:
What is secondary syphilis
Secondary syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease, when all tissues and organs in the human body are affected. The causative agents of the disease spread throughout the internal organs, lymph nodes, and nervous system and affect them. Infection occurs more often through sexual contact, and in rare cases, through household use of a patient’s personal hygiene items for a long time. The disease develops systemically.
The duration of the disease reaches 2 to 5 years.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
On the surface of the epidermis and mucous membranes of the patient, rashes of various types usually appear.
Signs of secondary syphilis resemble the flu state:
- migraine attacks;
- body aches;
- fever.
Common symptoms of secondary syphilis:
- hair loss on the head;
- the manifestation of discolored spots on the neck or in the chest, their diameter reaches 0.3 - 1 cm and is surrounded by a dark border;
- hoarse voice due to damage to the ligaments;
- peeling of the surface of the skin.
The resulting rashes tend to disappear without scarring and atrophy.
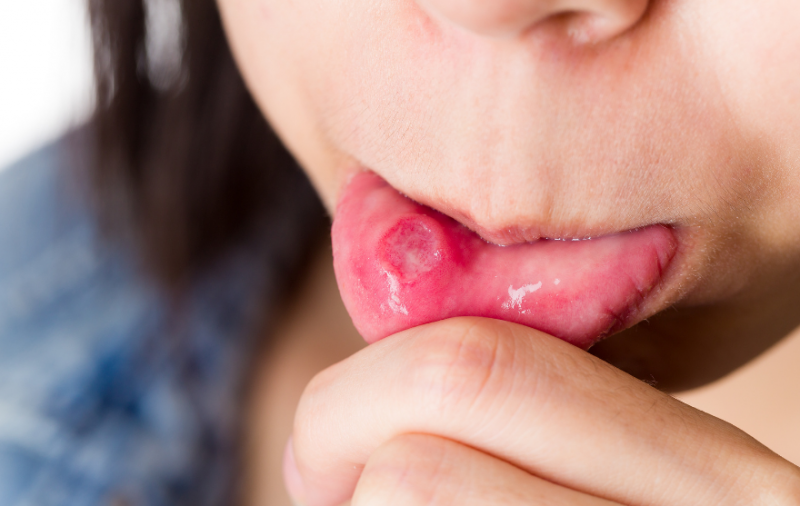
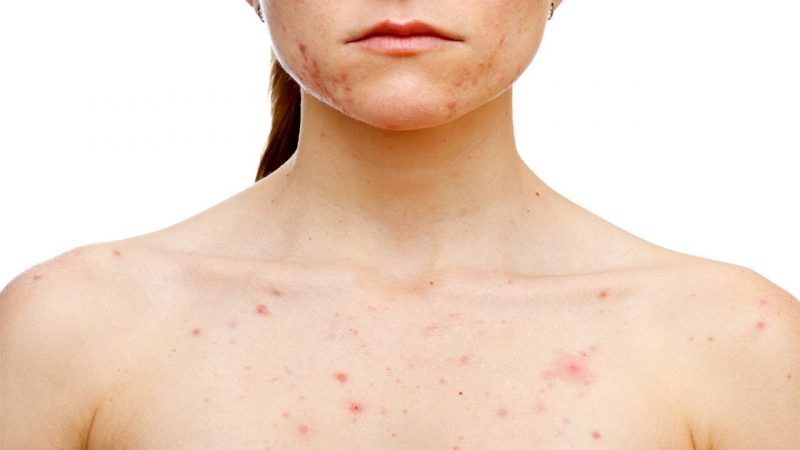
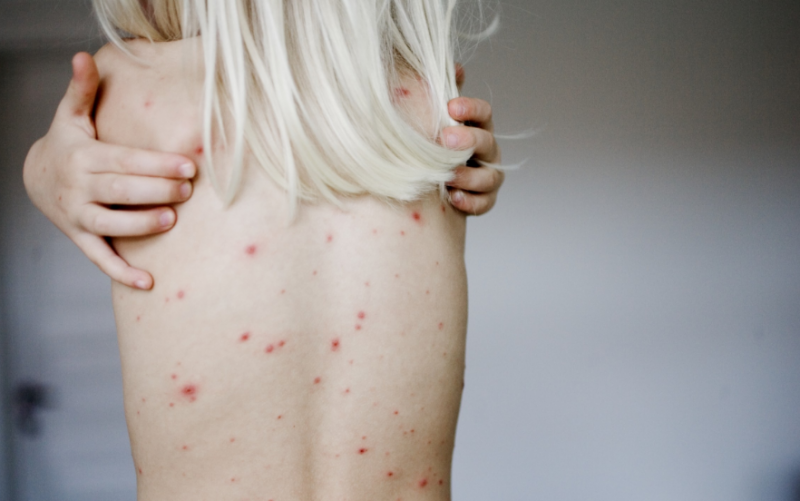
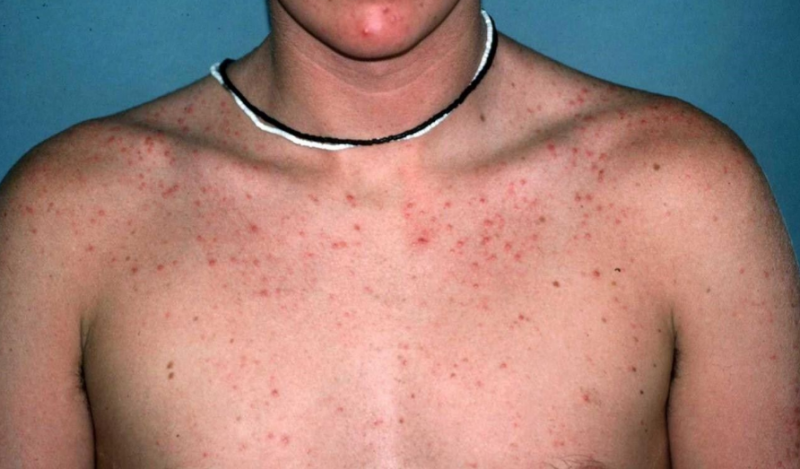
Rash
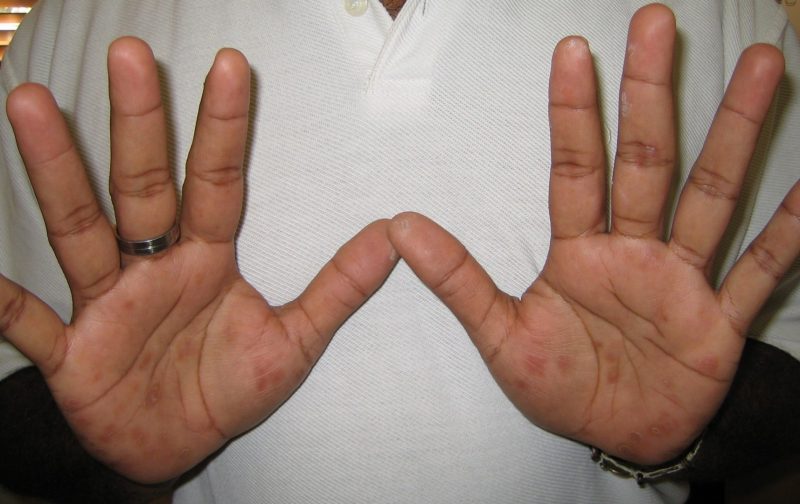
The main symptom of secondary syphilis is a rash that has arisen and spread over the surface of the whole body, including on the palms and soles.
Basically, a rose-colored rash appears in the form of pink or red spots - razole. It is observed in 75 - 80% of victims of syphilis. It can disappear without treatment after 3 to 6 weeks after manifestation.It occurs due to a violation of the integrity of blood vessels.
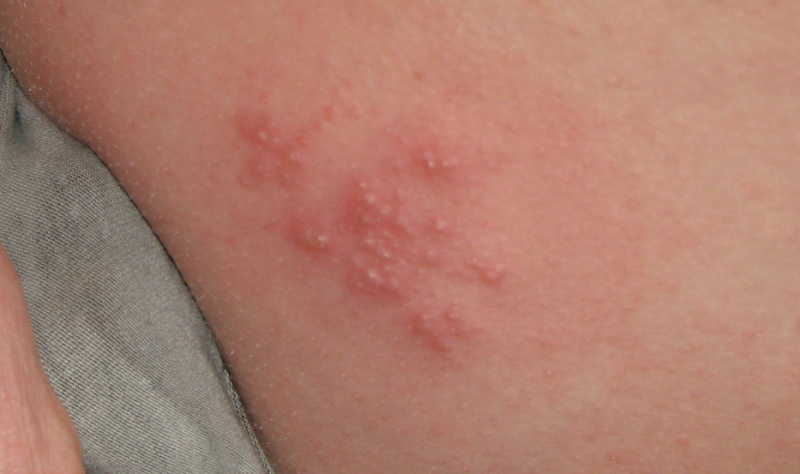
Papular Syphilis
A papular rash, or nodular, can also occur at this stage of the disease. It is represented by nodules (papules), which are sometimes combined with spots already described. They spread on the surface of the skin, oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, appear on the gums, lips, tongue.
There are several types of rash, depending on its size:
- lenticular;
- milky;
- coin-like;
- plaque-like.
Papules can grow and merge with each other.
Pustular
Pustular syphilis often develops simultaneously with nodular. Sometimes it is a monomorphic rash. Pustules in the form of pustular elements develop a second time by the disintegration of the papule in the middle. There is a rise in the epidermal cover of pustules. At the end of the process, a cavity containing pus appears.
This type of disease is not common, mainly in people with some other serious illness or with weakened immunity. Such people include drug addicts, alcoholics, malnourished people or those with hypo- and vitamin deficiency.
Pustular syphilis happens:
- acne;
- pockmarked;
- impetiginous;
- ectimatous;
- syphilitic rupee.
Pathology is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. With rashes, tissue destruction occurs.
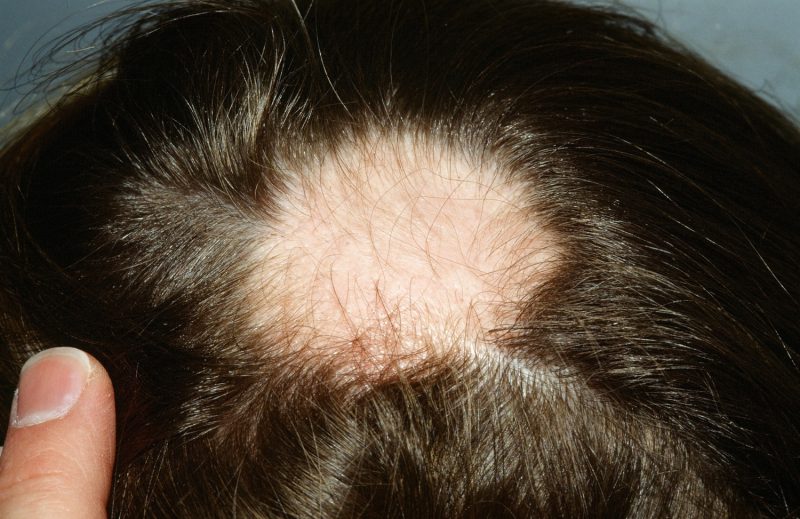
Alopecia
Syphilitic alopecia is a massive hair loss. More often it begins to appear 6 months after the discovery of the first signs of the disease. Alopecia occurs due to intoxication and a sharp defeat of the endocrine and nervous systems under the influence of infection.
In medicine, 3 main types of alopecia are distinguished:
- Small focal. Small bald spots appear on the head in a chaotic order, not interconnected. The hairs fall out partially, but not completely. Visually, this picture resembles a moth-eaten fur hat.
- Diffuse. It appears, starting with the temples, spreading gradually throughout the head. Hair loss does not look typical for syphilis, the doctor "by eye" will not immediately be able to correctly determine the cause.
- Mixed. It is a combination of small focal and diffuse alopecia. This type of baldness spreads quite quickly. Hair does not grow back earlier than 1 - 2 months after resorption of the infiltrate.
Diagnostic Methods
Dermatovenerologists conduct modern highly sensitive and specific laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Direct. They are aimed at identifying pathogens or their genetic material in the affected foci.
- Indirect. Contribute to the detection of antibodies to pathogens in the blood.
Direct research methods:
- TPM - conducting microscopy in the dark field of a microscope;
- UIF - the use of direct immunofluorescence in order to identify samples of lesions in the mouth or other foci;
- PCR - polymerase chain reaction.
Indirect serological tests are nontreponemal and treponemal. The first (NTT) include:
- a microprecipitation-based reaction with plasma and inactivated serum (RMP);
- Plasma-response test (RPR)
- a study for the sign of sexually transmitted diseases (VDRL);
- testing with toluidine red unheated serum (TRUST);
- Reagin Screening (RST);
- Unrefined Serum Reagin Test (USR).
For the use of TT, an antigen with treponemal origin is used by conducting such studies:
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA);
- passive hemagglutination (RPHA);
- immunofluorescence (RIF);
- immunoblotting;
- immunochemiluminescence (IHL);
- At the patient’s bedside, quick tests of PBT and RIBT are performed to detect the immobilization reaction when pale treponema appears.
Treatment features
In order for the treatment of secondary syphilis to give a result, it is necessary to carry out a number of procedures:
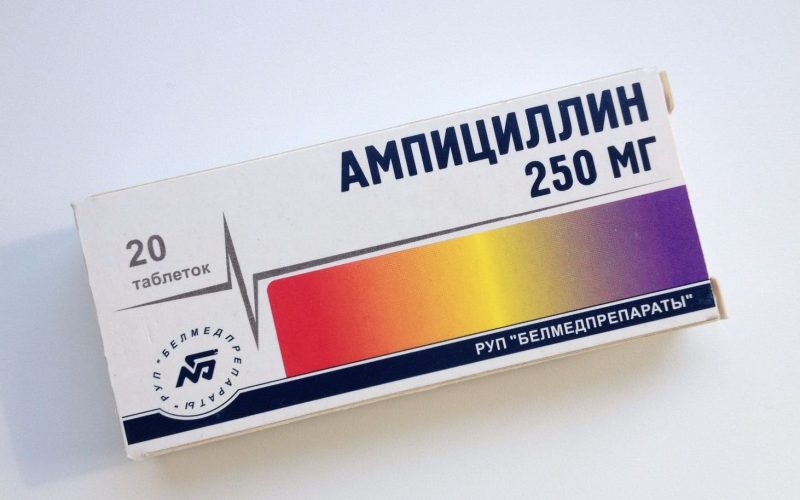
- Antibiotic therapy.In view of the sensitivity of the causative agent of syphilis to antibiotics of the penicillin group of drugs, they are used for the treatment of the disease. The most common are Oxacillin, Carbenicillin, Ampicillin, Doxacillin. They are able to be easily absorbed into the blood and quickly excreted from the body. For the effectiveness of their impact, it is necessary to constantly maintain the concentration of drugs in the patient's blood at the proper level. Intramuscular injection is carried out every 3 hours for 24 days. It is advisable to do this in a hospital setting.
- Nonspecific method of treatment with immunostimulants (Pyrroxan, Diucioron, Metirolacil, Levamisole). It is worth using as an injection biogenic stimulants in the form of an extract of the placenta, vitreous humor, aloe. Ultraviolet therapy is also prescribed. Do not give up vitamin therapy.
A sexually transmitted disease cannot be cured immediately. The use of the advertised "miracle means" that destroy the causative agent of syphilis with one injection can significantly complicate further therapy.
The dangerous effects of syphilis
Secondary fresh syphilis with improper treatment or refusal of therapy proceeds to the next stage - tertiary syphilis.
The disease can carry a number of health consequences and complications:
- there is a breakdown of the mucous membrane in the mouth;
- collapses the nasal septum and the hard palate;
- the voice is changing;
- upset breathing;
- the process of eating is complicated;
- sometimes loss of vision and hearing occurs;
- bones and cartilage on the face are affected, a cavity in the nose is formed.
The patient may become disabled or die, as vital organs (heart, liver, brain, blood vessels) are involved in the destruction process.
Forecast and preventive measures
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary to listen to the general recommendations of specialists:
- Avoid casual intimate relationships
- use high-quality condoms in any form of sexual intercourse;
- go through systematic examinations at the doctor;
- regularly take smears for laboratory tests;
- Do not contact closely with unfamiliar people;
- keep personal hygiene items in use;
- Check the cleanliness of bathrooms and towels in hotels.
If there is a person with a diagnosis of syphilis in the environment, do not use his personal belongings.
An emergency form of prevention is carried out in case of unprotected sexual contact:
- it is necessary to wash with a soap solution;
- thoroughly process the genitals and deeply rinse with antiseptic agents (Gibitan, Tsidipol, Miramistin);
- visit the bathroom and urinate.
In the near future, you should consult a venereologist with a detailed description of the situation, since the above procedures cannot accurately prevent the disease.
At the first suspicion of infection, you should contact a specialist for diagnosis and for individual selection of antibiotics in case of confirmation of infection.