Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, the symptoms and treatment of which directly depend on the form of the disease. Pathology can be acute as well as chronic. It is important to notice the signs of the disease in time and seek help, since ignoring the body's signals can lead to unpleasant consequences, even death.
Material Content:
Pancreatic Inflammation: Causes
According to statistics, the two main causes of the development of inflammation in the gland are excessive alcohol consumption or gallstone disease.
In 70% of cases, pancreatitis occurs due to alcoholism, in 20% due to obstruction of the duct with calculus, and the remaining 10% have several triggering factors:
- frequent food poisoning;
- injuries of the abdomen in the pancreas (left hypochondrium);
- infectious or viral diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- malfunctions of the sphincter located in the gland;
- fungal diseases.
In addition, the disease can develop as a complication after surgery in the abdominal cavity or after endoscopic procedures.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
The nature of the manifestations of the disease depends on the form of the course of pancreatitis, the individual sensitivity of the patient, as well as the area of the affected area. Symptoms of pancreatic inflammation in women are important to distinguish from problems with the ovary, when the pain can only radiate under the left rib. And in children, such symptoms can occur during banal poisoning.
A chronic course is characteristic of chronic pancreatitis, often, patients are not even aware of the presence of the disease until the first serious exacerbation. The acute form of pathology, on the contrary, has pronounced symptoms. During the attack, the patient without fail requires qualified medical care.
Acute form of pancreatitis
The pancreas is a small organ, but it performs the most important functions in the body - it produces insulin, which is necessary to maintain normal blood sugar levels, as well as digestive enzymes that help break down food that gets into the intestines. During inflammation, all functions of the organ are impaired, and serious damage can lead to a chronic disease such as diabetes.
To avoid this, you need to recognize the symptoms in time and help the patient:
- The girdle pain, which is localized in the hypochondria, is often greater on the left. The painful sensations are intense, can not be relieved by the use of medications, provoke nausea, vomiting. In severe cases, pain shock may develop and, against this background, death may occur;
- aversion to any food, the presence of inclusions of bile in the vomit;
- a change in key indicators - fever, palpitations, rapid breathing, lowering blood pressure;
- severe heartburn and dry mouth;
- frequent burping, hiccups;
- bloating of the upper abdomen due to digestive dysfunction;
- disorder of the stool - carrying, constipation, the presence in the feces of particles of undigested food.
The general well-being of the patient is gradually deteriorating. Particular attention should be paid to the appearance of the skin. White or bluish tint of the skin appears most often, it is not as dangerous as the yellowish color. Jaundice speaks of the reactive (most dangerous) form of pancreatitis, it occurs due to compression of the gallbladder and its duct is greatly increased in size by the pancreas.
At the slightest yellowing of the sclera or skin, you need to urgently seek medical help.
Chronic inflammation of the pancreas
Chronic pancreatitis has a hidden course and makes itself known only during an exacerbation of the process. An attack of pain can provoke a violation of the diet, alcohol intake, severe stress and so on.
The clinical picture of exacerbation is similar to the acute form of inflammation:
- localization of pain - the upper abdomen, in the hypochondria. Sensations are girdle-like and can be given to the shoulder blade, back or sternum;
- violation of the digestive tract - nausea, belching, vomiting, bloating, loose stools, constipation;
- changes in heart rate, pressure, temperature.
During the period of the disease calming down, the symptoms disappear, but pancreatitis still makes itself felt. The patient complains of constant constipation or carrying, which arise as a result of insufficient digestion of food in the intestines, flatulence. Fragility of hair and nail plates, dryness and peeling of the skin, and the rapid onset of fatigue also appear.
It is interesting:dry mouth
Diagnostic measures
To diagnose acute or exacerbated pancreatitis, a clinical picture and anamnesis are usually sufficient, and an examination of the body will be necessary to detect latent inflammation.

Upon admission to the hospital, the patient is prescribed the following studies:
- routine blood test - shows common signs of inflammation in the body (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, increased white blood cell concentration);
- determining the level of glycemia (glucose) in the bloodstream - is carried out to exclude the development of diabetes or a pre-diabetic condition due to damage to the islets of Langerhans - areas of the pancreas in which insulin is produced;
- blood biochemistry - not a comprehensive study is carried out, but the determination of exclusively gland enzymes (trypsin, amylase, lipase);
- ultrasound of organs located in the abdominal cavity;
- Esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy - allows using the thin tube with a small camera to examine the gastrointestinal tract from the inside;
- X-ray examination of the abdominal organs;
- general analysis of feces and urine.
In unclear cases, the patient may also be prescribed computed tomography, but they rarely resort to it due to the high cost of the procedure and long bursts.
Treatment for pancreatic inflammation
To maintain the remission of chronic pancreatitis, it is usually sufficient to follow a diet and take enzymatic drugs. The tactics for treating exacerbation and acute inflammation are no different. The patient must be hospitalized, carried out detoxification therapy, stabilize the pancreas.
Medications
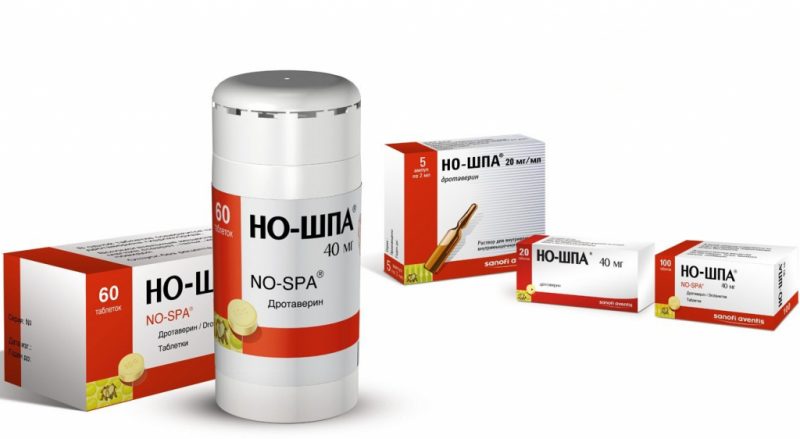

To alleviate the condition of the patient and eliminate inflammation, the following medications are used:
- antispasmodics (No-shpa, Baralgin);
- anticholinergics (Atropine, Metacin);
- H2 blockers (famotidine);
- pancreatic enzymes (Festal, Mezim);
- adsorbents (Sorbex, Enterosgel);
- antibiotics
- eubiotics.
In the first day, the patient should starve, it is allowed to drink ordinary water. Starting from the second day, various products are gradually introduced, however, a person can return to his usual diet only after a few months.
Folk remedies
Treatment of inflammation of the pancreas with folk remedies can only begin after the acute stage has faded. Non-traditional methods should be applied only at the same time as conventional medicine and only after consultation with your doctor. Self-medicating, a person can cause irreparable harm to his health.
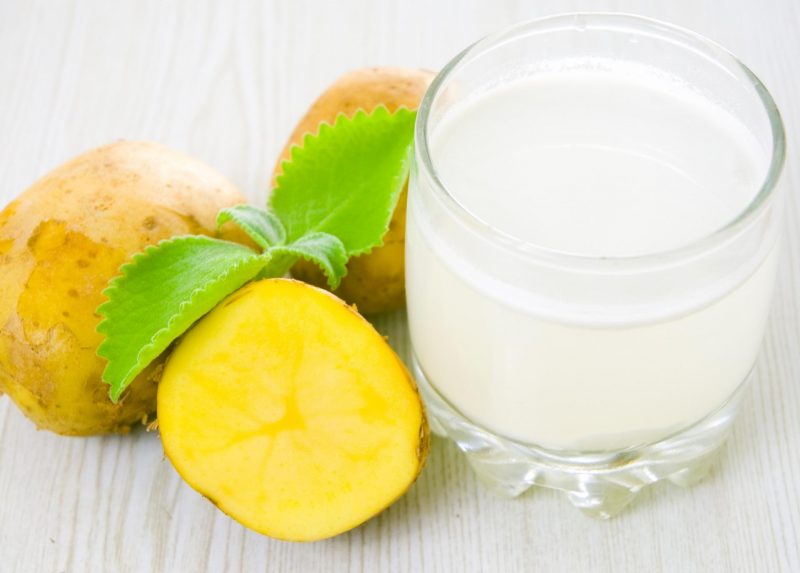

Well established as a medicine for pancreatitis, potato juice. It should be drunk 100-150 ml before a meal, 1-2 times a day is enough. It is important that each serving of juice is squeezed immediately before use.
Also, traditional medicine often resortes to herbal preparations:
- yarrow, chamomile, calendula:15 g of dried herbs pour 200 ml of boiling water, let cool. Drink 70-100 ml of infusion half an hour before meals.
- barberry bark:in a glass of boiling water add a large spoonful of crushed bark, cool. Take a tablespoon before each meal.
- immortelle, wormwood, chamomile (flowers):mix these herbs in a ratio of 3: 1: 2, five tbsp. tablespoons pour 1.5 cups of boiling water and allow to cool. Drink 100 ml three times a day.
Read also: Chamomile pharmacy: medicinal properties
Nutrition and diet - what can you eat and what can not?
Diet for inflammation of the pancreas plays a big role in the treatment process. During acute pancreatitis, the patient is forbidden to eat any food for up to 2 days, then foods are gradually introduced into the diet. At first, you can eat thin cereals strictly on the water, without adding salt, sugar, milk and other things. With a good course, after a week it is allowed to eat vegetable soups, boiled fish and dietary meat a little. The patient should be on a diet for several months.
In the remission stage, it is important to exclude food products that load the pancreas and can trigger a new attack:
- alcohol;
- chocolate;
- smoked meats;
- fatty food;
- fried foods;
- dairy products from high fat milk;
- legumes, cabbage;
- Tea coffee.
You need to eat often and little by little, observe the temperature regime of food (about 50 degrees), select foods that have a beneficial effect on digestion.
Possible complications
Both acute and chronic pancreatitis can lead to complications. Moreover, the latent form of the course often provokes unpleasant consequences, since the gradual destruction of tissues is almost asymptomatic.
Possible complications:
- impaired glucose tolerance, diabetes;
- gland abscess;
- damage to other organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cysts in glandular tissues;
- mechanical yellowness of the skin.
In advanced cases, pancreatitis leads to severe intoxication of the body and death.
Exacerbation
For the prevention of exacerbations, it’s enough not to violate dietary rules and take medications prescribed by your doctor. In addition, it is recommended to periodically undergo examinations, take tests and do an abdominal ultrasound. You also need to avoid stress, maintain immunity at the proper level, eliminate or sharply limit glucose intake.