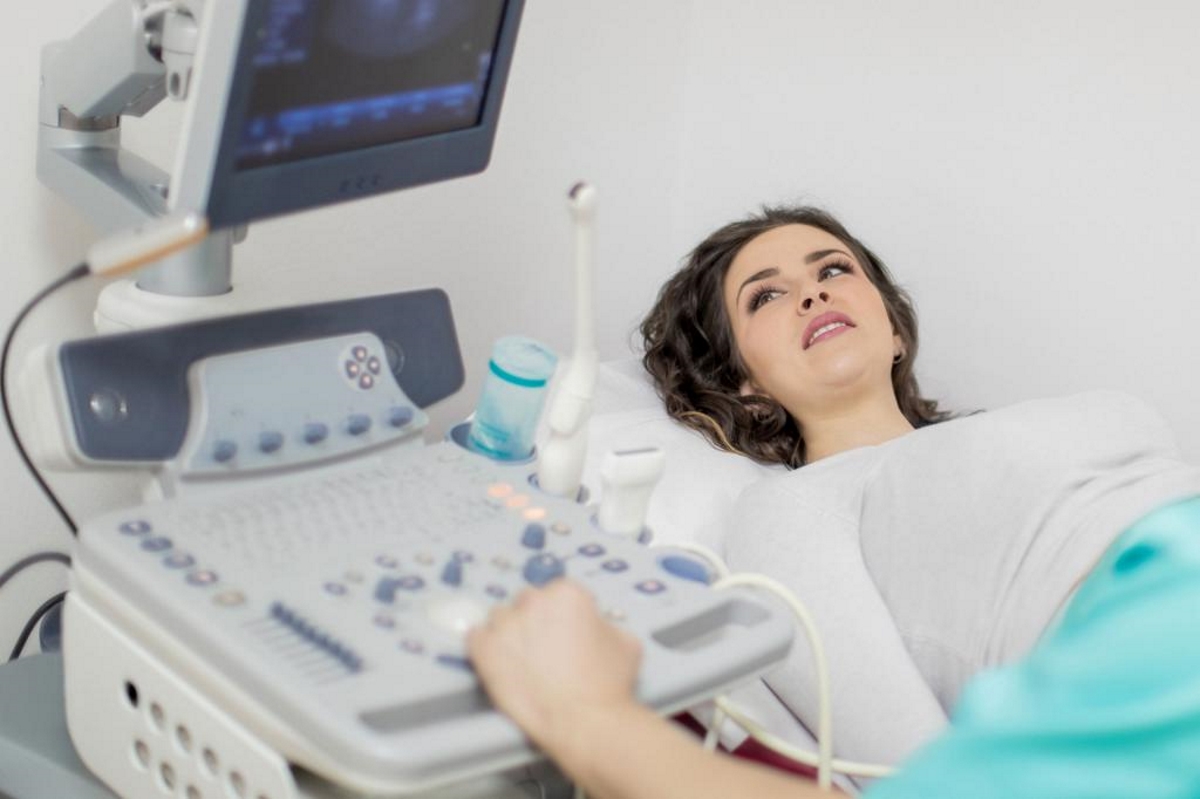
Ultrasound monitoring of internal organs has long ceased to be a curiosity. Today, transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound of female genital organs is able to show the most detailed picture. An additional bonus of such a procedure for expectant mothers is the opportunity to find out the gender of the unborn child.
Material Content:
Description and features of the method
Ultrasound examination is recognized as one of the safest and most accurate ways to diagnose the condition of the human body.
The ultrasound method has many common features with echolocation. The sound wave sent by the ultrasonic sensor is reflected from the organs and returns back to the device. This data exchange forms a picture on the screen of the device, and a specialist can observe what is happening inside the patient’s body.
Given all the positive aspects, it is the ultrasound method that is recommended for examining the reproductive female organs. With its help, it is realistic to track the condition of the fallopian tubes, ovaries, bladder and uterus. In addition, this method allows you to detect pregnancy in the early stages.
Note! There are several types of ultrasound OMT, the most common of them are transabdominal and transvaginal. The first is considered external and is carried out through the front wall of the abdomen. In a transvaginal study, the inner wall of the vagina is involved.
When transvaginal pelvic ultrasound is prescribed
Transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs is indicated in such cases:
- the need to monitor the maturation of follicles in the ovary;
- tracking early pregnancy (up to 12 weeks);
- finding out the cause of infertility;
- diagnosis of gynecological pathologies;
- monitoring the condition of the cervix (especially relevant for the threat of premature birth);
- malfunctions of the menstrual cycle;
- frequent pain in the lower abdomen;
- suspected ectopic pregnancy;
- tracking the presence of tumors in the pelvis;
- urinary incontinence;
Note! Transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs is acceptable for prevention, i.e. if the patient is not worried. For women under the age of 40, studies are shown once every two years. After 40 years - every year. This approach will allow timely identification of existing gynecological and urological pathologies.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for transvaginal pelvic ultrasound should take into account the type of diagnosis: each of them involves a certain number of preliminary actions.
Nevertheless, there are general preparatory points, consisting in the following:
- A few days before the examination, it is recommended to refuse food that can provoke gas formation (fiber-rich foods, legumes, alcohol, dairy products).
- If a few days before the examination, the patient underwent an X-ray procedure using barium, it is recommended to transfer the ultrasound. The chemical element can affect the accuracy of the results of ultrasound diagnostics.
- Immediately on the day of the examination, the intestines should be cleaned first.
Advice! If the patient has problems such as bloating or gas, a few days before the study, it is permissible to take Espumisan or Mezim Forte. But immediately on the day of the ultrasound, you should refuse to take the medicine. Before trans vaginal ultrasound, a small need should be addressed.
There are practically no contraindications to the ultrasound examination. The exception is periods of menstruation: blood discharge makes the carrying out of a diagnostic procedure impossible.
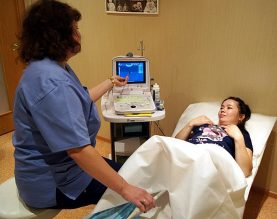
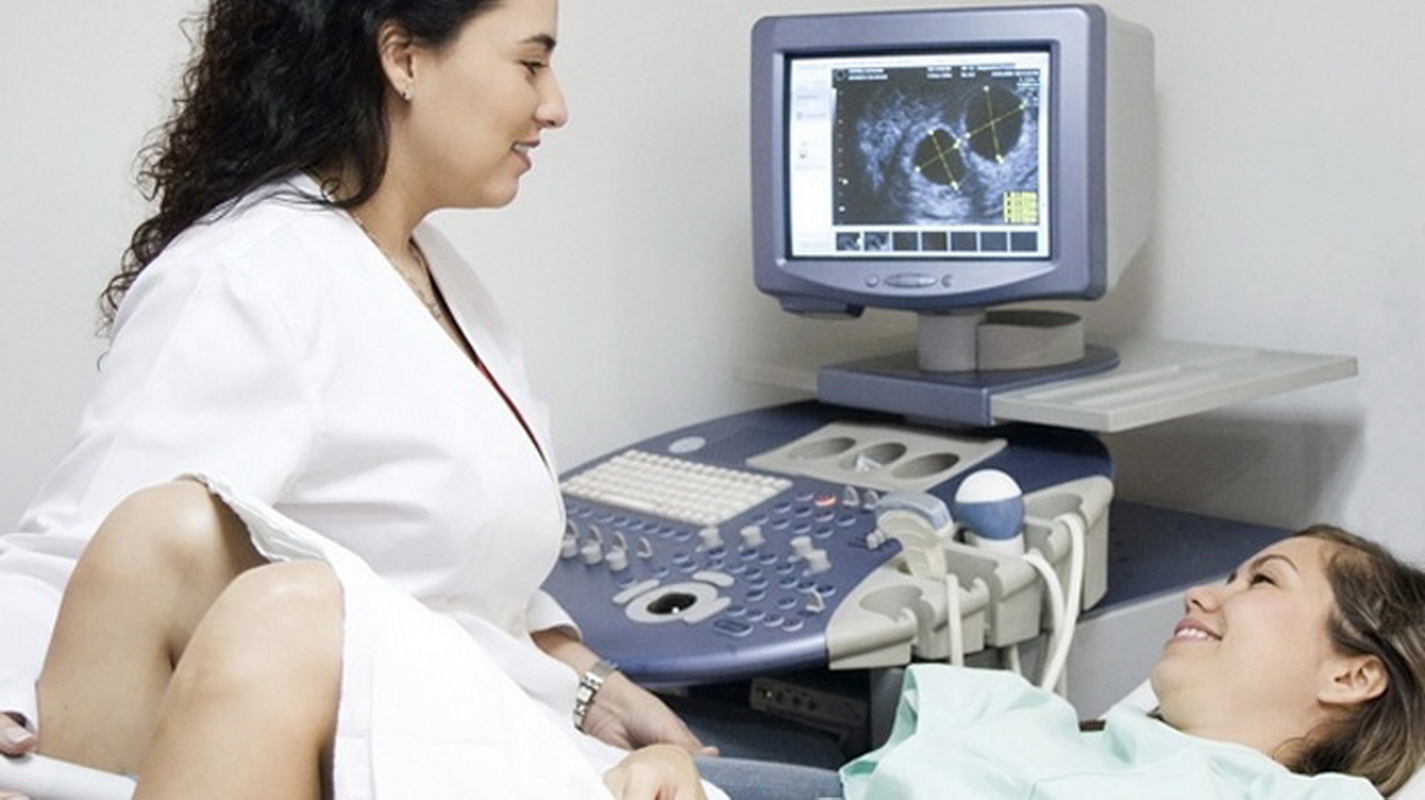
How is the study going
In order to examine the uterus and appendages, diagnose erosion, polycystic, ultrasound should be performed on the 7-10th day of the menstrual cycle. If you suspect uterine fibroids, the examination is best done after the completion of menstruation. Endometriosis is most effectively monitored immediately before menstruation. To assess follicular maturation, for example, when planning conception, ultrasound is performed on 5.9 or 14-17 days.
Research is carried out by a specialist in ultrasound diagnostics or a gynecologist who has the skills to conduct such a diagnosis.
The latter comprises the following steps:
- The patient undresses below the belt, is located on the couch, placing a diaper under the buttocks.
- The specialist applies a condom to the device’s sensor and lubricates it with a conductive gel composition.
- The sensor is not deep in the patient’s vagina (for ease of review, the doctor can move it in different directions).
The specialist fixes all the observed data for subsequent decryption.
What shows the transcript of the results
Based on the image placed on the screen, the doctor makes a conclusion and determines the diagnosis. Previously, a specialist determines the size of organs, their echogenicity. Additionally, a specialist can track the presence of formations in the colon.
Diagnosis ends with a written fixation of all the features of the study. Additionally, the doctor comments on what he saw and expresses an opinion on the condition of the patient's reproductive organs. Diagnostic protocol, or in other words, transcript of ultrasound, must certainly be given to the woman's hands.
Important! An ultrasound specialist is able to comment on the patient’s health status and issue her a study protocol. The verdict regarding the treatment of pathologies identified during the procedure should be made solely by a narrow-profile doctor.For this reason, the patient provides all the data recorded during the ultrasound to the gynecologist to draw up further treatment tactics.
Transvaginal ultrasound during pregnancy
Transvaginal ultrasound allows you to conduct the most accurate and complete examination of a pregnant woman. It is this method, in contrast to the transabdominal one, that makes it possible to identify the fact of an accomplished conception at an early date.
For transvaginal ultrasound, pregnant women are not charged with the obligation to prepare for the procedure in a special way.
A sound examination conducted before 12 weeks of pregnancy helps to identify:
- the presence and confirmation of pregnancy (uterine, ectopic, frozen);
- threatened miscarriage;
- condition of the future mother.
Later pregnancy suggests transabdominal ultrasound. Although in some cases, vaginal administration of the sensor is indicated (with the aim of measuring the length of the neck or examining the placenta, determining the possibility of bearing the fetus).
This type of ultrasound examination is not able to harm the fetus or the woman herself, and therefore can be carried out at a regular frequency.
If there are no specific indications for additional research, an ultrasound scan is performed three times during the entire pregnancy:
- Genetic examination (9-10 weeks). Identifies the presence or absence of genetic abnormalities of the fetus.
- The first screening examination (16-20 weeks). Helps determine the sex of the future baby
- Screening examination (32-34 weeks). Helps fix the main parameters of the fetus - height and weight.
The ultrasound research method has long and firmly entered the life of a modern person. It is an ultrasound that helps to track possible problems of internal organs, including those that are in the pelvis in women. The Uz-examination is allowed not only for indications, but also for prevention, as well as during the period of bearing a child.