Tympanum is an acute expansion of the stomach, most often resulting from overfeeding of animals in which there is a general lethargy in the digestive tract. Sometimes the cause is a lack of calcium in the blood, which leads to spasms in the digestive organs. It can also be an idiopathic disease caused by a change in feed. This form is most often found in turtles aged 2-3 months and can not be treated. In addition, a foreign object that has entered the intestine or pyloric sphincter can provoke a violation.
Material Content:
Symptoms of a tympanum in a turtle

You can recognize the disease by the following signs:
- the animal does not sink in the water, when swimming heaps, more often on the right side;
- the red-eared turtle does not eat, but in some cases the appetite may persist or be somewhat reduced;
- swelling appeared near the paws and neck, it is difficult for the animal to hide under the carapace;
- feces consists of the remains of undigested food;
- the reptile can blow bubbles from the mouth; vomiting may occur.
How to distinguish tympany of the stomach from pneumonia
Tympanum and pneumonia have a number of common symptoms: shortness of breath, discharge from the sinuses and roll to the left or right side when swimming. However, acute expansion of the stomach is manifested by other signs. If the colon is swollen, the front of the reptile's body will be lowered when moving under water, and the back will be raised. In addition, the animal can stretch its neck, and in the inguinal fossa, cervical and axillary regions, swelling is found on the skin.
In addition to examining the symptoms, an x-ray of the dorso-ventral projection will help differentiate tympany from pneumonia. With its help, it is possible to identify the accumulation of gases in the intestinal loops, which is typical for acute expansion of the stomach. This is due to the fact that with this disease, reptiles develop dynamic intestinal obstruction. In addition, during an X-ray examination, you can see a foreign object that has fallen into the digestive tract of the turtle and caused the violation.
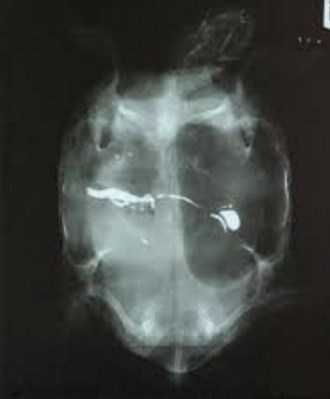
And also a cytological analysis of exudate released from the mouth is carried out. During tympanum, mucus contains the flat, non-keratinizing epithelium of the mouth and esophagus, and the cylindrical epithelium of the stomach. And with pneumonia - the respiratory epithelium, markers of inflammation and many pathogens.
Treatment of tympanum of the stomach
In the process of treatment, calcium preparations, enterosorbents, antispasmodics and drugs that stimulate peristalsis are used.
Therapy scheme:
- Calcium borgluconate 20% at a dosage of 1 ml / kg every other day for 5-7 days.
- Children's Espumisan at 0.2 ml / kg. The medicine is diluted so that 0.1 ml of water falls on 0.1 ml of the drug. The solution must be introduced into the stomach of the reptile using a probe every other day. The procedure will be required 4-5 times.
- Eleovit injections 0.6 ml / kg, the course is determined by a specialist.
If the general condition of the turtle is satisfactory, it has not lost its appetite and is active, you can let it starve for 3-4 days, and then injections are not required.
Important! Do not self-medicate, therapy should be prescribed only by a specialist after diagnosis. Symptoms of tympanum are similar to signs of pneumonia, and first of all you need to understand which of these disorders you are dealing with.
Disease Prevention: Tips for the Care of a Red-eared Turtle
To reduce the risk of gastric tympanum in the rubella tortoise, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Install a UV lamp in the water tank. Ultraviolet irradiation promotes the absorption of calcium and vitamin D.
- Do not overfeed the animal. It is better to consult with your veterinarian about what kind of food and in what quantities the pet should be given.
- Avoid sudden changes in diet. New products and feed should be introduced gradually, in small portions, and observe the reptile reaction.
- Remove small decor elements from the aquarium. Often foreign objects swallowed by a turtle lead to intestinal problems.
- Monitor the general condition of the pet and, at the first sign of trouble, seek help.
Knowing the causes, symptoms and methods of preventing tympanum in turtles, you can maintain the health of the pet, and if the problem still arises, help the animal get rid of the disease and prevent complications.












