Pleasant taste, medicinal properties and affordability made beets an indispensable product for the preparation of not only everyday, but also holiday dishes. However, even experienced housewives may not know how important it is to take into account the benefits and harms of beets, since excessive passion for vegetables can cause malaise.
Is it true that in such a popular root crop there is a threat to health, let's try to figure it out.
Material Content:
The composition and calorie content of beets
The nutritional and medicinal value of beets was discovered by the inhabitants of the Mediterranean several millennia BC.

Initially, the plant was eaten in the wild, but over time, the cultural forms of the root crop were also bred. By the beginning of the XI century, beets appeared on the territory of Kievan Rus and gradually gained mass distribution around the world.
The beneficial effect of beets on the body was also noted by antique gourmets. However, scientific confirmation of the unique properties of the vegetable was obtained only in our time.
The therapeutic potential of beets is due to the presence of valuable substances and elements in its composition:
- vitamins - group B, (folic and pantothenic acid, niacin), natural antioxidants and antiseptics A and C, PP (equivalent of niacin), K (phylloquinone);
- minerals - iodine, iron, calcium, copper, potassium, magnesium, zinc, sulfur, cobalt, rubidium, cesium, chlorine, phosphorus, boron, vanadium, silicon, quartz;
- fiber and organic acids - citric, oleanolic, malic, lactic, tartaric, oxalic;
- carotenoids;
- flavonoids.
In addition, 100 g of beets contains 8.8 g of carbohydrates (sucrose, glucose, fructose, pectins), 1.5 g of proteins (betaine, lysine, arginine, valine, histidine), 0.1 g of fat and 40 kilocalories.
Health benefits and harms
The biochemical potential of beets allows you to successfully use the vegetable not only for prevention, but also for the treatment of a huge number of ailments. The healing power of the root crop is expressed in the healing effect on all systems of the human body.

Gastrointestinal organs. Thanks to fiber and organic acids, metabolic processes are normalized, stomach function and digestion are improved, peristalsis is enhanced, and even chronic constipation is eliminated. Pectin substances inhibit the activity of putrefactive microorganisms, contributing to the normalization of microflora and the natural cleansing of the intestine.
Metabolism. Betaine in beets is a lipotropic substance that provides a natural level of lipid and cholesterol metabolism. Lipotropics have the ability to regulate blood cholesterol levels, as well as stimulate the removal of fats from liver cells, preventing fatty tissue infiltration and the formation of cholesterol stones in the bile ducts.
Vessels and heart. A large amount of magnesium helps strengthen the heart muscle, prevents the development of atherosclerosis, and reduces the risk of hypertension.
Immunity. Vitamin C and provitamin beta-carotene enhance the protective potential, resist the development of tumor processes.
Blood formation. B vitamins, iron, copper, phosphorus and cobalt improve blood formation processes, increase hemoglobin and blood quality, strengthen capillary walls, dissolve blood clots, cleanse blood, improve heart function, and prevent the development of anemia and leukemia.

Musculoskeletal system. The presence of quartz in the beets is the key to the strength and functionality of bone and cartilage, as well as arteries and epidermis.
The brain and vision. Beetroot nitrates stimulate blood circulation, improving the nutrition and functioning of the brain and corneal cells. In addition, zinc in beetroot strengthens the retina, preventing its detachment.
General well-being. Beetroot strengthens the nervous system, stabilizes the mental and emotional background, fights depression. Folic acid promotes cell regeneration, rejuvenates tissues.
Thyroid. The endocrine system is supported by iodine in the root crop.
In addition, beetroot provides a urinary effect, normalizes kidney function, removes toxins, helps prevent the development of rickets in children, is used to treat scurvy, and also has a tonic effect in case of a hangover syndrome.
Both scientists and representatives of official medicine are sure that the health benefits of beets are exceptional, and there are no other vegetables that can fully replace the root crop in the diet.
Contraindications to the use of beets
Despite the powerful healing potential of the root crop, its use is not always justified, from a medical point of view. Especially in large numbers.

The use of beets is contraindicated in:
- exacerbation of gastritis and peptic ulcer. Patients with increased acidity of the stomach should be wary of dishes with root crops;
- kidney dysfunction and urolithiasis. Oxalic acid of the root crop promotes crystallization of the fluid and provokes exacerbations in the organs of the urinary system;
- low pressure. Buriak causes a decrease in blood pressure, provoking hypotension;
- osteoporosis, as the root crop slows the absorption of calcium by the body;
- diarrhea and chronic indigestion. Strengthening intestinal motility, beetle stimulates an additional laxative effect and worsens overall well-being;
- tendency to allergies.With individual susceptibility to the elements in the root crop, an allergic reaction may develop - skin rashes, swelling of the nasopharynx, enlarged lymph nodes;
- rheumatoid arthritis and gout. It is not recommended to drink freshly squeezed vegetable juice - its action causes an exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the joints.
Patients with diabetes need to limit the consumption of beets - this is due to the large number of sugars in the vegetable. Portions within 100 g are considered optimal.
In general, the possible harm from the use of beets is minimized, since the root crop is used in small quantities and for cooking dishes consumed no more than one to two times a week.
Useful properties for women, men
A distinctive feature of the therapeutic potential of beets is its ability to regain male power and restore women's health.

As studies have shown, the substances contained in beets are extremely beneficial for the female body. The root crop contains folic acid and valine, which have the ability to stabilize the hormonal background. Therefore, the use of beets is appropriate for any manifestation of hormonal imbalance - with premenstrual syndrome, or during menopause.
But the root crop is especially useful for expectant mothers. Thanks to the regular use of beets by pregnant women, the fetus receives the necessary minerals and amino acids for development, which contributes to its development and ensures the proper formation and growth of bone tissue. And iron stores in beets reduce the risk of fetal hypoxia.

In addition, beetroot improves the functionality of the genitourinary and digestive systems, which during pregnancy experience increased stress.
It is interesting:beets - planting and care in the open ground
Many women use the beneficial properties of beets for weight loss. In addition to the fact that root-based dishes stimulate metabolic processes and accelerate the breakdown of fats, beetroot diets provide satiety without increasing calorie content and overloading the stomach.
The benefits of beets for men's health
Along with the general strengthening and rejuvenating effect on the body of a man, beets are distinguished by the ability to restore male power. The body of many men is weakened by the effects of nicotine and alcohol, which often affects potency.
Regular use of beets allows not only to neutralize the harmful effects of toxins, but also to restore an erection and sexual desire.
Moreover, the substances in the root crop effectively fight against the formation of atypical cells, inhibiting their growth and development. Thus, beets prevent the occurrence of tumor processes in prostate adenoma, a disease that affects most men over the age of 50 years.
What is useful and harmful beet juice?
Using freshly squeezed beet juice, we saturate the body with the maximum amount of nutrients contained in the vegetable, with the exception of fiber. Nevertheless, it should be remembered that the concentration of trace elements in a glass of juice is several times higher than the norm obtained with a portion of a dish from the root crop.

Moreover, beetroot juice contains compounds that can aggressively affect internal organs.
Therefore, when treating with juice, doctors recommend that you adhere to the following rules to avoid overdosing with the active components of beets:
- Before use, the juice should be left to stand for three hours. During this time, the most aggressive compounds will partially volatilize and decompose;
- the maximum allowable volume of a drink per day cannot exceed 600 ml, and a single dose - 125 ml;
- root vegetable for making juice should be at room temperature;
- the optimal therapeutic effect is provided by a drink drunk 15 minutes before meals in small sips;
- start taking beetroot juice better with small portions.And making sure that there are no side effects, the volume of a single serving can be increased;
- the use of beet juice is not recommended along with acidic products or products from yeast dough.
Nutritionists believe that it is possible to enhance the therapeutic effect of beet juice if you use sweet vegetables and fruits — apples, celery or carrots — to make the drink.
What is more useful: boiled or raw beets?
Beets are one of those vegetables that are able to maintain maximum beneficial properties even after heat treatment. The answer to the question whether boiled beets are useful is unambiguous - heating, boiling and roasting the root crop do not affect the content of minerals or the amount of amino acids.

However, raw beets have an intense irritating effect on the intestinal mucosa, so patients with digestive tract problems should be very careful about eating fresh vegetables.
Tasty recipe:beets with garlic and mayonnaise
Some nutritionists claim that boiled beets are more healthy than fresh. This is not entirely true. Indeed, during cooking, part of the vitamins contained in the root crop is destroyed - C, B5 and B9 (that is, ascorbic, pantothenic and folic acid). Also, with prolonged heat treatment, beets lose most of their nitrates and fiber.

On the other hand, coarse fiber can injure the tissues of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and intestines with gastritis or peptic ulcer.
The beneficial substances of beets are better absorbed if taken in boiled form. Therefore, for dietary nutrition, it is recommended to use only boiled beets.
Application in cosmetology
In earlier times, girls used beets to enhance the cheekiness. Nowadays, the properties of the root crop have found application not only in the decorative, but also in the medical direction of cosmetology.

As part of masks or compresses, beets do an excellent job of healing wounds, acne, ulcers, cracks and swelling. A beetroot juice is drunk to improve complexion.
To nourish oily skin, add a chicken yolk to the mask; to eliminate inflammation, apply a mask of raw beets and grated potatoes to the face. Rinse off the mask from beets is recommended milk, half diluted with water.
To moisturize the skin, use this mixture: two teaspoons of beet juice, honey and strong black tea are boiled in a water bath and, after cooling, apply a thin layer on the face. After a quarter of an hour, wash off with warm water and moisturize with cream.
Besides, beetroot masks help strengthen hair follicles, eliminate dandruff and restore healthy strength and shine to hair.
Culinary healthy root recipes
The regular use of beets in cooking makes the whole family healthy and well-being. Borsch, beetroot, okroshka and botvini, as well as various snacks and vitamin salads are prepared from the root crop.

A serving of grated boiled beets with the addition of apple and vegetable oil is a great alternative to dinner for those who want to not only lose weight, but also to improve their well-being.
Steam cutlets, puddings and casseroles are the best way to diversify the diet of patients with pancreatitis.
With liver diseases, a decoction from the root crop is useful. To do this, finely chopped beets are boiled until the broth is completely thickened. Take three large sips three times a day before meals.
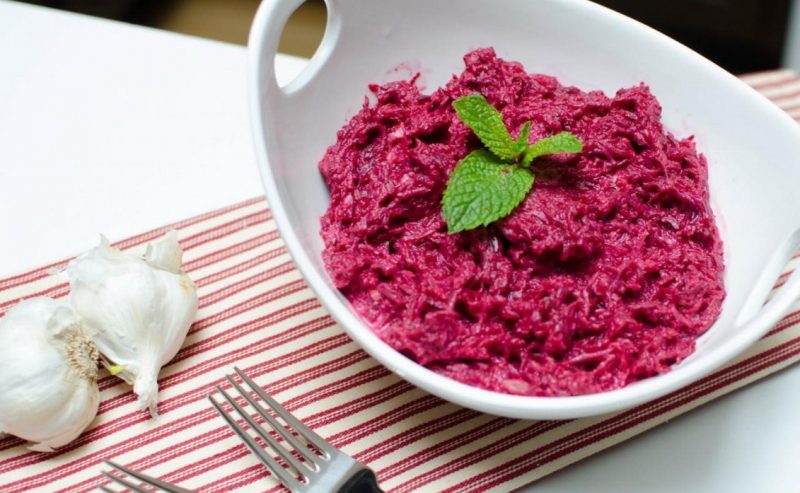

Almost a full range of valuable properties of beets is preserved in pickled beets. To do this, peeled and coarsely chopped root vegetables are placed in a three-liter sterilized jar, add horseradish leaves and cherries, a few peas of black pepper and a pinch of cinnamon and pour in the marinade.
Preparation of the marinade: two liters of water, 100 g of coarse salt and 100 g of sugar are brought to a boil and cooled.
Read also: beetroot hot - classic recipe
Beets, covered with brine and covered with gauze, are kept at room temperature for two days, and then cleaned in the cold for five days. When serving, season with vegetable oil.
Dishes from beets and beetroots were valued in the aristocratic society of pre-revolutionary Russia. But in our time, the popularity of a vegetable has reached its climax. The main thing to remember is that excess consumption always harms the body, even if it comes to such an impeccable root crop as beets.