Subclinical hypothyroidism is also called "hidden", since the disease has no obvious symptoms. This form is the initial stage of the disease and is characterized by a defeat of the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. The disease is detected by analysis, where the level of TSH will be significantly exceeded. Studies have shown that about 20% of women over the age of 50 suffer from this disease, but the disease can develop at a younger age, even in children.
Material Content:
Causes of subclinical hypothyroidism
At each age, the development of the disease is facilitated by the same factors. Without concomitant causes, the disease does not occur.
In which cases a person is at risk:
- Iodine deficiency. This is the first and main reason why the thyroid gland begins to malfunction. Particularly at risk are people living in harsh climates, away from the sea and ocean. To compensate for the lack of iodine in the body, you need to not only take special preparations, but also use iodized salt when cooking, which manufacturers specifically produce for consumers from risk regions.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis is under development.
- Treatment of the thyroid gland with a tumor by radiation.
- Removal of an organ for medical reasons (partially or completely). This happens when a malignant tumor that is not treatable is detected.
- Abnormal development of the thyroid gland in utero.
- Inflammation in the gland. The risk group especially includes women after childbirth.
- Long-term use of drugs that suppress the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. It can be hormonal drugs, drugs for treating heart diseases.
- The use of radioactive iodine in the treatment of organ.
As can be seen in the description of the causes, the development of the disease does not depend on the person. The factors of the appearance of the disease are beyond our control.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Subclinical - a latent type of hypothyroidism.
There are no obvious signs of the disease, so they can easily be confused with the common cold, overwork, loss of strength.
Symptoms of subclinical hypothyroidism in women are manifested as follows:
- a constant feeling of a certain chilliness, slight chills;
- drowsiness, distraction;
- lethargic state, fatigue from everyday affairs;
- low body temperature;
- slowness, which is very pronounced;
- galactorrhea (spontaneous leakage of milk from the breast, even when the woman is not pregnant and is not nursing);
- loss of appetite;
- decreased libido;
- refusal to perform standard, familiar work;
- decreased attention;
- stresses.
As the disease progresses, the following symptoms appear:
- decreased intellectual ability, memory impairment;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- fast weight gain;
- vaginal bleeding;
- failure in the menstrual cycle;
- the skin becomes rough, dry, icteric in color;
- problems with stools (constipation, bloating, flatulence often torment);
- infertility;
- stomach pain, frequent heartburn;
- bradycardia;
- muscle pain
- hair becomes dry, begins to break and fall out;
- swelling on the face;
- anemia.
Symptoms in children:
- weight gain is slow;
- crying baby with hoarseness;
- language increases, it is difficult for a child to completely close his mouth, so he is always ajar;
- decreased appetite;
- the child begins to lag behind in education;
- physical activities, normal earlier, become too complex, the child does not tolerate them.
If similar symptoms begin to appear in adults and children, you should immediately go to the doctor, who will prescribe a diagnosis, consisting of a series of studies.
Diagnostic measures
To identify the presence of a disease or to refute this, you need to undergo a diagnosis.
The study consists of several stages:
- Blood sampling to determine the norm of the thyroid hormone. In a healthy person, the level of triiodothyronine is 2.5-5.7 mmol / l, thyroxine - 9-22 mmol.
- Determination of the presence of antibodies to AT-TG in the blood. During normal operation of the body, indicators are absent, or they may have a minimum value - 0-19 and 0-5.7 units. If the final figure is too high, then it is worth talking about the presence of the disease.
- Analysis to determine the amount of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone). The norm of TSH for a healthy body is 0.5-4.3 Honey / L, if the indicator is exceeded, the doctor diagnoses subclinical hypothyroidism.
- Another study is scintigraphy, which is based on the use of radioactive isotopes. In the presence of the disease, the thyroid gland is poorly saturated with iodine, and during this study it is clearly noticeable.
A blood test will also show the presence of anemia in hypothyroidism, which develops due to a decrease in hemoglobin synthesis, lower levels of vitamin B12 and iron.
Additional research:
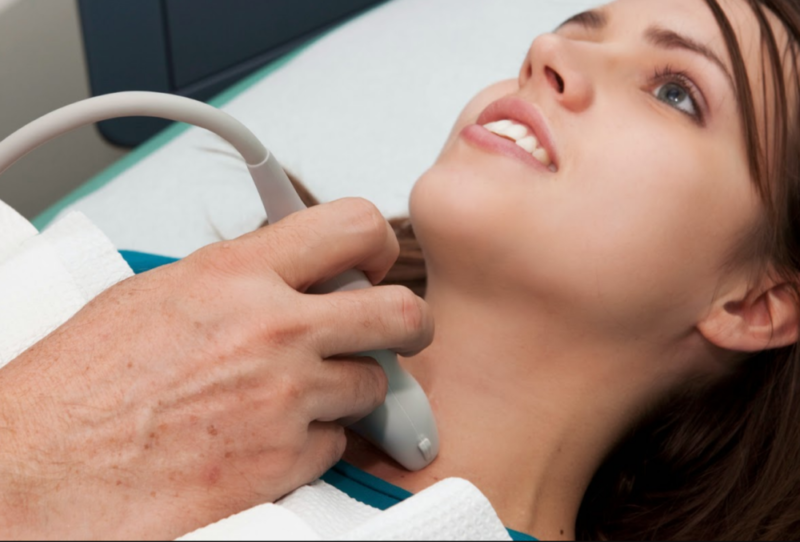
- Determining the size of the thyroid gland - ultrasound will help in this.
- An ultrasound scan is also performed for the abdominal cavity, which helps to determine the neglect of the disease.
- If hypothyroidism is suspected in a child, a chest x-ray is taken. The study reveals changes in the skeleton, as well as the presence of fluid if the disease is started.
- Electrocardiography will help to identify pathology, as its evidence is a decrease in the number of contractions of the heart muscle.
The testimony of one of the studies is not enough to make a diagnosis, so diagnosis is mandatory for all items.
Treatment of hypothyroidism in adults and children
The treatment has no specifics and is based on taking medications that help normalize the amount of thyroid hormone.
In case of malfunctions of the endocrine system, the doctor prescribes various kinds of drugs:
- Means that contain thyroid hormone. The medication should be monitored by an endocrinologist.
- Be sure to have medications in therapy that are aimed at eliminating the cause that led to hypothyroidism.
- With such a disease, it is necessary to take daily preparations with vitamins and minerals, which, as they recover, will maintain immunity.
With a malfunction in the functioning of the thyroid gland, the metabolism is also disturbed. To avoid the harmful effects of this factor on the body, you need to follow a special diet.
From the menu it is worth removing:
- sugar;
- high soy foods
- reduce fluid intake to half a liter per day;
- foods rich in polyunsaturated fats are fish of fatty breeds, peanuts, oils (vegetable and cream), avocados.
During the diet, be sure to include the following foods in your daily diet:
- beef, turkey, chicken, rabbit;
- fresh fruits;
- seafood (they contain a high iodine content);
- meat broth;
- sea kale;
- coffee (a drink will enrich the body with magnesium and vitamin B).
Once again, we recall the need to use iodine-containing salt in food.
Features of the course during pregnancy
Diseases of the thyroid gland affect the ability of a woman to produce viable children (fertility). If the diagnosis of the pregnant woman revealed the presence of subclinical hypothyroidism, the woman will be offered to lie down for the entire period of further bearing in the hospital, since the risks for both the fetus and mother are very high.
The disease can cause:
- detachment of the placenta;
- premature birth;
- intrauterine death of the child.
For a woman, this disease during pregnancy threatens diabetes mellitus, eclampsia.
As for the born child, hypothyroidism becomes the cause of a decrease in mental abilities and physical development.
Studies have shown that in children born to a mother with hypothyroidism, IQ is lower by an average of 7 points than in those born to a healthy parent.
The disease negatively affects the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus. If an ailment is detected, immediate therapeutic measures should be taken.
Possible complications after treatment
The disease in a neglected form is dangerous in that it gives complications. Self-medication is not so dangerous for a person, it is more dangerous not to use therapy.
The consequences of the disease for children are the following conditions:
- developmental lag - both mental and physical;
- the child loses interest in past hobbies - even his favorite toys become not interesting to him.
As practice has shown, timely treatment reduces the possibility of complications to a minimum.
Having restored the level of hormones, many children continue to lead a full-fledged lifestyle, keeping up with their peers.
Thyroiditis in adults can cause a coma, if you do not start treatment on time. Also, the disease leads to disruption of all important organs. But with timely diagnosis of the disease, with proper therapy, adherence to the diet, the most sad consequences can be avoided.
Disease prevention
Today it is difficult to guess who is facing latent hypothyroidism and who is not at all affected by it. If we are unable to avoid malignant tumors in the thyroid gland, then iodine deficiency can certainly be prevented.
The following actions will serve as prevention:
- Once a week, eat foods rich in iodine: seafood (it is especially important to eat sea kale, although many do not like it).
- Cook daily using iodine-enriched salt.
- Take iodine-containing drugs, it is especially important for pregnant women to understand this.
- When deciding where to go on vacation, give preference to the sea coast.
Treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism is not a cure for the common cold, and it will take time to fully recover. The main thing is to be patient, not to worry (stress reduces immunity), to understand that the disease is well treatable. Follow the doctor's recommendations and will soon recover. Health to you and your loved ones!