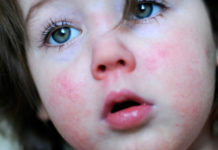
Any diseases of the oral cavity give the child a lot of unpleasant sensations, especially when it comes to childhood stomatitis. This inflammatory process is very often accompanied by a weakening of the immune system against the background of a cold, when the body spends all its strength in the fight against pathogenic bacteria. What other reasons can provoke stomatitis in children - we will examine further.
Material Content:
What is stomatitis
Despite the fact that stomatitis is often the result of a cold infection, these two ailments are in no way interconnected. Unpleasant symptoms appear as a result of constant drying of the oral cavity, as during the common cold the body undergoes severe dehydration.
Against this background, the reproduction of pathogenic microflora occurs in the mouth, which is the main culprit in the formation of an inflammatory process called stomatitis. The lack of timely treatment leads to serious complications, as a result of which the child experiences severe pain. In addition, the disease is aggravated by an increase in body temperature, and each meal gives the patient a lot of uncomfortable sensations due to the presence of ulcers in the oral cavity.
The number of inflammatory elements directly depends on the following factors:
- forms of the disease;
- the complexity of the course of the disease;
- the body's ability to fight infection.
The manifestations characteristic of stomatitis have a pronounced clinical picture, so a competent specialist will not have any difficulties at the time of determining the diagnosis.Parents just need to immediately seek help from a dentist or pediatrician, as soon as the baby's mouth has noticed the appearance of ulcers of unclear etiology.
Causes of Children
The state of the oral cavity is affected by both external factors, whether it is a chemical or physical effect on the mucous membrane, or the internal characteristics of a particular organism.
Among the main causes of stomatitis are:
- injury to the oral mucosa due to a bite, burn, or chemical attack;
- reproduction in the oral cavity of harmful microorganisms of viral, fungal or bacterial nature of origin;
- individual intolerance of the body to any irritant that causes an allergic reaction;
- disorders of the hematopoietic and digestive systems;
- hormonal disruptions in the body;
- HIV infection.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
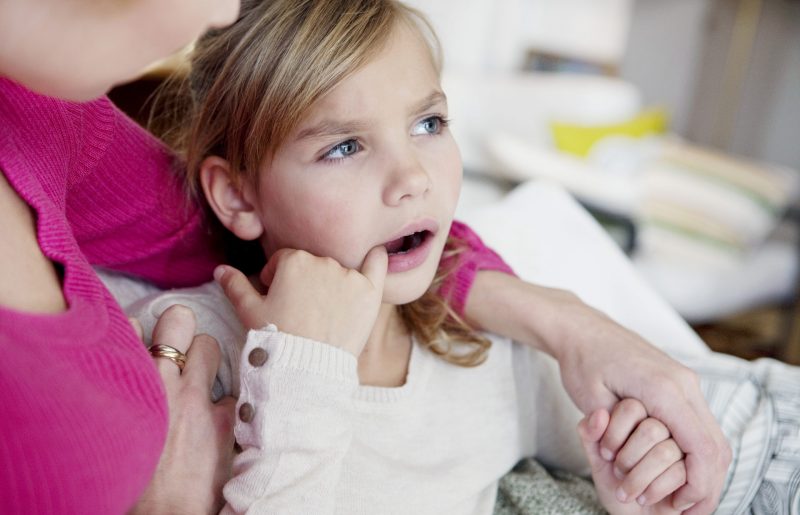
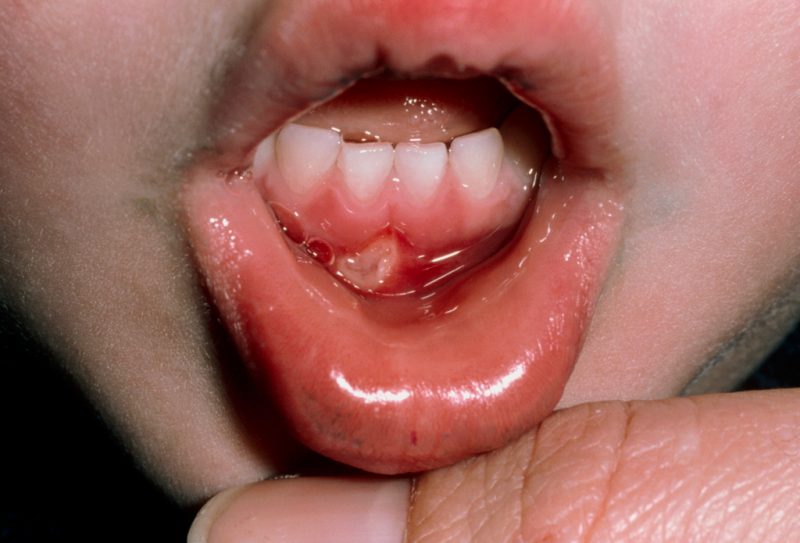
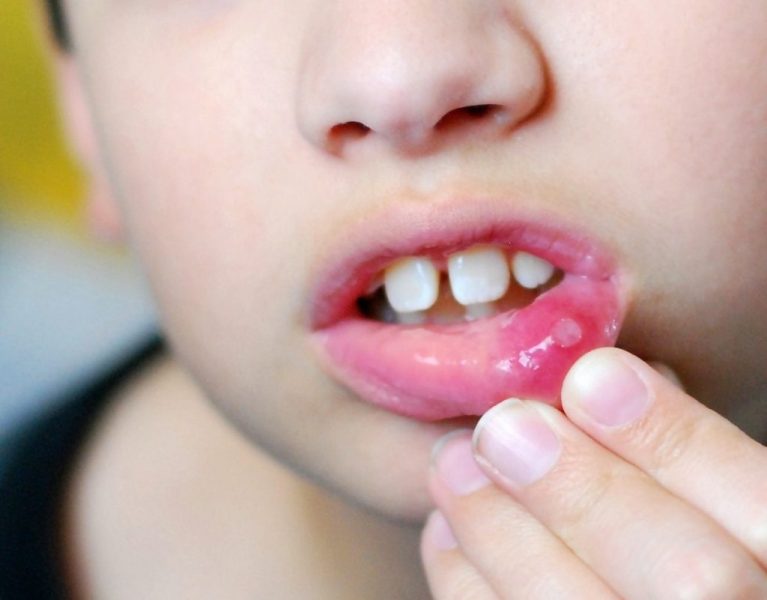
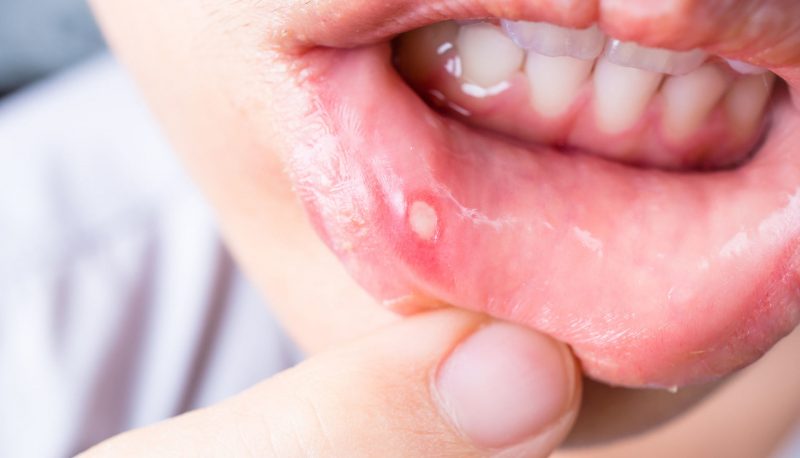
As noted earlier, the main symptom of stomatitis is ulcers that form on the oral mucosa. It is easy enough to notice such neoplasms, so parents who find any wounds in the oral cavity of their child should immediately consult a doctor. The location of the ulcers, as well as their shade and size, depend on the stage of development of the disease.
At the initial stage, only a slight swelling or pimple may appear in the mouth, which will cause some discomfort during meals. In addition to visual manifestations of an inflammatory nature, the child may also experience significant changes in behavior. Due to pain and discomfort, he becomes more emotional and irritable. In addition, the patient, as a rule, has problems with sleep and impaired appetite.
In addition to the above symptoms, depending on the form of the disease, a number of other manifestations develop:
- the remaining parts of the oral cavity are affected;
- the course of the disease is characterized by stages of calm and worsening: at the initial stage, inflammatory elements appear that cause severe pain, and after some time the symptoms cease to bother the child, however, this relief is quite short-lived, and after a couple of days a new relapse is noted;
- in the language, in addition to the wounds, a characteristic white coating is visible;
- gum disease occurs, leading to bleeding and pain in the teeth.
Before treating stomatitis in children in the mouth, it is necessary to determine the form of the disease, the main causes of its occurrence and identify the main causative agent of infection. The choice of drugs and the duration of therapy will depend on this.
Types of Stomatitis
Doctors distinguish between several types of pathology.
- Viral. The causative agent of this form of stomatitis is herpes of the first type, which affects more than 90% of all people. This virus, after entering the body, does not manifest itself in any way if there are no factors affecting the immune system. However, in the case of weakened immunity, when the body is not able to overcome a common cold, herpes of the first type undergoes reproduction, which, in turn, leads to the appearance of viral stomatitis.
- Bacterial. It occurs in response to complications in the body caused by pathogens of bacterial etiology. As a rule, tonsillitis or pneumonia that is not cured on time leads to such consequences.
- Chronic aphthous. The mucous membrane of the mouth is affected by painful aphthae, which have a grayish yellow tint. Until now, specialists have not established a pathogenic microorganism, which is the causative agent of aphthous stomatitis in children. This disease is chronic, therefore, the patient has stages of relapse and remission.
- Fungal. The disease provokes a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida, which penetrates the baby's body in several ways.There are frequent cases when the cause of the candidal form of the disease becomes the mother's thrush, transmitted to the child at the time of delivery. Stomatitis also provokes prolonged use of antibiotics, which kill both harmful and beneficial microflora in a child.
- Traumatic. Wounds in the oral cavity can occur as a result of injury to the mucous membrane. These effects are caused by a thermal burn with hot food or liquid, an accidental bite of the cheeks or tongue during chewing. An ordinary wound develops into a dangerous ulcer if any infection from the outside gets into the damaged areas of the mucosa. The condition noticeably worsens amid weakened immunity.
Diagnostic measures
Parents are able to evaluate the first symptoms of the disease on their own, carefully examining the child's oral cavity. If characteristic signs of stomatitis have been noted, you should immediately contact the appropriate specialist to more accurately determine the diagnosis.
Note: not only the dentist, but also the therapist can detect the disease. Therefore, parents can seek help in the first nearest hospital, where the doctor will clearly assess the condition of the child.
It is enough for a specialist to see the oral cavity of a patient with characteristic inflammations to determine the diagnosis. However, to identify the cause of the disease and its causative agent, a number of additional clinical studies will be required.
These include:
- blood and urine tests;
- pharynx sowing to determine a pathogenic microorganism;
- smear of the affected area of the mucous membrane.
How to treat, depending on the form of the disease
Usually, specialists prefer local therapy in the form of rinses, since it is not recommended to treat stomatitis with more effective antifungal and antibacterial drugs at an early age. Local treatment should be aimed at correcting the acid-base balance of the oral cavity, and only in case of serious complications special drugs are prescribed with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Drug therapy
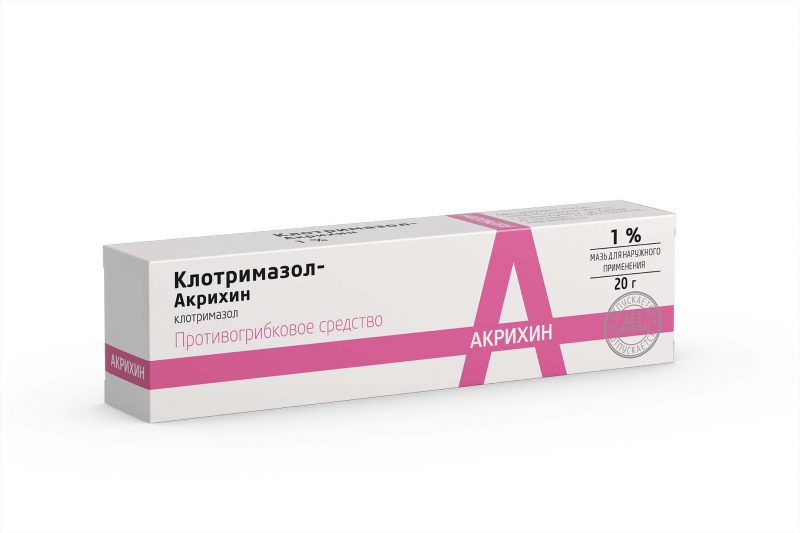
Treatment of candidal stomatitis is carried out through antifungal drugs, among which the most popular ointments are Clotrimazole and Pimafucin. These funds are used exclusively in accordance with the appointment of the attending physician. Otherwise, if the therapy was carried out incorrectly, pathogenic organisms become more resistant to the effects of active substances, which will further complicate the treatment of the disease.
To strengthen the baby's immune system, vitamins are additionally prescribed, and it is also recommended to exclude from the child’s diet any sharp, hot and sour dishes that can irritate the oral mucosa. To cope with severe pain will help medications with analgesic effects (Metrohex, Piralveks, Hexoral).
For the treatment of aphthous stomatitis, as a rule, local preparations are used. Depending on the form of the ailment, antihistaminic drugs aimed at eliminating pain, as well as anti-allergic medicines and means to restore the functioning of the digestive system, are additionally prescribed.
Folk remedies
The following methods are considered the most effective.
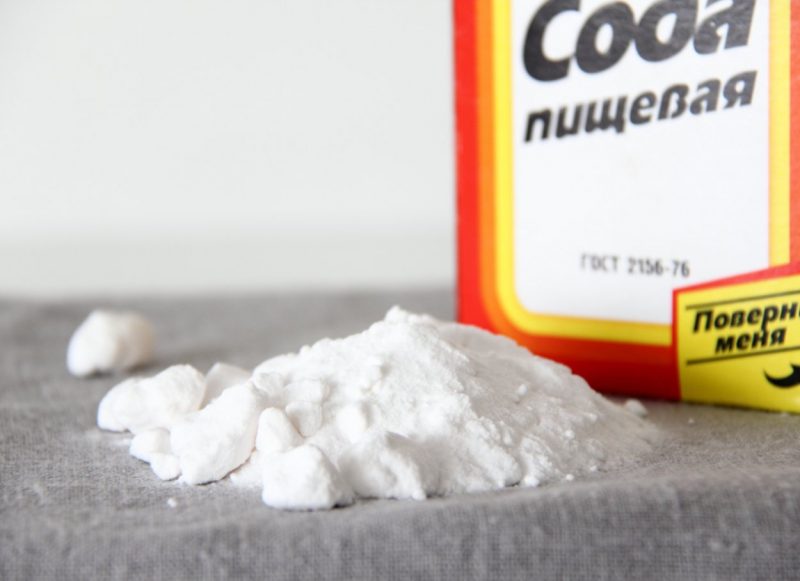
- Baking soda. Pour 2 tsp. component with a glass of water, and then moistened with a cotton pad moistened in the resulting mixture, treat the entire surface of the patient’s oral mucosa, including the lips. Repeat the procedure after each meal.
- Herbal decoctions. For rinsing, you can use infusions prepared on the basis of inflorescences of calendula, chamomile and sage. For 1 cup of boiling water, you will need a tablespoon of the ingredient. Inflorescences flooded with water insist for half an hour, after which the damaged sections of the mucosa are wiped with a ready-made broth.
How to rinse your mouth
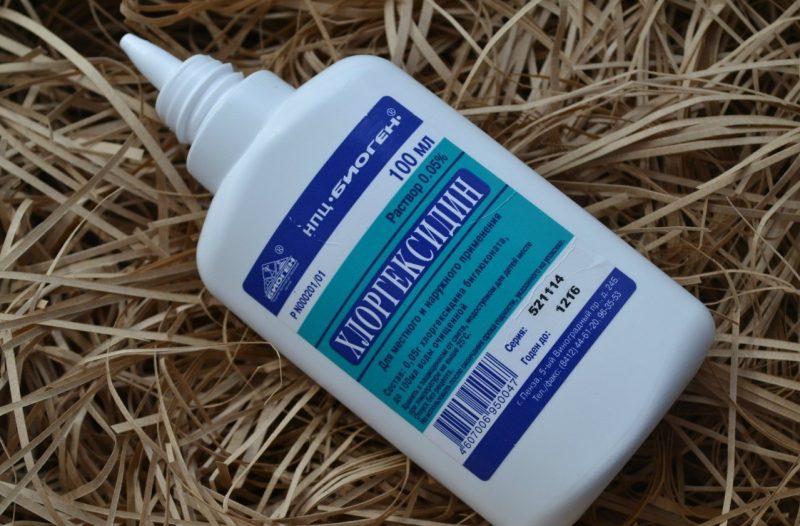
Stomatitis caused by herpes of the first type, in the initial stages amenable to local treatment.To do this, the doctor prescribes rinses with special solutions based on furatsilina or hydrogen peroxide. To prevent the further growth of bacteria, the patient is prescribed antimicrobial solutions, such as Chlorhexidine or Septofort. Oil solutions with the addition of retinol and rosehip oil will help to quickly restore the integrity of damaged sections of the mucosa. Also, to improve regeneration, rinses with propolis alcohol tincture are prescribed.
Disease prevention
Each parent will be able to protect the child from the unpleasant consequences of stomatitis, if from childhood he will instill in the baby all the necessary hygiene rules.
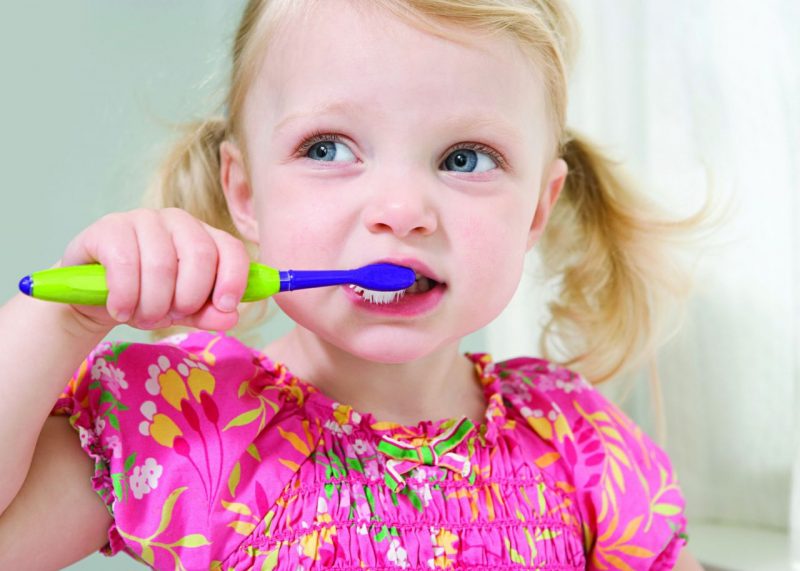
- Daily brushing should be done in the morning and evening. After eating, it is recommended to use dental floss and special rinsing agents.
- Teach your child to keep their own hands clean. It is imperative to wash them after a walk, going to the toilet, and also before eating.
- Make sure that the baby does not take foreign objects in its mouth, on which there is a huge amount of harmful microbes.
In addition, during feeding, the mother needs to carefully monitor the hygiene of her own breast, since the unformed immune system of the newborn is not able to withstand even a minimal amount of bacteria.