Do not give up on the diagnosis of steatohepatitis - this is not a sentence. When maintaining a healthy lifestyle, following a diet and vigorous physical activity, you can not only protect yourself from the serious consequences of cirrhosis of the liver, but also not remember this disease for the rest of your life.
Material Content:
What is steatohepatitis?
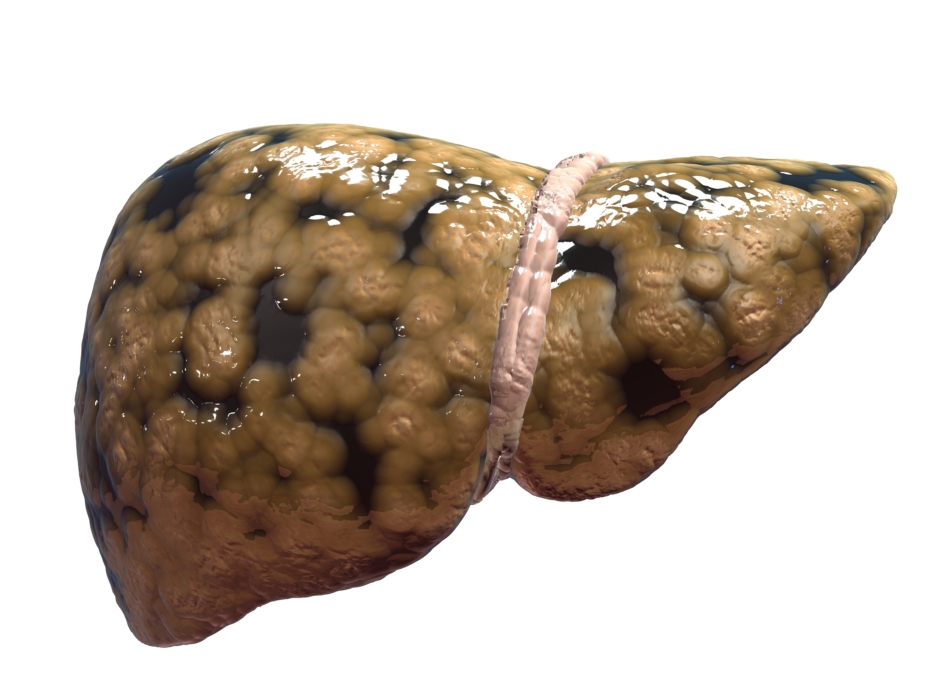
The diagnosis of steatohepatitis is given to people in all corners of the globe. This is a pathological liver disease characterized by organ obesity. The main causes of its destruction are: the intake of alcoholic beverages, the use of certain medicines and obesity. A similar ailment affects both adult patients and children. In the latter, steatohepatitis may be accompanied by increased body weight or diabetes.
The main thing is to make a diagnosis in time so that the disease does not find complications that are fraught with serious consequences. The lack of proper treatment of the pathology is fraught, first of all, with cirrhosis of the liver.
Depending on the type of disease and its dynamics, appropriate therapy is selected for the patient. A special diet, taking medications and playing sports will help stop the process of organ destruction and improve the liver.
Important: do not go to extremes and lose weight dramatically or load the body with excessive physical exertion. The process of losing weight should be gradual, sports should be arranged in a moderate mode, depending on the level of preparation of the person.
You should also not self-medicate and think that everything will pass by itself, on the contrary, you need to seek qualified help in time.
Classification of the disease and its types
The destruction of the liver, the "fouling" of the body with fat can begin for several reasons, depending on which different types of the disease are distinguished.
Classification of steatohepatitis for developmental reasons:
- Drug. This form of pathology is formed against the background of taking various medications, among which the side effect of the liver is becoming a side effect. Among the drugs marked antibiotics, synthetic hormones, antifungals, drugs for HIV-infected, Aspirin, nicotinic acid.
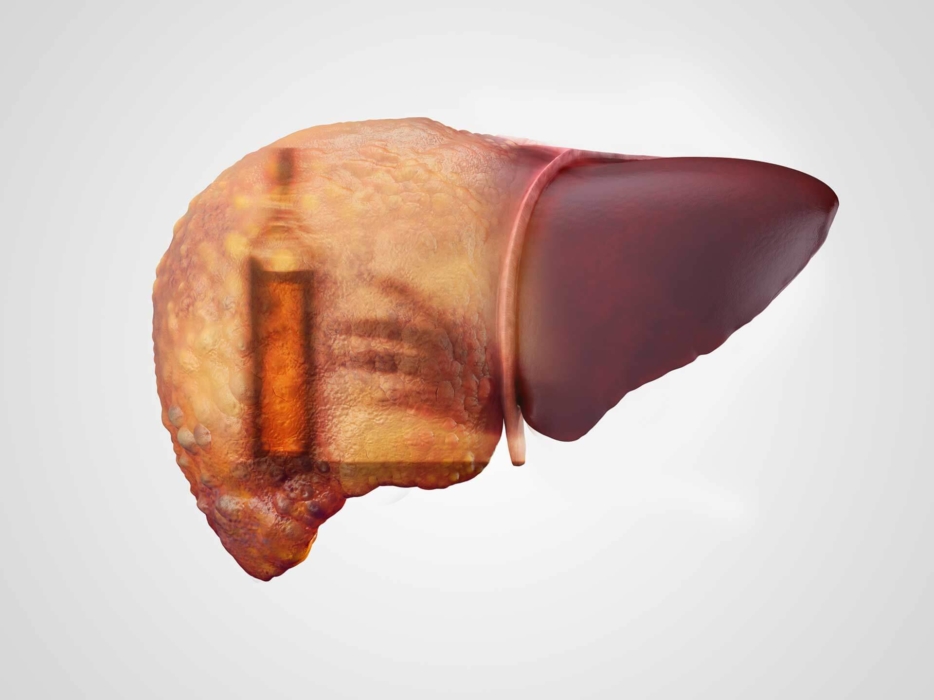
- Alcoholic. Alcohol abuse. Alcoholic fatty degeneration of the liver can occur even in a child.
- Non alcoholic steatohepatitis. The causes of this disease can be: obesity, diabetes mellitus (namely the lack of the necessary treatment), hypothyroidism, hyperlipidemia.
According to the dynamics of development and the degree of activity of hepatitis, two types of disease are distinguished:
- Chronic. As a rule, this type of disease is characteristic of patients who regularly drink alcoholic beverages. The liver does not have time to cope with the constant intoxication of the body and inflammation begins, which in the absence of treatment (and in this case, a complete rejection of alcohol) leads to cirrhosis.
- Moderate. This type of disease is difficult to recognize due to the absence of obvious symptoms or their manifestation in a mild form.
Steatohepatitis of minimal activity can develop in a person leading a sedentary lifestyle, coupled with malnutrition. The use of a large number of calories with a lack of all kinds of physical activity leads to the formation of cholesterol plaques.
The disease can also occur during pregnancy due to taking medications necessary to maintain the body in such an important period of life, as well as against the background of a genetic predisposition.
The mechanism of development and causes of the disease
The causes of the disease are most often bad habits. At risk are patients suffering from obesity and (or) alcoholism. These are people of completely different age categories. Given the high likelihood of developing liver cirrhosis in patients with steatohepatitis, it is very important to diagnose it.
List of possible causes of the disease:
- The abuse of drinks containing alcohol. In some cases, there is a risk of getting sick by consuming once a large share of alcohol and getting intoxicated.
- Combination of alcohol-containing drinks with drugs.
- Insulin resistance (diabetes mellitus).
- Poisons, toxins, production and entering the body with poor-quality food, taking hepatoxic drugs.
- Starvation, sudden weight loss.
- Unbalanced diet, protein deficiency.
- Avitaminosis.
- Pancreatitis
- Hyperlipidemia.
- Aryl dehydrogenase deficiency.
- Infectious diseases such as hepatitis.
- Complications during pregnancy.
- Uncontrolled intake of antibiotics and antipyretic drugs.
- Tuberculosis, autoimmune diseases, hepatitis and other chronic pathologies.
The mechanism of development of fat hypotension begins with the formation of insulin resistance, decreased sensitivity to insulin. This sugar-lowering hormone plays an important role in maintaining the body's immunity and metabolism. The causes of steatohepatitis may be genetic. With the development of the disease, bubbles appear in the liver layers with fatty components that press on the cells and prevent them from working fully. Then the septum of connective tissue begins to grow. At this moment, fatty degeneration of the liver occurs. And the faster the process goes, the sooner cirrhosis occurs.
Characteristic symptoms and signs
Depending on the type of steatohepatitis, the symptoms may be different. But the main signs include the following:
- dull pain under the rib on the right side;
- rashes, itching;
- yellowing of the mucous membranes;
- enlargement, compaction of the liver and its soreness;
- feeling of thirst;
- heaviness in the stomach, abdomen;
- digestive disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- sweating
- fatigue, decreased performance, weakness and irritation.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that very often the disease develops slowly and does not manifest itself in any symptoms, it can be difficult to make a diagnosis. Often the only sign is an enlarged liver and painful palpation. This serves as a signal for the necessary diagnosis of the liver.
First of all, the patient is examined for alcohol abuse. The verification includes a number of steps:
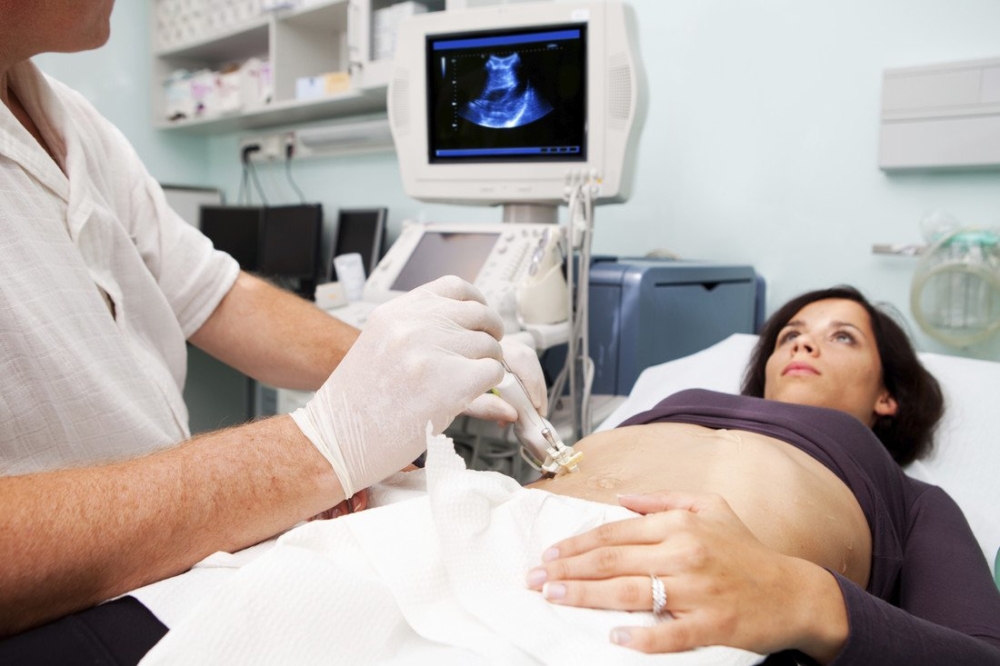
- Ultrasound examination of the liver (ultrasound) allows you to evaluate how much the organ is enlarged. This type of test is especially relevant for patients with diabetes mellitus and patients with obesity, as well as if a biopsy is impossible for objective reasons.
- Computer diagnostics.
- Laboratory tests (biochemical blood tests) for cholesterol, immunoglobulin A and others.
- Liver biopsy - analysis of the sample allows you to assess the degree of development of inflammation and organ damage (performed if the patient does not abuse alcohol).
A doctor who has prescribed appropriate drugs that are dangerous for the liver is also able to diagnose “drug steatohepatitis”.
Steatohepatitis Treatments
It is possible to overcome the disease, the main thing is to find out about it in time.
Steatohepatitis treatments include:
- medication;
- folk: dieting, taking herbal decoctions.
It is important to understand that using only the second method of getting rid of the disease is not enough - the therapy should be comprehensive and agreed with the attending physician. In addition, it must be borne in mind that allergies can occur for certain products and medicines, therefore the course of treatment and diet for each patient are selected individually.
List of approved products:
- inedible flour products;
- weak coffee (milk is welcome) and tea (black, green, herbal);
- sugar;
- butter, but not more than 50 g per day;
- sour cream, cheese, cottage cheese, milk and other dairy products with a low fat content;
- vegetable broths and soups with the addition of various cereals;
- cereals;
- sweet berries and fruits;
- greenery;
- fresh and heat-treated vegetables;
- honey;
- dietary meat: rabbit, turkey, beef, chicken (cook and eat poultry without skin);
- river fish;
- egg white (not more than one per day).
Food is recommended to be steamed or in the oven without adding oil. Do not eat too hot or cold food. If the cause of steatohepatitis is the use of alcohol, then completely exclude it from the diet.
Doctors recommend regular moderate physical activity to patients: walking, swimming, dancing and other activities.
The main thing: when making the diagnosis "non-alcoholic fatty liver disease" and the presence of excess weight, it is necessary to gradually (not abruptly) get rid of it.
It is important to understand that diet is not a temporary measure, but a way of life. When you return to the old eating behavior, the disease will return, and it is likely with renewed vigor and serious problems.
In addition to the diet, a gastroenterologist often prescribes a complex of therapeutic drugs:
- it can be medicines to increase insulin susceptibility: bagomet, metfogamma and others;
- medical substances, the main component of which is ursocholic acid: ursochol, ursofalk;
- hepatropic drugs: syrin, essential fort;
- drugs that control cholesterol: rosuvastatin, simvastatin.
You can cure liver obesity only by refusing junk food.People say that nothing disciplines a person like steatohepatitis.
Possible complications
Steatohepatitis is a liver disease that is associated with impaired fat metabolism. The ailment is becoming very common. Due to this pathology, the structure of the organ changes. The absence of a timely diagnosis threatens with a complication in the form of cirrhosis of the liver, necrosis of its cells of varying severity. The negative point is that a person may not feel any ailments, changes are imperceptible.
If you do not adhere to the treatment for steatohepatitis and start the disease before cirrhosis occurs, only liver transplantation can save life.
Important: medications should be taken only as directed by a doctor.
Treatment Prediction and Prevention
Steatohepatitis, unlike cirrhosis of the liver, can be cured.
To do this, follow the doctor's recommendations, as well as follow a special diet. It is necessary, first of all, to abandon spicy, fatty, fried and smoked foods, to include in your diet components that are rich in vitamins and minerals. It is necessary to constantly monitor the level of sugar and cholesterol in the blood.
It is very important for steatohepatitis not to self-medicate, but to seek qualified help from a therapist who will give a referral to a gastroenterologist and nutritionist.
Prevention of the disease is maintaining a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, protecting liver cells and normalizing its energy metabolism. It is necessary that the diet contains the right amount of protein, which is required for liver renewal.