Today, 5 main classes of drugs are used to treat conditions that are accompanied by the accumulation and deposition of cholesterol (cholesterol). Among them, statins for cholesterol deserve special attention, the benefits and harms of which are discussed since the 50s of the twentieth century. The passions around them do not subside to the present day, and the story of the creation of drugs resembles an exciting adventure novel.
Material Content:
Statins to lower cholesterol - a characteristic of the drug

The fact that drugs blocking the synthesis of cholesterol will do more harm to the body than good, they started talking in the middle of the last century. After all, cholesterol is a plastic component - it is part of the cell membrane, participates in the synthesis of sex hormones and hormones of the adrenal glands, cholic acids. Skeptics doubted that it was possible to create such drugs that would be strictly controlled, capable of eliminating only excess cholesterol, without interfering with lipid metabolism.
General information
Statins to reduce cholesterol in their effect are blockers of HMG-CoA reductase - a “bioactivator” of the initial stages of the reaction of synthesis of cholesterol from precursor substances. A group of scientists from Japan, led by Akir Endo, conducting experiments to improve penicillin, as early as 1971 noticed that some types of microscopic fungi produce not only antibiotics, but also substances that interfere with the creation of cell membranes in bacteria and disrupt the lipid metabolism necessary for their growth and livelihoods. So from a mold producing antibiotics, a component of bioactive substances, called Compactin, was obtained. It took more than 15 years before the first commercial statin appeared on the world pharmaceutical market - Lovastatin (Mevacor), which was a specific inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase.Almost simultaneously with Akira Endo, statins were also obtained in a research laboratory, the British pharmaceutical company Beecham, famous for its work on improving penicillin.
It is interesting: last generation statins, drug names
But in 1980, the Japanese pharmaceutical company Sankyo So stopped all research, without explanation. On Wednesday, rumors leaked that intestinal cancer was detected in experimental animals as a result of statin therapy trials. The possible carcinogenic effect of statins made the conservative Japanese company curtail development.
The company's decision to stop introducing statins into medical practice could cost the lives of patients with familial hypercholesterolemia, the most common hereditary disease in the world. Without treatment of the disease, patients experience early and rapid development of atherosclerosis, heart attacks, strokes, stenosis (narrowing) of the aorta and sudden death.
According to Professor John J.P. Casteleina (Netherlands), who has been dealing with the treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia for many years, without statins, the outcome of the disease is just as bad as that of AIDS patients.
Only thanks to the support of practical clinicians who have seen firsthand the efficacy of statins, and Merck's research has managed to defend statins.
Scientifically proven that statins:
- do not show side, and even more carcinogenic properties, subject to a therapeutic dose of the drug;
- lower cholesterol to target values much faster than diet therapy and drug therapy with other types of lipid-lowering drugs;
- 42% reduced mortality from heart failure;
- even aggressive therapy with statins does not upset the lipid balance of the body;
- helps stop the progression of atherosclerosis;
- reduce the absorption of exogenous cholesterol;
- affect inflammation and immune activation, responsible for the progression of chronic heart failure.
Long-term studies have proven the need for early use of statins, the use of high doses of drugs and long-term treatment.
Indications for appointment
Statins are prescribed for hereditary or acquired high levels of cholesterol.
Hypolipidemics are prescribed for:
- prevention of chronic heart failure and stroke in risk groups;
- rehabilitation after myocardial infarction;
- rehabilitation in the postoperative period (bypass surgery, stenting, angioplasty);
- treatment and prevention of coronary heart disease;
- reducing the rate of development of atherosclerosis;
- treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease;
- metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes mellitus);
- hypercholesterolemia therapy - high hereditary or heterozygous.
In modern therapy of chronic heart failure and familial hypocholesterolemia, statins are included in a comprehensive treatment regimen.
How to use?
Dosage and duration of taking statins of different generations vary. On average, the recommended daily dose of drugs is 20-40 mg. An increase in the amount (~ 80 mg) is indicated with a decrease in high cholesterol. The table shows the daily doses for modern statins:
| International name statin | Daily Dose (mg) |
|---|---|
| Atorvastatin | 10-80 |
| Pitavastatin | 2-4 |
| Pravastatin | 10-40 |
| Rosuvastatin | 5-40 |
| Lovastatin | 10-80 |
| Simvastatin | 10-80 |
| Fluvastatin | 20-40 |
Since statins have a different degree of lipophilicity, their ability to penetrate through cell membranes is different. This factor causes side effects, which affects the dose of the drug.
Since the synthesis of cholesterol depends on the time of day, it is recommended to take drugs after dinner, before bedtime.
If the expected effect when using a therapeutic dose is not achieved, then:
- dosage is increased;
- treatment is supplemented with a special diet and other drugs;
- replace one statin with another, stronger.
Distinguish between therapeutic and maintenance dosage. After the level of cholesterol returned to normal, the patient is transferred to a maintenance dose of statin.
It interacts differently with medicines. Therefore, it is prescribed individually, depending on many factors, including those drugs that the patient should take at the same time as statins. You can not take the discussed drug with drugs for the treatment of HIV infection (protease inhibitors, cyclosporin, gemfibrozil), they increase the dose of statin by 5-6 times.
They can increase the effect of the anticoagulant Warfarin. The simultaneous use of erythromycin reduces their effectiveness. It enhances intestinal motility and accelerates the elimination of statins from the body.
Mechanism of action
The pharmacodynamics (mechanism of action) of statins is the blocking of glycoprotein, which catalyzes the production of cholesterol in cells capable of synthesizing it (in the reproductive organs, gastrointestinal tract, liver, adrenal glands). They also increase the number of receptors sensitive to low density lipoproteins (LDL) receptors in hepatocytes, thereby reducing the activity of these lipoproteins in the blood. Statins lower cholesterol, blocking the synthesis of LDL precursors - very low density lipoproteins. To a lesser extent, statins inhibit the synthesis of triglycerides. Since their amount decreases in the blood, the level of anti-atherogenic substances - high-density lipoproteins, accordingly increases. This mechanism determines the activity of statins as a lipid-lowering and atherosclerotic drug.
The great advantage of using statins is that they do not affect the synthesis of steroid hormones in the adrenal glands and gonads.
In addition, statins reduce absorption in the gastrointestinal tract of cholesterol, which enters the human body with food. In addition to the pronounced hypolipidemic effect, statins affect the endothelium (inner surface) of blood vessels. Statins improve migration and balance the process of "creation / destruction" of smooth muscle tissue cells and epithelium, thereby improving the mechanical and plastic characteristics of the vascular wall.
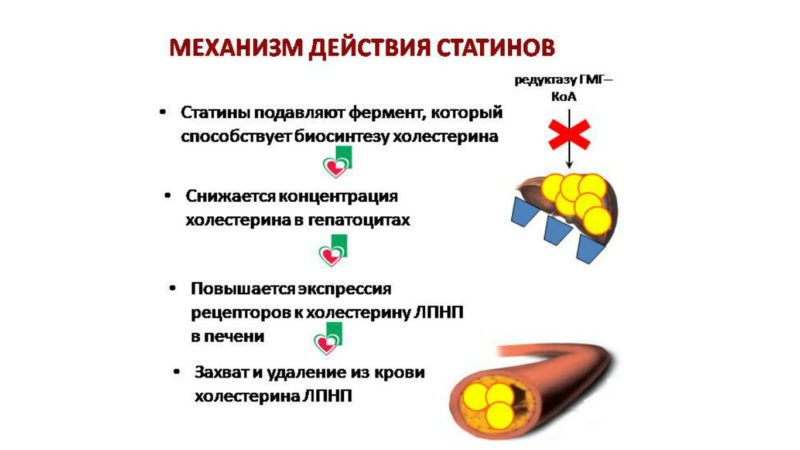
The drugs not only improve the structure of the endothelium, but also affect the synthesis of cytokines - substances that contribute to the occurrence of inflammatory processes. The anti-inflammatory mechanisms of action of statins reduce the risk of attachment and growth of cholesterol plaques. Also, the discussed agent inactivates macrophage cells, which synthesize substances that loosen cholesterol plaques and increase the risk of their detachment and vascular thrombosis.
Statins indirectly affect the volume and speed of blood flow, eliminating the factor for the development of tissue ischemia. Complex and multistage is the mechanism of their anticoagulant action. Such a variety of positive effects of statins on the body made the drugs leaders in the fight against hypercholesterolemia.
Classification of statins from cholesterol
There are several principles for grouping statins, depending on:
1. The origin of the drugs are divided into:
- natural, derived from lower fungi Aspergillus terreus;
- semi-synthetic, obtained as a result of chemical modification of natural compounds;
- synthetic, obtained as a result of chemical reactions, analogues of natural statins.
2. For drugs with a chemical structure in their structure:
- decalin ring;
- fluorophenyl group;
- methyl group.
Drugs are also subdivided by generations, but some scientists consider the separation of statins into generations incorrect, since they are very similar in their properties and effectiveness, and group them depending on the release chronology.
List of drugs - statins

All drugs have not only an international name, but also trade names:
| International Nonproprietary Names | Trade Name |
|---|---|
| Atorvastatin | Atomax; Atoris; Canon; Liptonorm; Liprimar; Torvacard Tulip |
| Rosuvastatin | Akorta; Crestor Mertenyl; Rosucard; Rosulip; Roxer; Tevastor AstraZenak |
| Simvastatin | Vasilip; Aries; Simgal; Simvakard; Simlo; Simvageksal; Simvastol; Simvor; Syncard; Zokor |
| Pravastatin | Lipostat |
| Pitavastatin | Livazo |
| Lovastatin | Cardiostatin; Holartar |
| Fluvastatin | Leskol Forte |
Statins are gradually losing ground. Clinical studies of new lipid-lowering drugs are already underway, the pharmacodynamics of which are based on completely different mechanisms.
But for now, statins are indispensable. In order to increase their effectiveness and reduce side effects, scientists from Amsterdam proposed to supplement the treatment regimen for family hypercholesterolemia with the new drug Praluent (Alyrokumab). However, statins are still leading in terms of sales and frequency of appointments.
Cholesterol statins are good
The main benefit of using statins is their ability to lower cholesterol.
In addition, drugs have an effect on:
- vascular endothelium, while maintaining its integrity and smoothness, which prevents the ability of cholesterol to "cling" to surface irregularities and form plaques;
- synthesis of inflammatory cytokines. By eliminating inflammation, statins reduce the risk of destruction of vascular endothelium, blood clots, impaired function of the heart muscle, reduce the level of soluble protein, which is associated with the recurrence of chronic cardiac pathologies and the progression of atherosclerosis;
- blood composition. By normalizing the blood coagulation process, statins reduce the risk of blood clots;
- nitric oxide synthesis. This compound has a relaxing effect on the muscle layer of the blood vessel wall, increasing blood flow;
- the state of cholesterol plaques. Statins have a stabilizing effect on the state of atherosclerotic plaques, preventing their destruction and separation with the formation of a thrombus. The body adapts to the presence of dense plaques, forming additional blood flow paths. With prolonged statin therapy, plaque size gradually decreases.
There are a number of positive properties of statins, but they are rarely listed in articles, since the mechanism has not yet been adequately studied, and the facts have not been confirmed by scientific studies. For example, in a number of articles the effectiveness of statin therapy in the complex treatment of diabetes mellitus was noted. The drugs not only reduced glucose activity, but also minimized the risk of developing coronary heart disease and other circulatory pathologies. The drugs, increasing blood flow, restored trophic tissue, excluded their oxygen starvation and necrosis. It is noted that when treating statins with diabetes, the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy is reduced.
In addition, scientists in separate publications note the positive effects of statins. It:
- reduced likelihood of spasm of the coronary arteries;
- stimulation of the formation of new coronary blood vessels (angiogenesis);
- antioxidant;
- inhibition of the progression of Alzheimer's disease and prussic dementia;
- antiarrhythmic and antihypertrophic;
- immunosuppressive.
In addition, statins have a depressing effect on some tumors, disrupting the reproduction of DNA and cell reproduction. The drugs stimulate the synthesis of osteoblast growth factor, favorably affect the state and function of the thyroid gland.
But, since statins are drugs of long-term use, not only the effectiveness of treatment, but also their safety was taken into account when creating them.
Side effects and harm
In addition to benefits, statins also bring harm, which is most often caused by non-compliance with the duration of use and excess dosage of drugs. Statins of the first generation, despite the fact that they were of natural origin, had an impressive list of side effects and contraindications.
Statins of the III and IV generations have fewer side effects and, excluding individual cases of muscle cell necrosis (rhabdomyolysis) and myopathy, according to some scientists, their use is no more dangerous than treatment with aspirin.

However, with prolonged treatment with high doses of statins, the following side effects are noted.
1. From the gastrointestinal tract:
- dyspeptic manifestations;
- defecation disorders;
- loss of appetite;
- pancreas inflammation;
- flatulence;
- fatty and fibrotic degeneration of the liver;
- anorexia;
- increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood;
2. from the nervous system:
- mood swings;
- impaired sleep function;
- memory impairment;
- dizziness and headache;
- cramps
- increased risk of developing Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease;
3. from the musculoskeletal system:
- muscle pain;
- myopathy
- rhabdomyolysis;
4. from the genitourinary system:
- sexual dysfunctions;
- tubulopathy;
- proteinuria;
- renal failure.
However, these side effects are not so common (1-2% of cases) to refuse treatment with statins, and for many patients these drugs are the only way to prolong life. In addition, the side effects of statins can be significantly reduced or completely eliminated if taken together with them 200-300 mg / day Conzyme Q10.
List of contraindications for use
The instructions for each drug indicate a list of contraindications, complete or partial.

So the use of statins is not recommended for:
- pregnancy
- at the age of 16-18 years. As an exception, with hereditary hyperlipidemia, statins are allowed to be used from 8-9 years old;
- persistent increase in the level of renal enzymes in the blood;
- acute renal failure;
- allergic reactions to drugs.
Statins are not a panacea and, with normal cholesterol, their use causes side effects of varying severity.
Since the benefits and harms of the drugs under discussion are still debated in the scientific community, there are many recommendations on how to lower cholesterol without statins. As an alternative, natural cholesterol statins and drugs with a similar effect are offered.
Natural cholesterol statins
Some plants and foods have statin-like effects. So, for example, as a dietary supplement, red yeast rice is sold, which contains natural statins, but also has side effects.
A good alternative to statins is called:
- low carbohydrate diet;
- eating varieties of sea fish rich in omega 3 fatty acids;
- fiber-rich vegetables and fruits;
- greens rich in niacin;
- berries and fruits containing a natural antioxidant - vitamin C;
- garlic and turmeric containing natural statin analogues.
In all these products, the proportion of natural statins is quite high. With strict adherence to diet therapy in combination with drug therapy, you can count on the same effect in the absence of side effects.
In addition to useful products, natural statins are found in such medicinal plants as:
- plantain;
- fenugreek;
- Caucasian dioscorea;
- golden mustache or fragrant collision;
- mistletoe;
- fruits of Japanese sophora;
- cyanosis blue;
- dandelion root, etc.

Diet therapy and herbal remedies will not be able to quickly normalize blood cholesterol, so they are used as elements of complex therapy along with other drugs that have the ability to inhibit the cholesterol synthesis enzyme.
How to lower cholesterol without statins?

In addition to the above methods of naturally lowering cholesterol, the following lipid-lowering drugs can be used:
- fibrates - Lipantil 200M, Tricor, Lipanor;
- sequestrants - Colestyramine, Colestipol, Kolesevelam;
- Niacin - Nicotinic acid, Nicotinamide.
The decision to choose drugs to lower cholesterol is made only by the doctor.The effectiveness of statins has been proven by lengthy (over 5 years) randomized trials conducted in several countries. Therefore, if the doctor has prescribed statins, you should not replace them with similar drugs on your own.
- Svetlana