Spermatogenesis in the body of a man, in contrast to ovogenesis in women, occurs throughout life starting from the puberty. The process takes place in several stages and is characterized by biological changes in the reproductive organs, especially in the testes. The maturation of one sperm takes more than 70 days, but due to the fact that the cells are at different stages of development, millions of sperm mature in male gonads every day.
Material Content:
What is spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the formation and maturation of male germ cells, which go from primitive gonocytes to full-fledged spermatozoa that can fertilize an egg. The process is activated during the puberty (at about 12 years old) and lasts the whole life of a healthy person.
All spermatogenesis processes occur in various layers of the testicular tubules. The sperm life cycle lasts more than 90 days. About 70 days are spent on growth and development, another 20-30 days he can expect ejaculation. Outside the male body, the germ cell lives no more than 24 hours, and under the influence of certain factors (heating, cooling, chemical agents), dies in a matter of minutes. Once in the female reproductive system (uterus, fallopian tubes), the sperm can survive there for 3 to 5 days.
The main regulatory factor in sperm formation is testosterone, the sex hormone inherent in the male body. With its lack, the process of sperm formation is disrupted, which leads to permanent or temporary infertility.In addition, the development of sperm occurs only at a certain temperature - 33-35 degrees. Since they are very sensitive to its fluctuations, overheating of the testicles leads to malfunction of spermatogenesis and reproductive problems.
Where are the cells
The formation of a sperm cell occurs in the testes, but depending on the stage of development and its type, sperm are in different layers of the seminiferous tubules. Spermatogonia (the original type of germ cells) are located on the basement membrane along with Sertoli cells.
Three types of spermatogonia are distinguished:
- dark A - spare, stored in the ovaries and activated in the case of a sharp decrease in the reproductive ability of men;
- light A - are constantly divided by mitosis; in the process of reproduction, other types of germ cells are formed from them;
- B-cells - are formed on the basement membrane, but are immediately moved with the help of Sustentocytes.
In the process of their further development, B cells are located in special depressions on the Sertoli plasma membrane. At the end of ripening, the Golgi apparatus forms an acrosome (a protrusion on the head of the sperm with which it dissolves the egg shell), and the finished sperm cell moves closer to the lumen of the tubules.
Stages of the reproductive process
During the development of male germ cells, four stages of spermatogenesis are distinguished:
- breeding season;
- growth period;
- ripening period;
- final formation period.
Each stage takes place in a separate ball of the wall of the twisting tubule of the ovaries, which allows simultaneously more cells at different stages of development.
Active reproduction occurs simultaneously with the puberty period. It is characterized by frequent and rapid division of spermatogonia, the number of which increases significantly. It is important that at this time the boy is not affected by negative factors - alcohol, smoking, overheating of the body, wearing tight underwear, as a reserve of cells is formed for life.
At the stage of growth, type B spermatogonia move to the second zone, which is located closer to the lumen of the tubule. There they significantly increase, store a large volume of cytoplasm and form spermatocytes I, that is, of the first order.
In the ripening period, the spermatocyte undergoes several divisions by meiosis, and 4 spermatids are obtained at the exit. They gradually form and transform into full sperm.
Germ cells
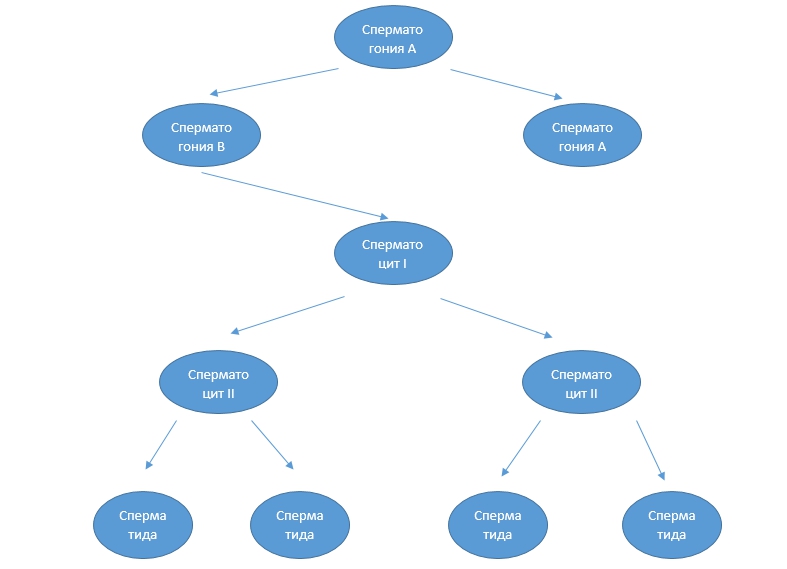
Spermatogonia A possess a large nucleus and a small volume of cytoplasm, acting in the role of spare cells. Therefore, we can say that the sperm development stage begins with type B spermatogonia, accumulating a large amount of intracellular fluid in the process, turning into spermatocytes I containing a diploid set of chromosomes (46 pieces).
First-order spermatocytes undergo two divisions by meiosis:
- initially formed 2 spermatocytes II with a haploid set (contain 23 chromosomes);
- after the second meiosis, 2 spermatocytes turn into 4 spermatids.
Under the influence of hormones, spermatids mature into spermatozoa.
Scheme of spermatogenesis:
Ways to stimulate sperm production
Male germ cells are extremely vulnerable. Sperm quality is negatively affected by factors such as smoking, age, inflammation, overheating, hypothermia, alcohol, irregular sex, and chronic diseases.
To stimulate the reproductive system to work better, you need:
- go to the andrologist who will prescribe special drugs to help identify the root cause of the violations;
- increase the amount of red meat, fish, dairy products, nuts in the diet;
- traditional medicine recommends decoctions of anise, rosehip, plantain seeds.
If the problem persists and the woman cannot become pregnant for a long time, sperm production can be temporarily stimulated using synthetic analogues of human hormones.This is done strictly under the supervision of the attending physician, who selects an individual therapy regimen.
Spermatogenesis is regulated by pituitary gonadotropin hormones and ovarian hormones. With an imbalance of at least one of them, the entire process of sperm production is disrupted - its quantity is reduced, defective sperm cells appear. By turning off the endocrine system of a man and replacing it with synthetic analogues, you can temporarily achieve a significant improvement in the quality of seminal fluid.
Differences between spermatogenesis and the formation of female germ cells
The formation of female germ cells - ovogenesis - is very different from spermatogenesis. The stage of reproduction of oocytes takes place in the womb, after birth, the appearance of new cells ceases. That is, girls have a stable set of eggs, the number of which does not change, but the spermatogenesis of men does not stop throughout life.
Four spermatozoa are formed from one spermatogonia, while one mature oocyte is formed from one first-order oocyte. And also in ovogenesis there is no stage of formation, since female cells have no need to move around, they practically do not change externally.
If spermatozoa are no longer being produced in a man, the process can be stimulated by acting on the body with synthetic hormones. In the absence of an ovarian reserve in a woman, stimulation does not make sense, since all cells have already matured and left during ovulation, and there is nowhere to get new ones.