Laxatives for constipation for the elderly are selected taking into account the characteristics of a middle-aged body. In old age, many diseases accumulate, in which some medications may be contraindicated. Older people drink a lot of drugs, so be sure to pay attention to the compatibility of drugs. The choice of laxative should also be based on a possible cause of constipation.
Material Content:
Possible causes of constipation in the elderly
With age, all body functions decline. Hormonal metabolism is disturbed. The influence of the autonomic nervous system, the one that is responsible for the work of internal organs, is weakened.

The innervation (nervous regulation) of various parts of the intestine worsens. Somewhere food lingers longer, somewhere faster. The interaction between the gastrointestinal segments is becoming less consistent.
Aging leads to a gradual extinction of the secretion of internal glands. Over time, the walls of the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines become thinner. Their main function weakens, which leads to problems with bowel movements.
The longer a person lives, the more breakdowns accumulate in his body. In old age, most people have chronic diseases. For this reason, they are forced to take various medications, against the background of which lesions of the digestive tract develop.Delayed stool can be a consequence of the disease itself.
Aging of the musculoskeletal system inevitably leads to a decrease in motor activity. With a passive lifestyle, the tone of all muscles, including those responsible for the digestive tract, decreases. Atony of the intestine helps to delay fecal mass and increase the frequency of constipation.
Not the least role is played by the power system. People with dentures prefer easily digestible food to vegetables and fruits, which cannot properly stimulate the intestines. It is proved that those who manage to preserve almost all of their teeth by senile age are less likely to suffer from constipation.
Types of Laxatives
For problems with bowel movements, it is first of all worth adjusting the diet and treating the underlying disease. Laxatives are used as a necessary measure to help prevent intoxication.
Depending on the nature of the action, medications are divided into several groups.
Irritant drugs
The principle of action of irritating drugs is to stimulate the nerve endings of the intestinal walls. Its active muscle contractions promote the pushing of contents.
This is a fairly large group of medicines, which includes drugs of various forms: drops, tablets, suppositories, etc. Among them, there are natural products (senna preparations, castor oil) and chemical derivatives (based on sodium picosulfate).

Annoying medicines are often used in the elderly. They have a quick effect, promote bowel movement within the next few hours. Effective in atony and lazy bowel syndrome.
The peculiarity of the medicines of this group is that they can be addictive. With the frequent use of such drugs, the intestinal walls lose their ability to respond to irritants. These drugs are used, as a last resort, and not at all on a regular basis.
Irritant drugs are contraindicated in violation of the integrity of the gastrointestinal mucosa. In the presence of ulcers, erosion, bleeding, cracks.
They also have side effects. Causes intestinal pain, bloating, rumbling.
Fillers
Intestinal fillers are agents of natural (flax seeds, agar-agar) or synthetic (methyl cellulose) origin. By themselves, they are not digested or absorbed. Swell under the influence of water, increasing the volume of the contents of the intestines. The walls of the intestines are stretched and then contracted, trying to push a food lump.
These funds are the safest, as they are not absorbed and are not addictive. They act slowly during the first day.
Such drugs are not effective in reducing the tone of the intestinal muscles, so they are rarely prescribed for the elderly. Instead of the effect, they can cause a feeling of fullness, gas, intestinal colic. Fillers are contraindicated in the presence of inflammatory diseases of the intestinal mucosa.
Laxative prebiotics
Prebiotics are the most delicate products of natural origin. They include fruit oligosugars (inulin, lactulose), which begin to be digested only in the lower intestine.
During the fermentation of plant substances, organic acids are released that stimulate the nerve endings of the intestinal mucosa. Simple components resulting from the digestion of oligosugars become a nutrient base for beneficial bacteria.
Thus, prebiotics restore the balance of microorganisms, eliminate the effects of dysbiosis, have a therapeutic effect.
These drugs are not intended for single use. They are prescribed a course. Improvement is observed only 3-4 days after administration. Despite the slow action, prebiotics give a lasting result.
They practically do not cause side effects.The first three days of admission go unnoticed. Subsequently, increased gas formation may occur.
Osmotic laxatives
Osmotic laxatives are products based on artificial or natural salt. Drugs interfere with the absorption of water in the intestines. The fluid accumulates in places of stagnation of feces. Under the influence of water, food debris softens and is easily evacuated.
Read also:constipation what to do - urgently
Such drugs are not addictive, therefore, they can be prescribed for a long time, however, over time they can provoke dehydration, therefore they are always taken with plenty of water.
Osmotic laxatives cause multiple stools. Most fully cleanse the intestines.
A contraindication to taking medication is ulcerative damage to the mucosa. Side effects may include: nausea, vomiting, acute intestinal pain, flatulence.
Traditional medicine

If the situation does not require an immediate response, before using pharmacy medicines, you can try folk laxatives:
- every day before each meal you need to drink a teaspoon of olive or flaxseed vegetable oil;
- in 100 ml of boiling water you should insist a teaspoon of chopped flaxseed, drink the cooled mixture every day before bedtime;
- squeeze fresh juice from pumpkin and carrots, mix in a ratio of 1: 1, drink a drink twice a day in a glass in the morning before meals and in the evening before going to bed;
- try sprinkling food with two tablespoons of dry bran during breakfast and lunch;
- a cup of kefir with a spoon of vegetable oil drunk before bedtime helps with constipation.
Traditional medicine is used to restore normal stool. If after a week no improvement is observed, tactics should be changed.
How to choose the right laxative?
The choice of drugs for the elderly carries a certain risk. First of all, you need to take into account the condition of the patient, as well as have a complete understanding of his underlying disease.
For the elderly with diabetes
Diabetes is an insidious disease that affects all body systems. With high blood sugar, degeneration of the nerve endings that regulate the activity of the intestine occurs. In this situation, the digestive tract organs begin to perceive the signal coming from the brain worse.
To get rid of constipation, you need to act directly - put the irritant where it will have an effect. The best drugs for diabetics are medicinal suppositories and prebiotics.
The former directly stimulate the receptors of the rectum, quickly causing the urge to defecate. The second works as an irritant and a bulking agent. During fermentation, prebiotics secrete acid, which not only activates the growth of beneficial microflora, but also directly affects the nerve endings of the intestinal membrane.
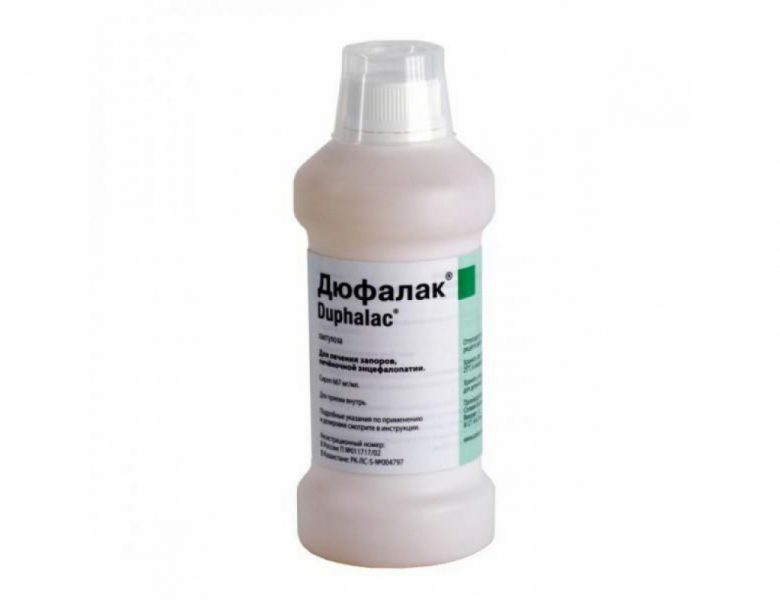

Despite some prejudices, oligosugar-based prebiotics (Dufalac, Lactulose) in normal dosage do not harm diabetes. But salt laxatives are allowed to be used only as a last resort, since they can provoke dehydration, which is extremely undesirable in this disease.
For bed patients
Constipation is a significant problem for bedridden patients. It requires a delicate decision. A long delay in feces leads to poisoning of the body. At the same time, the use of fast drugs is unacceptable, since they can cause additional discomfort to the patient.
For bedridden patients, delayed-action drugs are chosen, the same prebiotics that have a therapeutic effect and at the same time remove ammonia decomposition products. And osmotic laxatives, designed for long-term use, for example, macrogol preparations (Forlax).
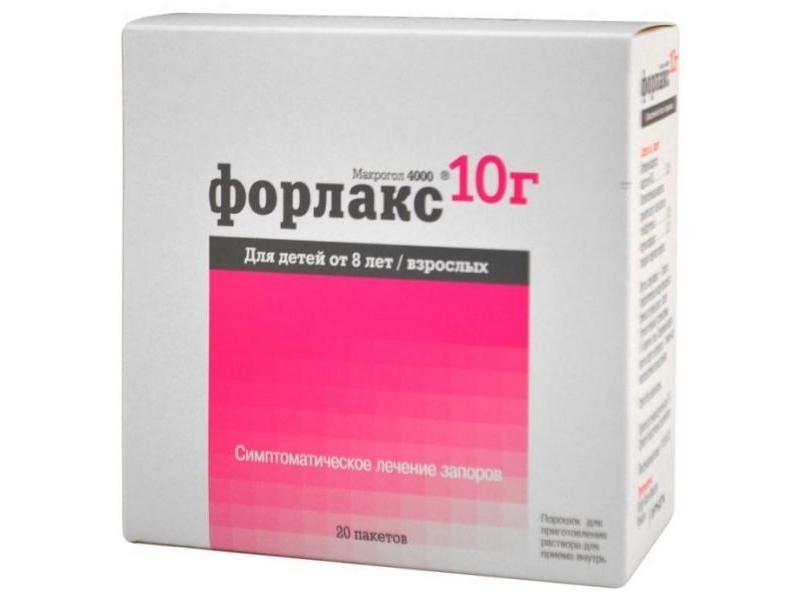
The latter does not cause a violent reaction. The discharge of feces begins on the second day.Laxative macrogol facilitate bowel movements and can be taken for 3 months.
In the postoperative period
After surgery directly on the intestine, the patient receives food through a vein. The digestive tract for better healing should remain alone.
Subsequently, a diet is appointed to restore motor skills. For a better discharge of feces, complex preparations of the Mukofalk type are prescribed.
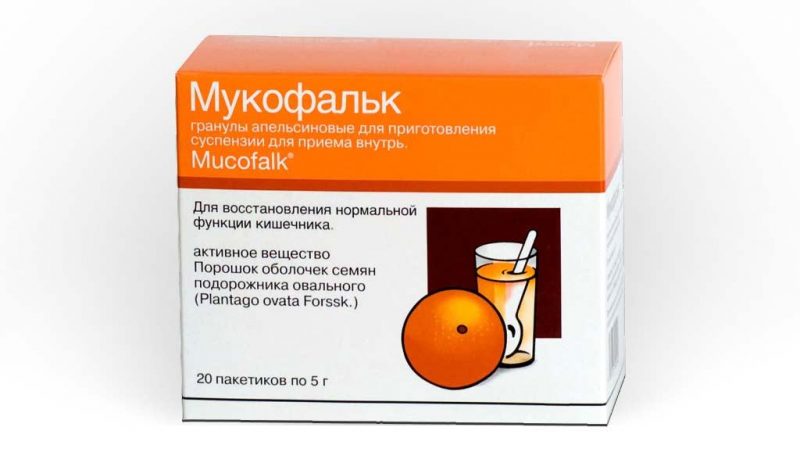
The composition of this tool includes plantain seed coat, salt and excipients. Laxative retains water in the intestines, softens feces, stimulates nerve endings and promotes regular gentle emptying.
For older people with gastritis or an ulcer
In patients with ulcers or gastritis, laxatives should not increase the acidity of gastric juice. In inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, soft plant-based motility-promoting drugs (Fitolax) and prebiotics with a therapeutic effect are used.
What helps with severe constipation?
Due to the nature of the action, strong laxatives for constipation should be used only as directed by a doctor. First of all, bran, flax flour, herbal preparations based on plantain seeds are tried.
If the effect is not observed, you can use annoying medicines from senna leaves. A strong stimulating effect is exerted by the drug Bisacodyl, which directly affects the intestinal receptors, rectal suppositories with glycerin and microclysters (Microlax). If none of the listed remedies helps, salt laxatives (Guttalax) are prescribed.
Most effective laxatives list
Among the means used by the elderly, the following drugs show the greatest effectiveness:
- Glycerin candles;
- Senade;
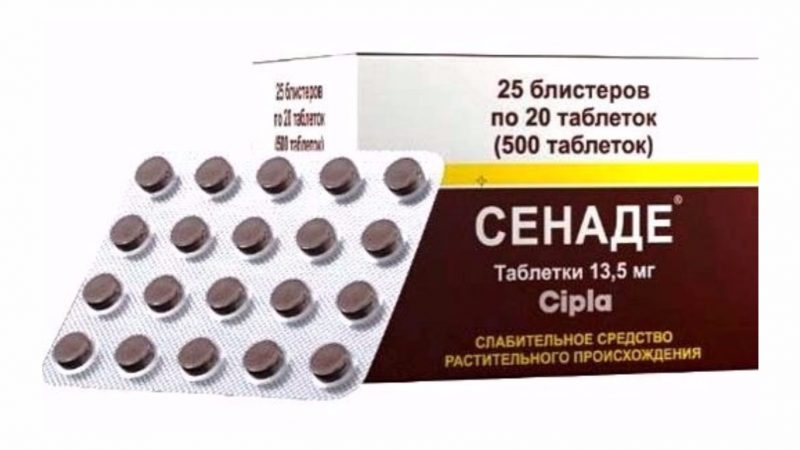
- Bisacodyl;
- Mucofalk;
- Microlax.
Glycerin candles contain glycerol - a component of irritating and osmotic effects. It retains fluid in the lumen of the intestine, softens feces and causes the urge to defecate. Candles are used one-time. Contraindicated in anal fissures, inflammation, intestinal bleeding, tumor of the rectum. May provoke the appearance of itching, burning and allergic reactions.

Senade - a drug based on an extract of senna leaves. Irritating bowel receptors, stimulates peristalsis. The drug is contraindicated in intestinal obstruction, cramping, gastrointestinal bleeding, abdominal pain of unknown origin. May be addictive, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
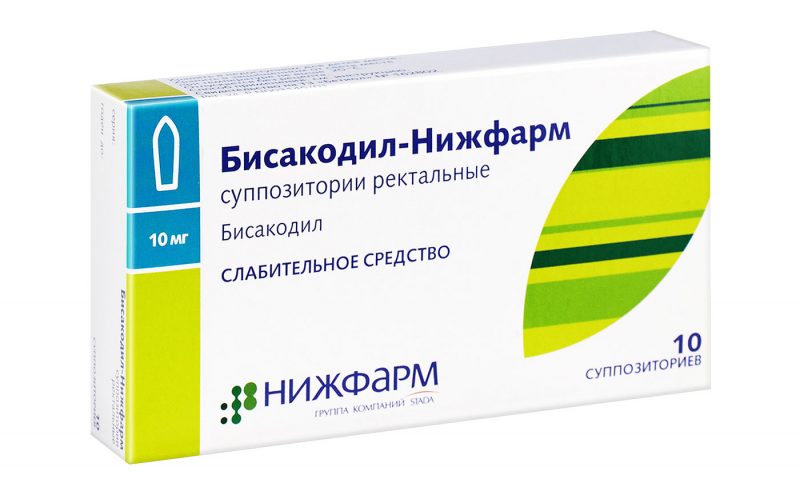
Bisacodyl - Available in the form of tablets and candles. The drug reduces the absorption of fluid in the digestive tract, irritates the walls of the rectum. Contraindicated in intestinal polyps, violation of the water-salt balance. May cause colicky abdominal pain, bloating, intestinal atony.
Mucofalk - contains a vegetable-salt complex. Stimulates peristalsis, softens feces. Contraindicated in diabetes mellitus, obstruction, intestinal bleeding, electrolyte imbalance. In the first days of admission, sometimes it causes increased gas formation.
Microlax - contains glycerol and sodium salts. Microclyster promotes the accumulation of water in the intestinal lumen, liquefies feces, facilitates bowel movements. Acts fast. Designed for single use. Contraindicated in patients with sensitivity to the components of the drug. During treatment, it can cause discomfort and a burning sensation.

Choose laxatives in old age should be careful. Be sure to take into account the general condition and do not forget to consult with your doctor about the possible combined use of certain drugs with your main medicines.