With insufficient production of hormones by the thyroid gland, a person develops hypothyroidism - one of the most common forms of diseases of this organ. The lack of treatment sometimes leads to very serious health problems. About how hypothyroidism manifests itself, about the symptoms in women, the treatment of the disease is described in our article.
Material Content:
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a functional disorder in the thyroid gland. It develops from a prolonged lack of certain hormones in the body, as well as due to a deficiency caused by their “digestibility” at the cell level.
The disease is more common among elderly patients (10%), in women of reproductive age occurs in 2%, in children - 1% of cases.
The participation of hormones is invaluable for the full functioning of all organs. This tiny gland is like a small conductor of a large orchestra of our body. Its hormones are directly involved in the regulation of energy metabolism in cells, and the level of oxygen consumption in tissues depends on how the thyroid gland works. With hypothyroidism, cell enzymes cease to be normally synthesized, its vital activity is disrupted.
When the disease develops, all processes in the body slow down, because a woman experiences weakness, drowsiness, speech slowdown and a host of other problems. Severe forms of hypothyroidism lead to even more complex consequences, the development of organ pathologies, and complications. One of the most dangerous is myxedema or hypothyroid coma, from which 40 percent of people die.
Varieties of ailment
It is customary to share several types of disease:
- primary - this type of hypothyroidism develops due to changes in the thyroid gland;
- secondary, associated with a lack of iodine, a violation of the body;
- tertiary - due to damage to the hypothalamus or pituitary gland (both produce thyroliberin and thyroid-stimulating hormone, respectively).
Congenital disease and acquired hypothyroidism are also distinguished. Today, the second is the most dangerous, since in most cases for a long time the disease does not manifest itself and proceeds secretly.
If hypothyroidism is congenital, then the prognosis is mostly favorable: thanks to mandatory examinations of newborns today, such a disease is detected immediately and treated quite effectively. If it is not recognized, then the lack of treatment can lead to a dwarf child, mental retardation, cretinism, underdevelopment of organs in the baby.
Of the cases of acquired forms of the disease, we can distinguish those that developed after an operation to remove or resect the thyroid gland or a course of radioiodine therapy. Such cases respond well to correction. However, women often suffer from autoimmune thyroiditis, a disease that develops gradually, it is difficult to diagnose, because it does not have pronounced symptoms and therefore is difficult to determine even by doctors.
Note! It is very important, at the slightest suspicion of a thyroid disease or other problems associated with its hormones, to conduct a full examination with a doctor with a blood sampling for examination. There are cases when hypothyroidism manifests itself even with a normal level of hormone production, but they simply "do not work" due to the decreased sensitivity of tissue receptors.
The causes of the disease
If we summarize all of the above, then the causes of the primary disease can be the following:
- chronic and long-running thyroiditis;
- iodine deficiency (expressed, as a rule, in the occurrence of goiter);
- surgical intervention with removal of the thyroid gland partially or completely.
The cause of the secondary disease is an infectious lesion, trauma, or brain tumor.
Symptoms and signs in women
The problem is that the symptoms and signs of hypothyroidism do not appear immediately. When the hormonal level decreases, there is a gradual slowdown in all metabolic processes, and metabolic disorders cause depression of the nervous system. As a result, a woman begins to feel the most diverse manifestations of the disease, which she does not immediately connect with the thyroid gland.
This can be weight gain, swelling of the face, swelling of the ligaments, as a result of which hoarseness is heard in the voice, and speech becomes slurred. The skin turns pale, dries, pressure drops, the pulse slows down. Many women feel a feeling of chilliness, discomfort in the muscles and joints. Sometimes thyroid failure leads to complete amenorrhea or delayed menstruation. The manifestation of certain symptoms depends on the degree and duration of the lack of hormones in the patient’s blood.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of the disease is primarily based on a blood test for the content of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), as well as the thyroid stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland (TSH). Hypothyroidism is characterized by a decrease in the first two and an increase in the third. Thanks to TSH concentration tests, even latent or subclinical hypothyroidism can be detected.
In addition to these analyzes, blood is subject to research for cholesterol, iron, which can also give rise to the onset of the disease. Other events may be held.
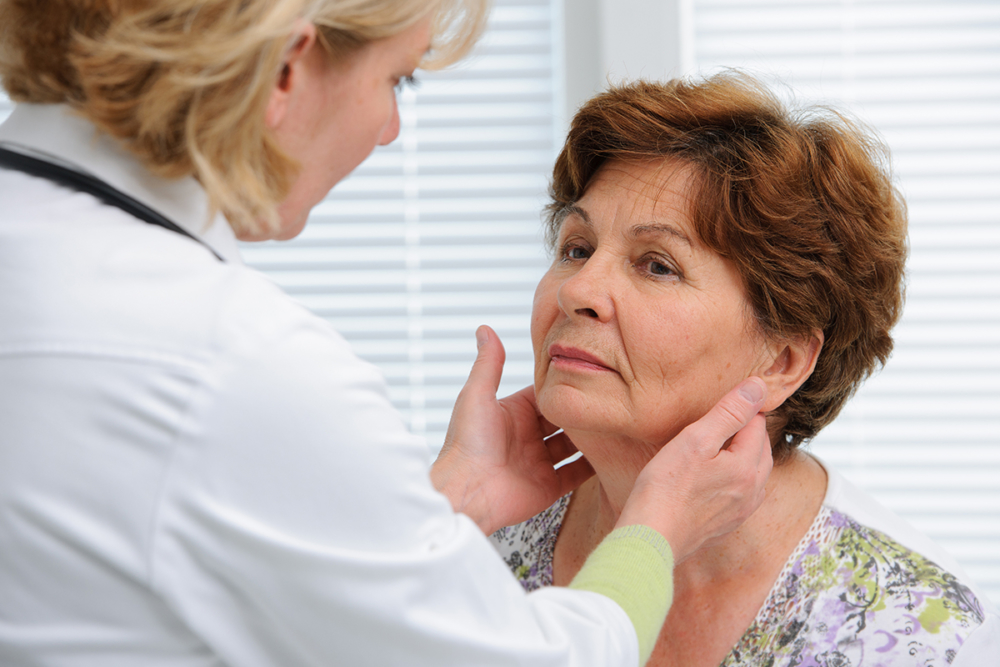
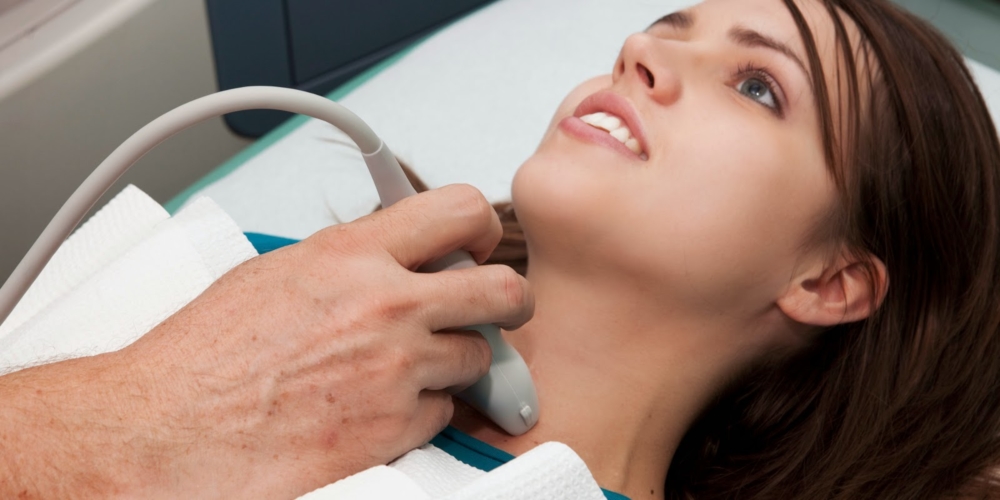
An important diagnostic method is ultrasound. Usually, a blood test for hormones is enough to detect the disease. In some cases, additional examination methods are prescribed, including a tomographic study. Sometimes a puncture biopsy of individual nodes of the thyroid gland is performed, an ECG and other instrumental methods are prescribed.
Hypothyroidism Treatment
Treatment of hypothyroidism in women involves replacement therapy with drugs containing synthetic hormones.
Drug therapy
The dose of drugs is adjusted, the effectiveness can be estimated within 1-2 months. Subsequently, the dosage can be corrected, corrected.
It can be combined preparations containing thyroxine and L-triiodothyronine together, or separate drugs.
Important! The TSH rate in women varies slightly with age. So, up to 25 years its value is 0.6-4.5 (mIU / l), up to 50 years old - 0.4-4.0, then - up to 4.5. Regular monitoring of hormone levels in the premenopausal period and after menopause is especially important.
Folk remedies
Important! Folk remedies can slightly improve the patient's condition with hypothyroidism, but you should not rely only on their healing power. First of all, consult a doctor and use replacement therapy. Everything else with untreated hypothyroidism is dangerous and ineffective!
Among the used folk remedies, the most popular:
- natural apple cider vinegar - it is used to restore the acid-base balance, it helps to reduce weight and regulate hormones, helps improve energy metabolism. Take vinegar with water and honey;
- kelp - valuable for its high content of minerals and iodine. To improve thyroid function, you can take either dried kelp, soaked in water, or as an additive to dishes;
- Melissa - increases the efficiency of the thyroid gland;
- fish oil - contributes to the production of thyroid hormones.
In addition, both traditional and traditional medicine are advised to take vitamins of groups B, A and D. They contribute to the improvement of the thyroid gland's daily walks, physical activity in general (it helps to accelerate metabolism) and proper nutrition.
Features of the course during pregnancy
Hypofunction of the thyroid gland in pregnant women occurs in 2% of cases, this is partly due to the fact that with hypothyroidism it is not possible to get pregnant often, more often in a woman hypothyroidism causes infertility.
However, if pregnancy has occurred, and a woman begins to experience weakness, cramps, drowsiness, and other manifestations of a lack of thyroid hormones, then this is a very dangerous condition not only for a woman, but also for the fetus. First of all, for the development of its central nervous system. A hormone deficiency in the mother's body can lead to irreversible consequences from the first weeks of pregnancy.
Currently, due to the diagnosis and proper replacement therapy, complications of pregnancy and childbirth are rare. But many researchers are inclined to believe that even a slight deviation and change in hormone levels in the first place becomes a threat to the health of the child, especially if subclinical hypothyroidism is observed.
The danger of hypothyroidism for women
Women more often than men develop hypothyroidism. This is primarily due to the fact that the female body is more sensitive to various kinds of hormonal changes.
On the other hand, these changes occur more often in her life than in the strong half of humanity. Childbirth, pregnancy can also precede it, and heavy bleeding can contribute to anemia and the risk of this disease.
Women also respond to the development of hypothyroidism with a violation of the monthly cycle, the inability to become pregnant and have a baby.
Possible complications after treatment
If you do not treat the disease or start treatment late, then complications arise that significantly lower the quality of life. Older people may even die from heart or respiratory failure, although improper therapy is extremely dangerous for young people.
One of the most formidable complications is hypothyroid coma. It can develop after an overdose of sedatives or drugs, as a result of thyroid surgery and in some other cases. Such manifestations as hypoxia, hypoventilation of the lungs, lowering of temperature, increase of cholesterol, hypoklemia are associated with it. If a person is not helped, death is possible. A sick woman may also have tachycardia, heart failure develop, which also sometimes leads to death.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of hypothyroidism, you need to visit a doctor at the first suspicion. Women, and especially the elderly, must periodically donate blood for hormone analysis.
For prevention, doctors advise you to consume foods rich in iodine - seafood, fish, herbs, vegetables, buckwheat, persimmons, feijoa. Iodized salt should be on the table for those who live in the natural zone of iodine deficiency, and it will not hurt residents of other territories either.