Keratoses are a group of diseases of the skin of non-inflammatory origin. Pathology is manifested in the appearance on the skin of benign neoplasms from single or multiple hardened and keratinized epidermal tissues. The appearance of keratomas (size, color) can be different, but they all bring both physical discomfort (itching, itching) and aesthetic, since these dark growths look extremely unpleasant.
Seborrheic keratosis of the skin is also called senile, since it develops, as a rule, in people of retirement and pre-retirement age.
Material Content:
- 1 Seborrheic keratosis: what is it?
- 2 Reasons for the appearance
- 3 What is dangerous?
- 4 Classification and characterization of forms of keratosis
- 5 Symptoms of the disease
- 6 Diagnosis of keratosis
- 7 Treatment
- 8 Drugs for seborrheic keratosis
- 9 Surgical removal
- 10 Traditional medicine - treatment at home
- 11 Preventative measures
Seborrheic keratosis: what is it?
Seborrheic keratosis is a benign tumor consisting of keratinized skin cells. The first manifestations are usually small, colorless, light pink or yellowish spots that do not irritate the skin. In the absence of treatment, over time, the disease slowly progresses, spots multiply, increase in size, rise above skin level, darken to a brown or burgundy heterogeneous color with black patches.
Neglected keratosis has a flaky, itchy, irritated surface that looks like a pile of small warts. Touching them brings torment and pain, can lead to bleeding.
Reasons for the appearance
At the moment, there are many versions of the appearance and development of seborrheic keratosis, however, none of the reasons is 100% proven.Many doctors are inclined to age-related factors contributing to the formation of keratosis, but why then does not all of the elderly have it? Some scientists insist that seborrheic dermatitis is a consequence of prolonged exposure to sunlight, but how, then, can it be explained that it appears both in open and covered in clothing parts of the body?
Doctors suggest that the following factors may contribute to the occurrence of seborrheic keratosis:
- age-related changes in the structure of the skin (after 50 years);
- genetic predisposition (the chance of growths in blood relatives is much higher);
- frequent microdamage to the surface of the skin (e.g., chafing, peeling, corns, tight clothing);
- regular and prolonged exposure to sunlight;
- exposure to chemicals (acids, alkalis, detergents, deodorants, fresheners, eau de toilette, work in a chemical laboratory, factories);
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- immunodeficiency;
- poor uniform nutrition, lack of vitamins, minerals;
- taking hormonal medications, including contraceptives;
- period of pregnancy.
What is dangerous?
Despite the fact that seborrheic keratosis is recognized by medicine as a benign tumor, its danger is not only in external unaesthetic. Between keratosis and cancer, there is a connection and quite dense.
Sometimes the external similarities of skin cancer and seborrheic keratosis are so great that even the most qualified dermatologists and oncologists are not able to distinguish one from another in appearance. In this case, only histological analysis of tumor tissue can solve the problem.
In addition, cancer cells can at any time begin to develop right at the base of keratoma, without manifesting themselves externally. This is the most dangerous scenario, since in this case the cancer can be detected already at an advanced stage, then the doctors will not be able to help the patient. In this regard, large formations that protrude strongly from the level of the skin are most dangerous.
The accumulation of multiple seborrheic keratosis in one area of the body may indicate the development of a cancer of one of the patient’s internal organs. In case of detection of overgrown seborrheic tumors, doctors suggest a complete examination of the body.
Classification and characterization of forms of keratosis
Specialists subdivide keratosis into several types:
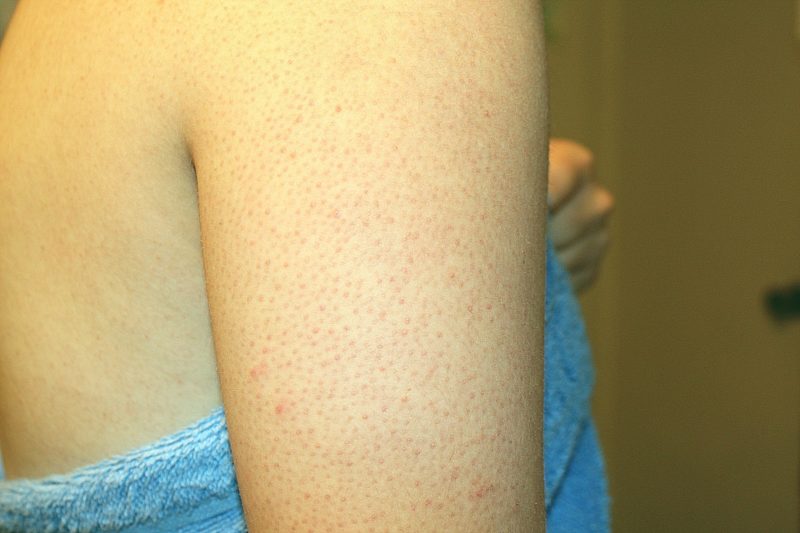
- Follicular keratosis is characterized by the appearance of light pinkish or yellowish nodules, may be accompanied by redness and inflammation of the skin around them. Nodules are located on the hair follicles, preventing them from opening. The reason for the appearance of such a syndrome has not yet been established.
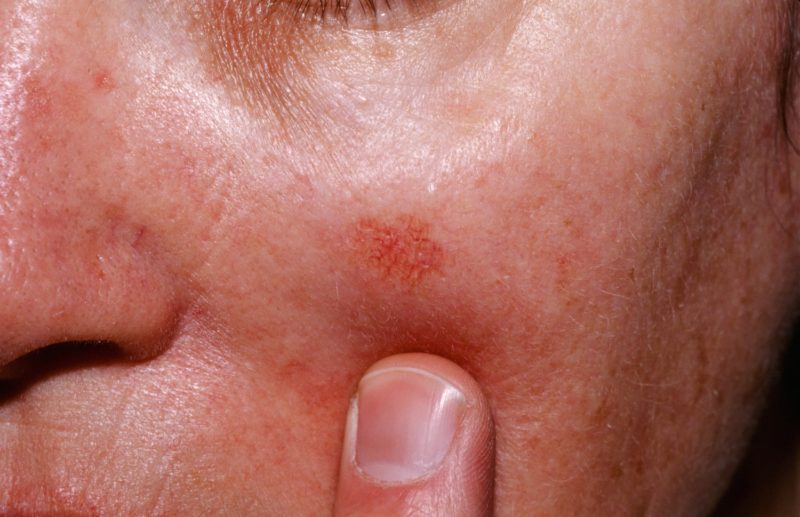
- Actinic (solar) keratosis affects fair-skinned people over 45 years old. In places constantly exposed to the sun, small transparent, pink or gray spots appear, covered with rough scales. The surrounding skin turns red and inflamed. Over time, the disease slowly progresses, if untreated, degenerates into squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma.
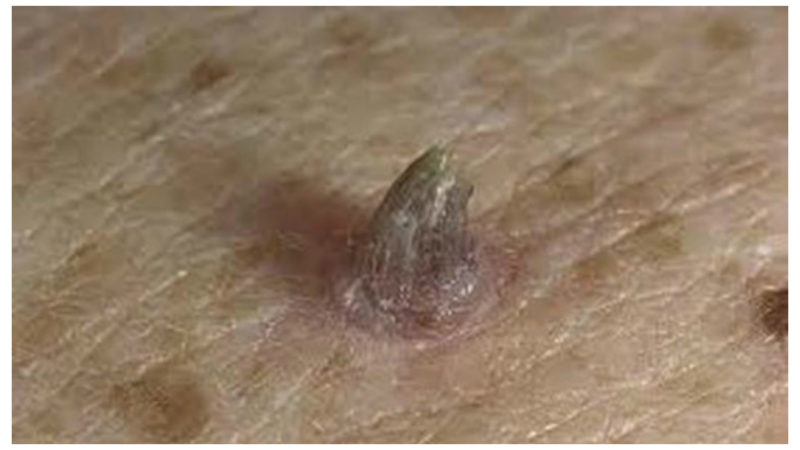
- Horn keratosis (cutaneous horn) - very similar to animal horns, is an elongated conical growth of a darkish color. The skin horn can grow alone or in bulk, in most cases, over time, degenerates into a cancer. Therefore, the treatment of horny keratosis can not be put off the bat, surgical intervention is required immediately after detection and diagnosis.
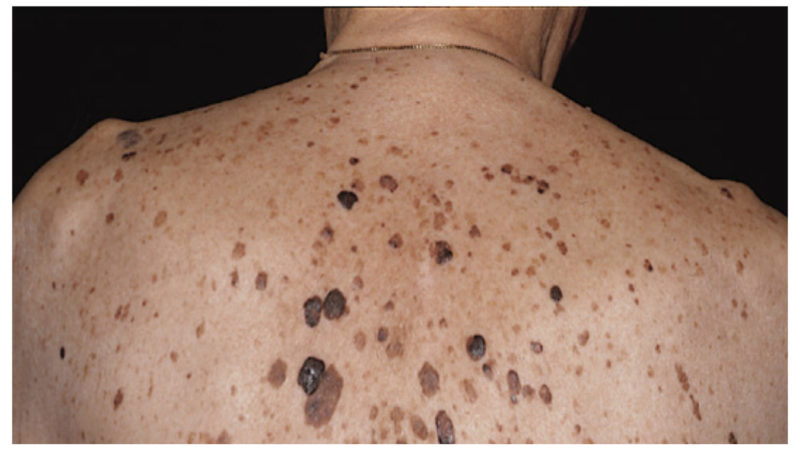
- Senile (seborrheic, senile) keratomas in appearance are very similar to warts: round or oval, slightly rise above the skin, covered with keratinized cells of beige, gray, brown or even black.Seborrheic keratosis develops for a long time, the risk of turning cells into cancer is minimal.
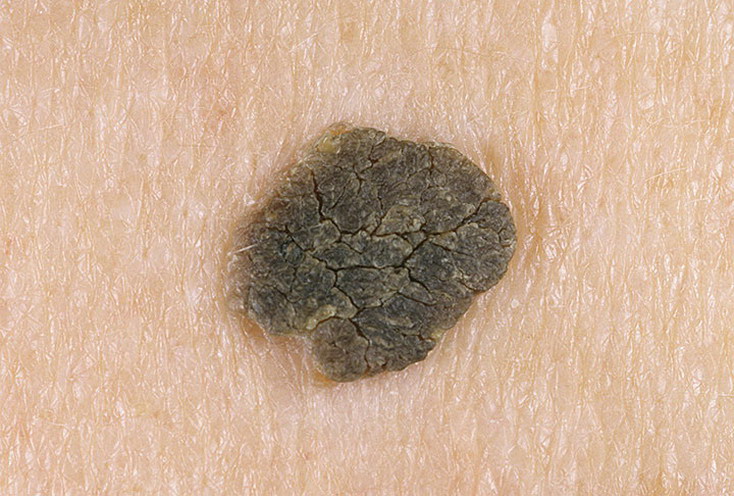
Seborrheic dermatitis itself also has several forms of manifestation:
- the flat form is characterized by the presence of flat spots that do not rise or are slightly elevated above the skin level, their color is almost always bright and dark;
- reticular keratoma is characterized by the presence of horn brushes on its surface;
- the irritated type of seborrheic keratosis is distinguished by the presence of an accumulation of a mixture of blood and lymph in the tissues of the neoplasm;
- the inflamed form is immediately noticeable by severe redness of the skin, swelling, bleeding, this is the most dangerous type of seborrheic keratosis in terms of oncogenicity.
Read also:keratoma - what is it, how to treat
Symptoms of the disease
The initial stage of seborrheic keratosis passes, as a rule, imperceptibly and asymptomatically. A flat, rough, colorless spot appears on the skin, which few people pay attention to. The fact that this is a seborrheic keratoma is known much later, when the spot becomes bright and dark, acquires smooth round edges, rises above the skin level and becomes covered with a rough horny layer with many folds. Keratoma may remain so alone or grow into two dozen neoplasms.
The growths can affect any part of the human body, except the palms of the hands, feet and mucous membranes. Most often, they can be observed on the chest, abdomen, back, shoulders and neck. The color gamut of formations is quite wide: flesh, yellow, gray, brown, burgundy, black. Size - from 1 mm to 10 cm. They may not be felt on the skin or itch, itch and bleed.
The development of the disease is not rapid, neoplasms grow slowly, from a few signs to a serious form it can take from several years to a dozen.
Diagnosis of keratosis
If you find any neoplasms in yourself, you should hurry to a qualified doctor, in no case should you independently conclude yourself by comparing your feelings with the symptoms from a medical reference book. By external signs, it is not always possible to accurately determine the nature and danger of growths.
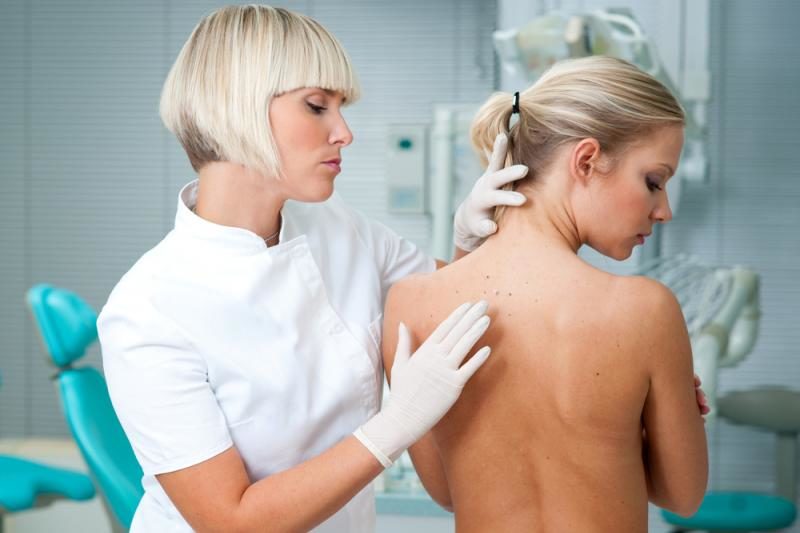
An experienced dermatologist-oncologist will be able to determine whether the neoplasm is keratosis, the stage of development of the disease and the degree of its danger in terms of degeneration into cancer. If factors predisposing to oncology are detected, the doctor prescribes the removal of growths using one of the available methods, followed by histological analysis of the excised tissue particles.
Treatment
After establishing the final diagnosis of Seborrheic keratosis of the skin, you should immediately visit a doctor and decide on further treatment. It is extremely important to realize that you can’t get rid of growths yourself. Even if you try to cut off a small growth with a knife, creating sterile conditions, the consequences can be disastrous. With the naked eye, it is impossible to determine the boundaries of keratoma cells from healthy ones, and trauma to the growth tissue can lead to the fact that the tumor will grow, multiply, and degenerate into a malignant tumor. Most conversions of seborrheic keratosis to squamous cell carcinoma occur on intentional or accidental damage to the surface of the growth.
Keratoma is a benign neoplasm, that is, it does not bring negative consequences to human life and health, therefore in most cases it does not need removal. With constant monitoring by a dermatologist and the absence of factors predisposing to cancer, you can live with it all your life without feeling discomfort. However, we should not forget that under certain conditions, the formation can degenerate into a cancerous tumor, so you should immediately contact a specialist to remove the growth, if he:
- regularly injured by friction against clothes, shoes, in the process of shaving, clings to a belt and so on;
- it becomes inflamed, itchy, itchy, bleeds, the skin around it turns red;
- quickly increases in size, becomes stiff and brings pain when pressed.
Often, keratomas have to be removed due to a cosmetic defect, especially if they are heavily pigmented or located on visible parts of the body (face, neck, chest, arms).
Read also: red spots on the face
Drugs for seborrheic keratosis

In the case of uncomplicated keratosis, it is possible to use special ointments, creams, gels, solutions and emulsions containing various active acids and cytostatics aimed at corroding the neoplasm cells. Despite the fact that we are used to using external preparations at home on our own, in the case of seborrheic keratosis, they can only be used in a special medical institution under the supervision of a qualified specialist. The doctor selects a specific drug with the appropriate components in this case, sets the dosage and time of exposure to the tumor, depending on its size, form and stage of development of the disease.
Surgical removal
Surgical treatment of seborrheic keratosis of the skin can be carried out by several methods. In each case, the method is selected individually depending on the state of health, the stage of development of the disease, the possible oncogenic nature of the tumor, the financial capabilities of the patient.
A standard removal of a layer of growth with a surgical scalpel is a reliable and cheap option, but after it there will be a noticeable scar or scar. If the doctor has a suspicion of the presence of cancer cells in the keratoma lesion, then the scalpel is the only chance to remove absolutely all damaged tissues and subsequently send them for histological analysis.
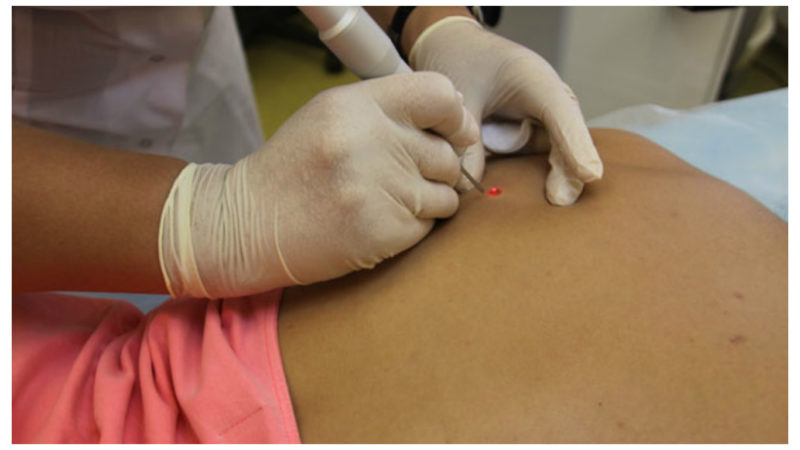
The laser method is currently considered the most optimal, since it has practically no contraindications, does not leave scars, and contributes to the rapid healing of wounds.
Liquid nitrogen provides the ability to remove small formations almost painlessly, does not require anesthesia.
Traditional medicine - treatment at home
The use of traditional medicine methods is possible only after the approval of the doctor, since in this matter it is extremely important not to harm. In no case should aggressive substances be used (for example, alcohol solutions), since damage to the external tissues of keratoma can lead to the rapid transformation of its cells into cancerous.
We'll have to be patient, the treatment of growths is associated with repeated daily procedures for a long period of time (from several months to several years).
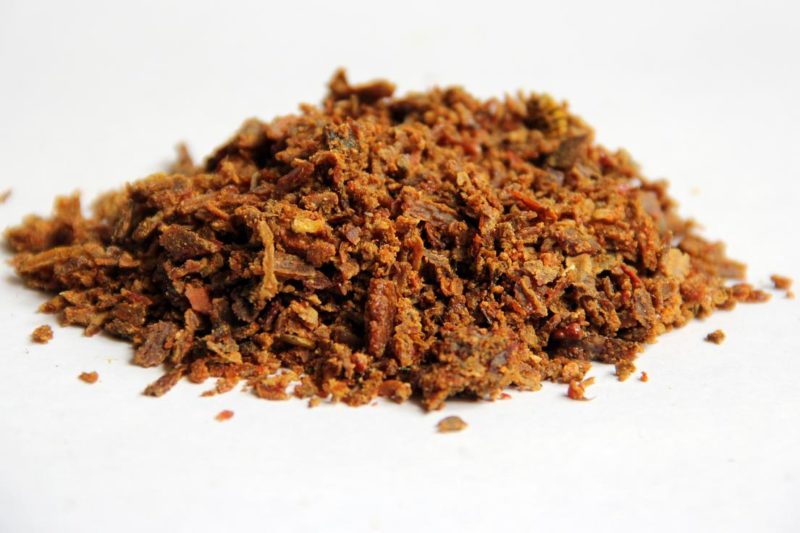

The most effective recipes:
- propolis should be crushed to a homogeneous mass and applied to the affected area constantly, changing the active substance and gauze bandage once a day;
- pass a piece of beets through a fine grater, apply to the skin through gauze for 4 hours daily;
- melted pork fat mixed with chopped celandine, lubricate the growths several times a day.
Preventative measures
Since the nature of the origin of seborrheic keratosis has not yet been reliably established, it is difficult to talk about specific preventive measures that will definitely help prevent the appearance of growths.
Experts recommend that you adhere to the following rules in order to minimize the risk of keratosis:
- less be in direct sunlight, protecting the skin from ultraviolet radiation with clothing, umbrellas, special creams;
- to develop a balanced diet and adhere to it, so that the body receives a sufficient amount of vitamins, minerals, using multivitamin complexes;
- lead a healthy active lifestyle, abandon bad habits, observe the regime of work and rest, enough to get enough sleep;
- minimize stressful situations.
- Nafisa












