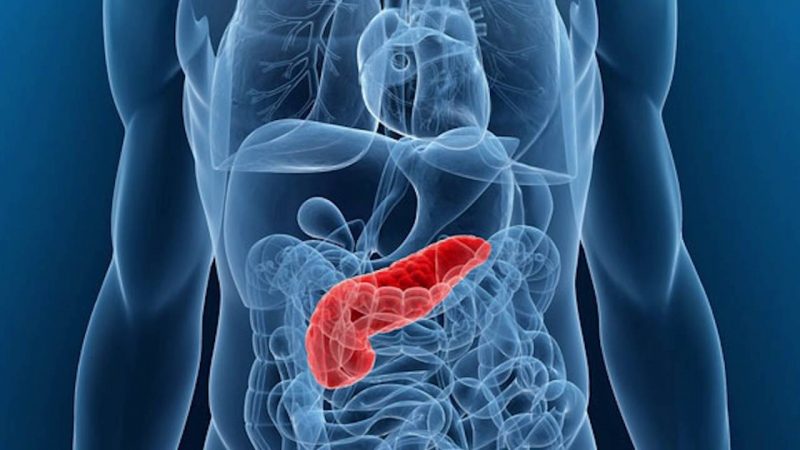
The pancreas is an important organ that enters the digestive system of the body. Inflammatory processes in it always give a pronounced clinical picture, accompanied by pain, fever and manifestations of intoxication. Reactive pancreatitis is one of the serious pathologies of the pancreas that gives severe complications if time is missed with the initial signs of inflammation.
Material Content:
What is reactive pancreatitis?
The onset of the disease is the result of an acute aseptic pancreatic inflammatory process.
This pathology is manifested against the background of gastrointestinal tract problems with errors in the diet, allergic mood of the body, and toxic poisoning. But most of all, such a reaction of the digestive system organ is due to the presence of calculi in the gallbladder.
A characteristic feature of this pathology is the rapid development of clinical symptoms after the action of a negative factor. And the same rapid reverse development of the disease with timely initiation of treatment in combination with a therapeutic diet.
The mechanism and causes
The cause of reactive pancreatitis can be various diseases of the digestive system, such as:
- viral hepatitis;
- calculous cholecystitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- gastritis in the acute stage;
- biliary dyskinesia.
In addition to diseases of the digestive tract, factors contributing to the development of inflammation in the gland are:
- eating disorders in the form of abuse of fatty and fried protein foods;
- the presence of bad habits - the use of strong alcohol and tonic drinks, colored soda, smoking;
- prolonged and uncontrolled medication;
- closed abdominal trauma with subsequent damage to the gland tissue;
- poisoning with poisons of various origins;
- chronic stress.
Negative processes in the pancreas begin to occur due to the premature activation of its enzymes and their aggressive action on the organ parenchyma.
Stagnation of the secret occurs due to cholelithiasis. In gallstone disease, small stones falling into the common bile duct cause spasm and irritation.
Stagnation of the secret entails damage to the cellular structures of the gland due to the negative effect of its own enzymes on it. As a result of such biochemical processes, many decay products appear in the blood, which provokes edema of the gland and intoxication of the body.
The first signs of illness
Inflammation of the pancreas develops acutely and quickly, only a few hours after the action of the toxic agent.
With progression, the disease in its development passes through several phases, manifested by various clinical symptoms:
- Enzymatic phase. Its duration is 3 days from the moment of acute onset of the disease. During this time, the formation of necrotic sites in the gland occurs. At the end of this period, a luminous gap appears during the course of the disease, characterized by a decrease in clinical symptoms with a subsequent transition to the next stage of development.
- Reactive phase. It is formed from 2 weeks of the disease and is intermediate, manifested by the formation of parapancreotic infiltrate.
- Sequestration phase. It develops from 3 weeks of illness and can end in one of several outcomes. The first is a successful outcome, in which there is a regression of infiltrate and recovery. In a more severe variant, cysts form, but without suppuration. The latter option is the most difficult when the patient’s condition is aggravated by the development of purulent and septic processes that pose a threat to life.
The first signs of the development of reactive pancreatitis include:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- belching;
- nausea;
- increased gas formation;
- temperature increase to subfebrile values.
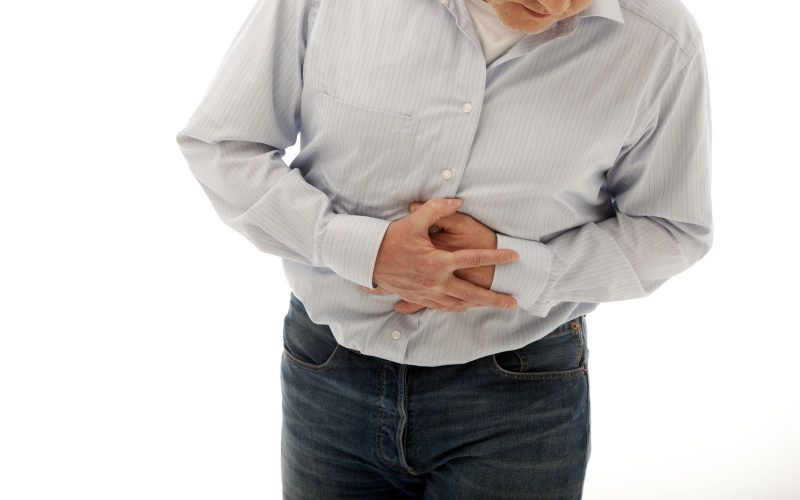
Acute pancreatitis is manifested by girdle pain, the intensity of which increases with food intake.
The pain syndrome, localized in the upper abdomen, in the right and left hypochondrium with a return to the back and shoulder blades, intensifies and becomes intolerable.
Symptoms of the disease
If timely medical assistance is not provided, the disease progresses rapidly, and pathological symptoms increase due to increased intoxication of the body.
Read also:nausea after eating - causes
With the intensification of pain, the following clinical manifestations appear:
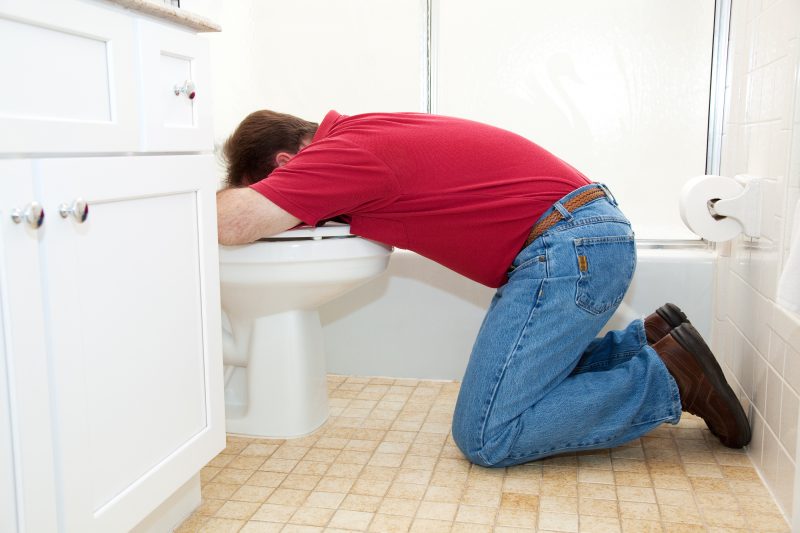
- vomiting mixed with bile and mucus;
- pallor and coldness of the skin;
- lowering body temperature;
- increased heart rate;
- the development of hypotension, that is, a decrease in blood pressure up to a fainting state.
Against the background of vomiting, the pain syndrome intensifies, as the tension of the abdomen leads to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and additional irritation of the pancreas. There are signs of an exacerbation of the chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, which can manifest itself in disruption of the intestines, hypersalivation (increased salivation).
Important! The appearance of a girdle pain syndrome, accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms, requires the most prompt provision of specialized medical care.Self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of reactive pancreatitis is based on patient complaints, objective examination data, laboratory and instrumental methods.
With the initial manifestations of pathology, the following studies give the most informative picture:
- general analysis of blood and urine;
- blood coagulogram;
- blood biochemistry with determination of the level of pancreatic enzymes;
- Ultrasound
- CT, MRI;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- angiography of the celiac trunk of the aorta.
In some cases, according to indications, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed, which allows to differentiate pancreatitis from other gastrointestinal pathologies.
Treatment of reactive pancreatitis in adults and children
As a rule, patients with this diagnosis are hospitalized. The main task of a doctor in the treatment of an acute condition is the relief of an attack, the removal of intoxication of the body, the inactivation of pancreatic enzymes with the normalization of the outflow of its secret.
The pathological process can develop not only in adults, but also in children, regardless of age, even in infants up to a year. Reactive pancreatitis in children in their clinical manifestations is similar to the course of the disease in adults.
The cause of the development of the pathology may be a viral infection, malnutrition, early transfer of the child to adult food. In infants, the onset of pancreatitis is provoked by a congenital pathology of the anatomical structure of the gland and its ducts.
The clinic of the disease in children is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the upper abdomen;
- dyspeptic symptoms - nausea, belching, vomiting;
- signs of intoxication;
- symptoms of an intestinal disorder - appearing constipation is replaced by diarrhea with a change in the color of the feces, which becomes yellow, characterized by the presence of mucus and fat;
- urine becomes a dark shade, and the skin turns yellow.
Breasts and newborns respond to the disease with periodic sharp crying and screaming. The appearance of any symptoms of the disease requires the obligatory consultation of a pediatrician, since in children the disease, unlike adults, is much more severe.
Drug therapy
Treatment of reactive pancreatitis in adults is carried out comprehensively and includes the following drugs:
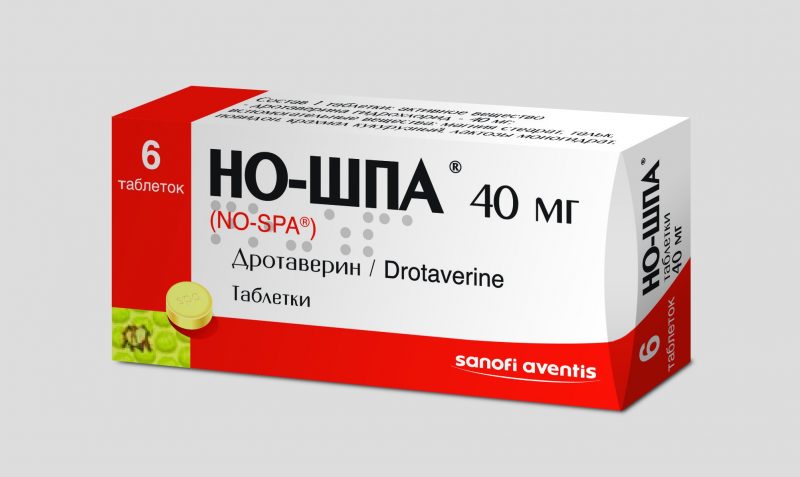
- Antispasmodics. No-Shpa, Drotaverin, Papaverin, Platifillin. Used to relieve spasm of the sphincter of Oddi, through which the secret passes into the duodenum. Drugs are administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
- Painkillers. Pentalgin, Acetaminophen, Baralgin.
- Carminative drugs. Espumisan, Meteospasmil, Duspatalin.
- Enzymes "Pancreatin", "Mezim", "Festal".
- Symbiotics for the restoration of intestinal microflora. “Bifido-Bak”, “Laminolact”.
- Antiemetics Motilium, Tserukal, Zofran.
- Antibacterial drugs. Ampiox, Amoxicillin.
- To remove intoxication - intravenous administration of solutions: “Hemodez”, “Polyglukin”, “Disol”, “Trisol”.
Timely initiated active treatment allows you to remove negative symptoms and prevent a further transition of the disease from one phase to another.
Traditional medicine recipes
After stopping the acute manifestations of pancreatitis and to improve the function of the gland, it is possible to use recipes of alternative medicine, but only strictly on the recommendation of a doctor. Herbal treatment gives a good effect, but only as an addition to the main treatment.
Of the traditional medicine, the most effective are:
- concoction of the immortelle;
- wormwood broth:
- rosehip infusion;
- infusion from the collection of dry raw materials in equal parts - corn stigmas, celandine, chopped dandelion root, tricolor violet, anise fruits, bird of the mountaineer.
Read also:immortelle: medicinal properties and contraindications
To prepare the broth, a tablespoon of the raw material is poured into 200 ml of water and brought to a boil, then the fire is reduced, and the broth is still boiled for 30 to 40 minutes. After cooling and filtering, the herbal remedy is ready for use.
To prepare the infusion, 15 g of dry raw material is poured into a glass of boiling water and infused for 2 hours, preferably in a thermos. It is taken on the recommendation of a specialist course in a dosage determined by a doctor.
Surgical method
The treatment of acute reactive pancreatitis is carried out mainly conservatively. But sometimes, in certain conditions of the patient, surgical intervention is required for health reasons.
Surgical treatment is carried out in the following cases:
- with extensive pancreatic necrosis;
- with the development of severe complications during the process, such as cystic formations, fistulas, abscesses;
- the presence of a malignant tumor.
The question of the operation to remove the gland is always solved taking into account the indications and individual characteristics of the patient's body.
Reactive Pancreatitis Nutrition
Nutrition, with pancreatic disease, plays a very important role, since any error in food will provoke an exacerbation of symptoms.
To avoid negative consequences, it is recommended:
- food intake is carried out in fractional and small portions up to 7 times a day;
- processing of products is carried out only by cooking or steaming;
- exclude smoked, canned, salted and pickled products from the diet;
- implement a complete rejection of the use of confectionery, fatty foods, alcohol;
- exclude the use of strong coffee and tea, tonic and colored carbonated drinks, ice cream, chocolate;
- give preference to first courses on vegetable or weak broth from dietary meat of chicken, turkey, various cereals, soft-boiled eggs.
Dieting for patients who have undergone reactive pancreatitis, becomes constant until the end of life.
Possible complications and prognosis for recovering
Reactive pancreatitis is a serious pathology, which, with untimely treatment, can cause various complications. In the clinical course of the process, early and late complications are distinguished, which develop after a few days and after 2 to 3 weeks from the initial manifestations of the disease.
Early complications include:
- painful shock;
- hepatic and renal failure;
- peritonitis of a different nature;
- heart and respiratory failure.
Later complications develop due to the attachment of a secondary infection.
These include:
- bleeding from the digestive tract;
- peritonitis;
- sepsis;
- abscesses;
- pseudocyst formation.
If reactive pancreatitis proceeds without complications, and treatment started in a timely manner gives a good result with the reverse development of the symptoms of the disease, and the prognosis will be positive for both life and disability.
With a complicated course of the process, the prognosis is unfavorable, since the disease leads to persistent disability or death, mainly with chronic alcoholism.
Prevention
To prevent the development of reactive pancreatitis, it is necessary to adhere to certain preventive measures, which include the following measures:
- exclusion from the use of alcoholic beverages of any strength, as well as smoking;
- timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and preventing their exacerbation;
- maintaining proper nutrition, avoiding the use of fatty, fried, canned foods, exclusion from the diet of drinks and foods containing artificial colors;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- playing sports;
- passing an annual medical examination with the control of laboratory tests and ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
By following these recommendations, you can prevent the development of such a serious disease as reactive pancreatitis.