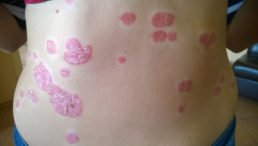
Psoriasis refers to chronic pathology, for which the occurrence of a skin rash of a nodular nature, covered with light scales, is typical. According to medical statistics, about 2% of the world's population is affected by this disease. Psoriasis is contagious or not, how does this disease develop?
Material Content:
Causes of the disease
The root cause of psoriasis is a genetic predisposition. This means that a child whose parents have been exposed to a psoriatic rash has an extremely high chance of getting sick later. Also at risk are people whose skin integuments are systematically injured, or in whose organisms the endocrine and nervous systems malfunction, or chronic skin infections occur.
There are also external causes of the development of psoriasis, among which:
- Inflammatory diseases (various types of fungi, dermatitis, lichen, etc.).
- Various mechanical damage to the skin (insect bites, burns, etc.).
- The negative impact of externally applied medications (they also include various insect repellents, etc.).
Internal factors that influence the occurrence of skin psoriasis symptoms include decreased immunity, various infections of the body (including HIV), as well as systematic stress and emotional stress.
Classification by localization
There are several varieties of psoriasis, based on the features of the localization of the disease
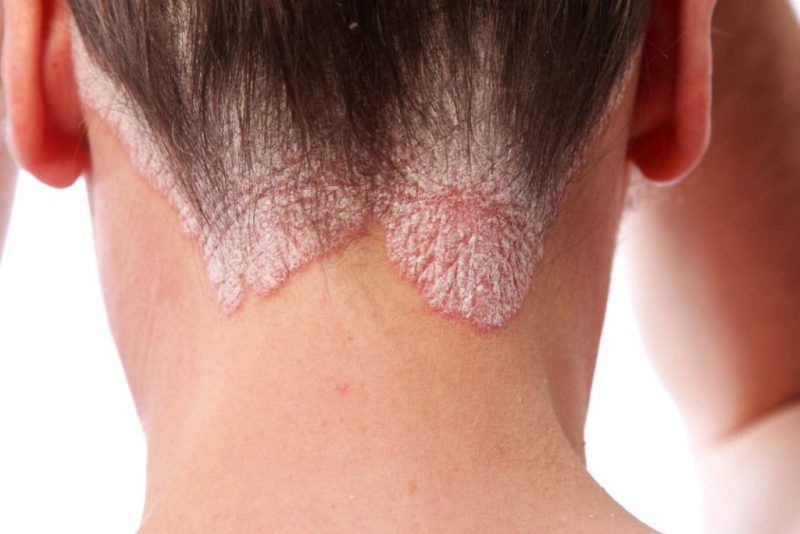
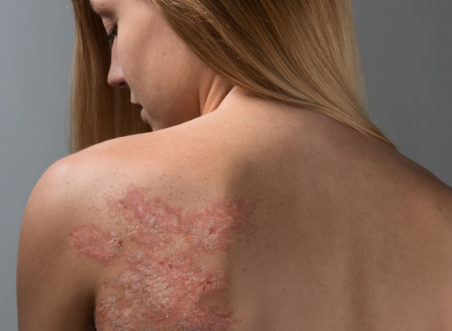
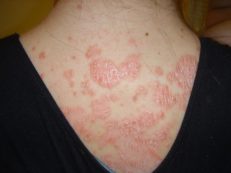
- Plaque-like psoriasis, called ordinary, simple, vulgar. This form is recognized as the most common and is observed in almost 90% of all sick people. For her, inflammation of the skin with grayish scales is typical.The skin under them is reddened, easily amenable to bleeding and friction. Such zones are called psoriatic plaques. They can grow and connect with the nearest inflamed areas.
- Reverse psoriasis. Red inflamed spots with this diagnosis are located in the skin folds and other areas. Often they can be found in the folds of the groin, armpits, under the mammary glands in women. This form is especially often exacerbated by friction, sweat and various injuries of the skin.
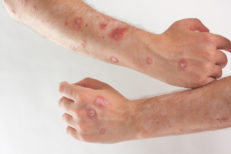
- Teardrop-shaped psoriasis on the head and body. The elements of the lesion resemble droplets of a lilac or reddish hue in shape. As a rule, such rashes are often found on the hips, neck, back, head. The teardrop-shaped form often results from an exacerbation of streptococcal infection.
- Pustular psoriasis, also called exudative. It is considered the most severe form of the disease. It is blisters and blisters protruding above the skin, and filled with inflammatory exudate, which can subsequently become purulent. The integument around the formations is hot and inflamed.
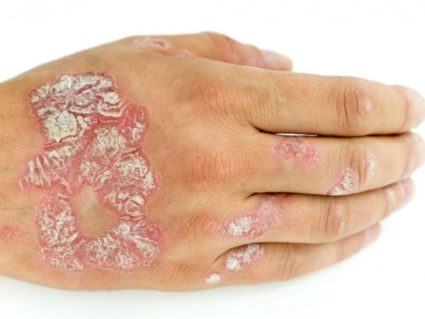
- Psoriasis of nails. It provokes a change in the shape of nails on the limbs. At the same time, their color changes and the formation of spots, dots, lines, as well as a thickening around the nail bed and the skin near it. The disease can lead to brittle nails and even their complete loss.
- Psoriatic arthritis. It is characterized by inflammatory processes of connective tissue and joints. This form can affect absolutely any joints, but often the phalanges of the fingers of the lower and upper limbs suffer from it. Pathology is able to affect the hip and knee joints, which can even cause disability.
- Psoriatic erythroderma. Often it affects large areas of the skin or completely captures the entire surface of the patient's body. This disease can be accompanied by itching, swelling and soreness of the integument.
 Some forms of the disease can provoke a fatal outcome, since peeling and inflammation of the integument prevent the body from fully regulating the temperature and violate the barrier function of the skin.
Some forms of the disease can provoke a fatal outcome, since peeling and inflammation of the integument prevent the body from fully regulating the temperature and violate the barrier function of the skin.
Read also:cracked heels
Psoriasis is contagious or not for others
Is psoriasis contagious to others? This chronic noncommunicable disease does not spread by airborne droplets or any other route. It is believed that such a pathology is transmitted exclusively by inheritance. That is why even the most direct contact with the patient does not threaten the people around him - it is almost impossible to become infected with this disease.
Primary signs of the disease
The primary signs by which psoriasis can be identified include:
- a feeling of chronic fatigue;
- depressed and depressed state;
- the manifestation of rounded papules of a pinkish tint (at the initial stage of the development of the disease, their size does not exceed several millimeters).
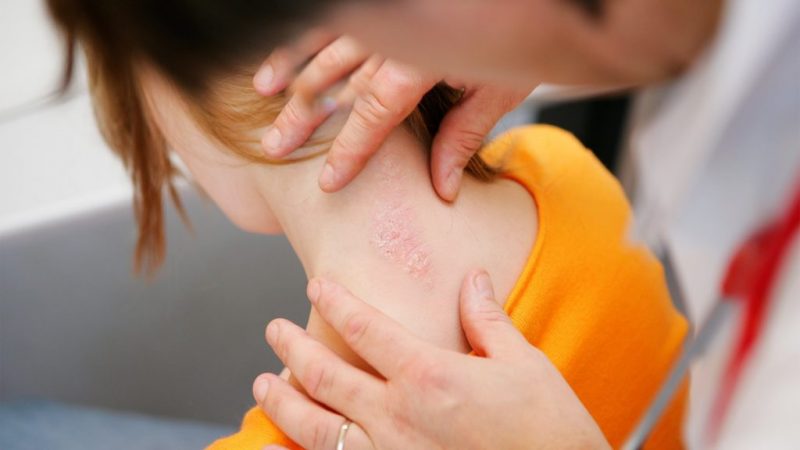 Depending on the form of the disease, the symptoms of psoriasis can occur not only on the condition of the skin, but also on the functionality of the internal organs. The nervous and endocrine systems and spinal column often suffer from this pathology, and the kidneys, liver, and thyroid gland are affected.
Depending on the form of the disease, the symptoms of psoriasis can occur not only on the condition of the skin, but also on the functionality of the internal organs. The nervous and endocrine systems and spinal column often suffer from this pathology, and the kidneys, liver, and thyroid gland are affected.
Symptoms and clinical presentation
Medical assistance is necessary for the patient if he has the following signs and symptoms of psoriasis:
- cracked skin, painful microtrauma;
- deformation of nails, a change in their color, exfoliation;
- the formation of pustules on the feet and palms;
- severe peeling of the epidermis;
- spots and rashes.
Running psoriasis can provoke numerous complications. Their main sign is swelling of the joints, their soreness, as well as affected nails. Additionally, the patient may develop hyperthermia, a general deterioration in well-being, chills, etc.
Psoriasis also affects children, most often preschoolers and primary schoolchildren, less often - babies. Parents often confuse the manifestations of psoriasis in a child with diaper rash.The skin of children is covered with pinkish areas, on which you can notice small scales. In older children, the disease is manifested by itching and the appearance of small nodules.
How is the diagnosis
All skin diseases are diagnosed by a dermatologist, psoriasis is no exception. A specialist, as a rule, is enough for a cursory examination to determine the variety of this disease. To make sure, and most importantly, to exclude other skin pathologies, the doctor must take into account the so-called triple of psoriasis, and simply put - 3 main companions of this disease:
- The phenomenon of stearin spots (affected areas by sight and touch are associated with stearin shavings).
- The phenomenon of the terminal film (if you remove the scales from the skin, the covers under them will be smooth and shiny).
- The phenomenon of point bleeding (when scraping the scales in their places, small droplets of blood form).
By decision of the doctor, the patient may be shown a general blood test or examination of flakes taken from the surface of the integument.
Forecasts and possible complications
The vulgar form of pathology does not pose a danger to human life. It is almost impossible to get rid of psoriasis, however, the right treatment is the key to long-term remission. Fulfilling all the recommendations of the doctor, the patient for a long time pushes back possible manifestations of pathology, without fear of further complications.
However, severe forms of the disease can be complicated, causing adverse effects, including:
- Erythroderma. Almost the entire surface of the patient’s skin is affected. Such extensive rashes are accompanied by fever with itching and redness of the skin.
- Psoriatic arthritis. Affected joints can greatly complicate the patient's course of his usual life. In the absence of the necessary treatment, such a complication can even provoke amputation of the limb.
- Generalized psoriasis. A neglected form of pathology can lead to an increase in the number of pustules on the skin.
- Various autoimmune diseases. They arise as a result of immune failure against psoriasis. The patient may suffer from manifestations of diabetes, obesity, as well as malfunctioning of the thyroid gland.
Psoriasis is an extremely unpleasant, and sometimes dangerous, disease. The positive point is that pathology does not spread in any of the usual ways. The main factor in the development of the disease is hereditary.