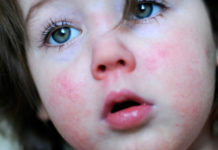
The initial manifestations of psoriasis in children are often mistaken for dermatitis. It is useful for parents to know the typical places of localization and the nature of skin rashes in different clinical forms so as not to miss the onset of the disease and avoid complications.
Material Content:
What is psoriasis and its causes
Doctors attribute psoriasis to the group of autoimmune pathologies with a hereditary predisposition. In a healthy person, epidermal cells renew keratinocytes every 28 days: they nucleate in the lower basal layer, move up, mature, die and exfoliate.
With psoriasis, keratinocytes divide and advance 7 times faster, the regeneration cycle is reduced to 4 to 5 days.
Violation of the immune cells provoke lymphocytes. This happens when the immune system fails for some reason and works against its own tissues.
Unripe keratinocytes cannot freely leave the surface of the skin, their excess accumulates in the form of papules. Gradually, the inflammation covers the deep layers, the secretion of sweat, sebaceous glands is disturbed. Affected areas receive less moisture and fat, dry, and crack. Blood vessels, lymph nodes, nerve cells are involved in the process.
Doctors do not name the unique cause of psoriasis in children.
The impetus for starting the described process is:
- Infectious diseases: acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, otitis media, influenza.
- Psycho-emotional overstrain, stress, fears.
- Vaccination.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Intestinal parasites.
- Violation of lipid, carbohydrate metabolism.
- Skin injuries: deep cuts, burns, bites.
- Climate change.
- Uncontrolled medication.
The risk of developing psoriasis increases when relatives get sick. However, the probability of passing the pathology by inheritance is not one hundred percent, because not only one, but a combination of genes is responsible for it.
Stages of the development of the disease
The development of psoriasis goes through 4 phases:
- Initial. Single rashes of red or pink appear. They do not bother, on the scalp go unnoticed.
- Progressive. Old foci increase, new ones appear. In 80% of cases, itching begins. At this stage, regular papules appear due to small cuts, scratches, detergents, and friction of tight clothing.
- Stationary. The disease freezes: new foci do not arise, the former do not grow.
- Regressive. Seals dissolve, psoriatic elements turn pale, peeling stops.
During the period of remission, the papules disappear, sometimes there are areas of hypo- or hyperpigmentation at the site of lesions.
Is psoriasis contagious
Psoriasis is inherited, but does not spread by airborne droplets, contact, household, sexual contact.
Pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and fungi do not participate in the development of the disease; therefore, it is not transmitted during communication, patient care, or blood transfusion. Children can safely go to school, kindergarten, sports sections, swimming pools. Fear of infection was the result of people's ignorance and prejudice.
Symptoms and signs in children
The manifestations of psoriasis depend on the clinical form:
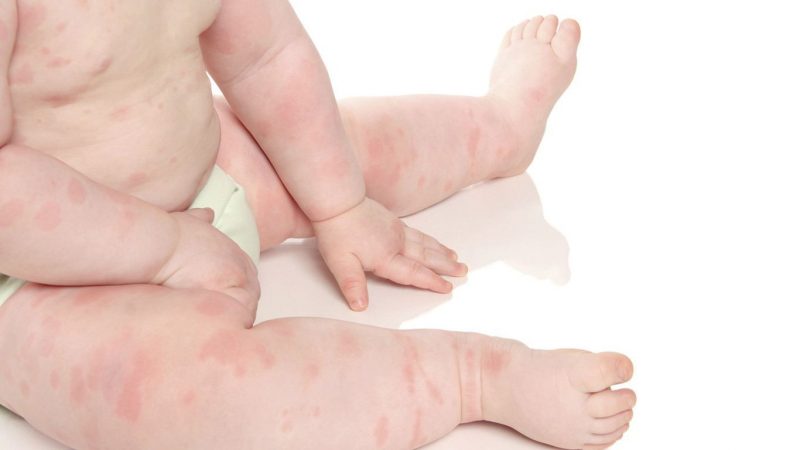
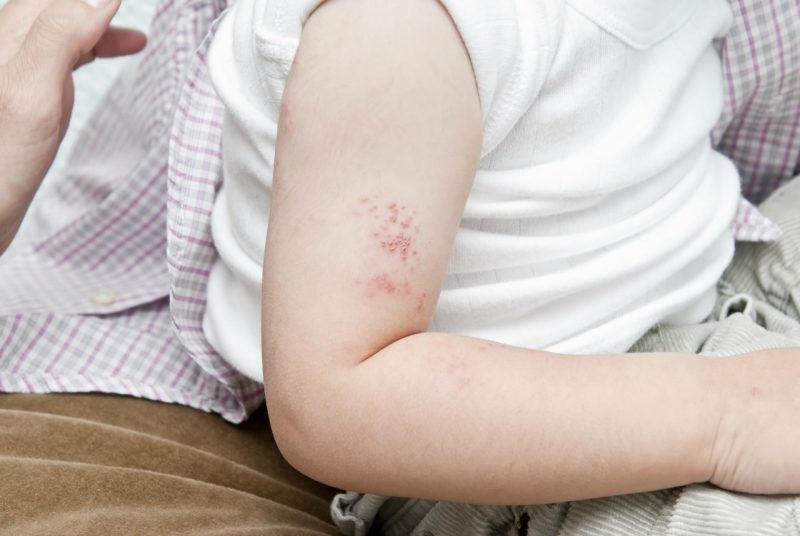
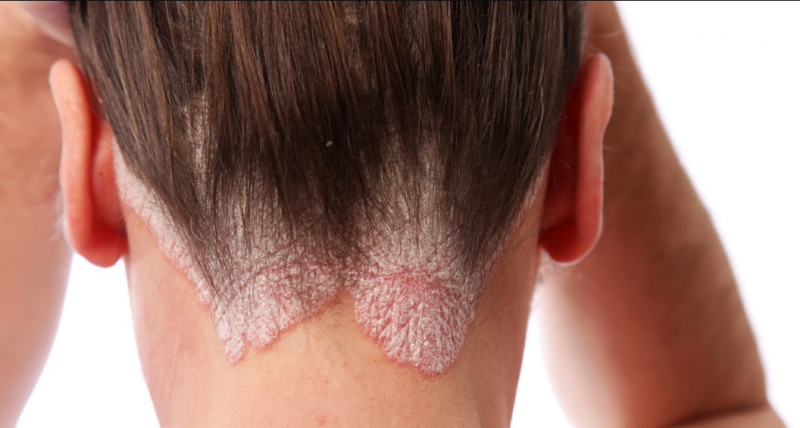
- Plaque-like begins with the appearance of single red spots, which quickly grow and condense. Gradually they become covered with grayish-white scales, for which psoriasis received the second name - scaly lichen. Typical lesions are the head, elbows, knees, but other areas are not excluded. When the scalp is damaged, papules go beyond the boundary of hair growth.
- Teardrop-shaped develops more often after an infection. Rounded red spots the size of a match head spread throughout the body, over time they increase and peel. Gradually, the drop-shaped form becomes plaque-like, but cases of spontaneous cure are recorded.
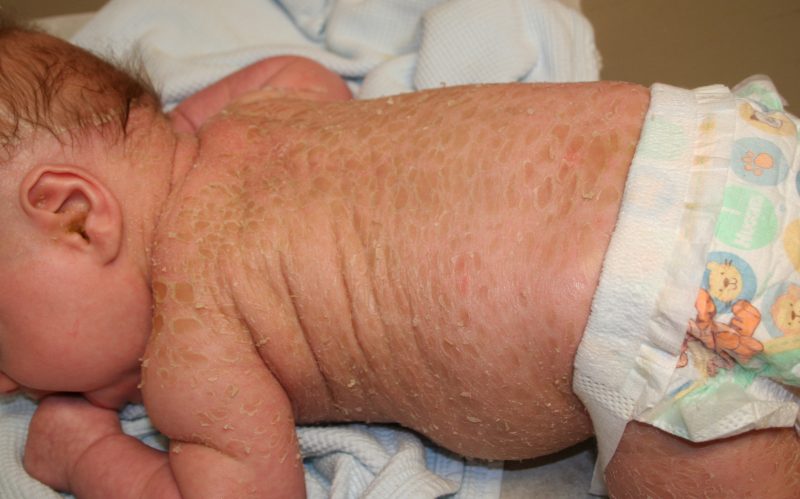
- Diaper membrane develops in infants, it is difficult to diagnose. The first signs of psoriasis in children up to a year resemble diaper rash, prickly heat, candidiasis. Pink spots with clear borders appear in the skin folds, more often they cover the axillary cavities, groin, buttocks, face.
- The reverse begins with smooth red spots without peeling on the inner surface of the hips, genitals, in the groin, under the knees, inside the elbow bends.
- Pustular in children is rarely diagnosed. The skin on the palms, fingers, feet turns red, swells, becomes covered with bubbles with liquid.
In a third of children, along with skin rashes, lesions of the nail plates are noticed. They are covered with recesses, change color, thicken or exfoliate.
Diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis in a child
If psoriasis is suspected, the task of the parents is to find a pediatric dermatologist. The doctor determines the disease by the nature and location of the rashes.
In a child older than a year, a triad of symptoms is revealed:
- when scraping with a blunt scalpel, peeling resembles stearin shavings;
- the spot after removing the top layer becomes shiny and smooth;
- with further friction, droplets of blood protrude.
Infants are diagnosed after examining the lesions through a dermatoscope, it increases the elements of the rashes and displays. To identify the general condition, clinical and biochemical blood and urine tests are prescribed. After making a diagnosis, the doctor assesses the severity of the disease: mild - affects up to 2% of the surface, medium - from 3 to 10%, severe - more than 10%.
With a third degree of severity, the child is treated in the hospital with oral and injectable drugs under the supervision of a doctor.
The treatment regimen for mild and moderate pathologies includes local drugs, phototherapy, nutrition correction, and folk methods.
Drug treatment
At the stationary and regressing phase of development, non-hormonal external agents are used. They soften papules, reduce inflammation, peeling, and prevent the development of bacterial infections. Drugs do not affect the functioning of internal organs, do not give negative side effects, with the exception of individual intolerance to individual components.
Widely used ointments:
- Salicylic;
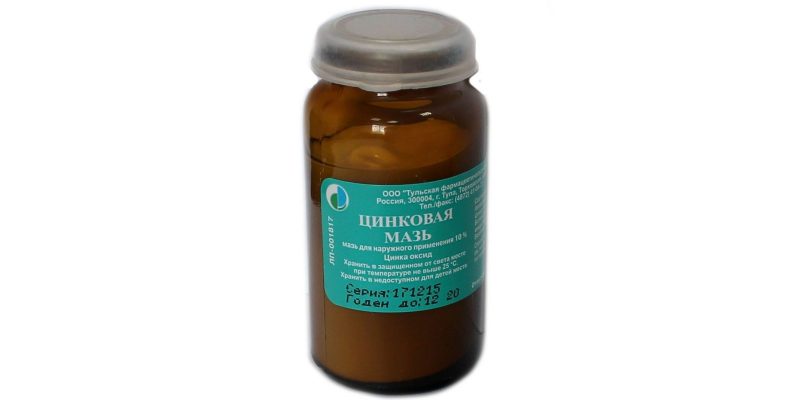
- Zinc;
- "Tsinokap";
- "Skin-cap";
- Psoriasis cream;
- "Losterin."
At a progressive stage of development, topical steroids are used - local preparations based on synthetic hormones. They act stronger and faster: inhibit excessive cell division, relieve inflammation. At the same time, they give more side effects, so they are used only to relieve acute symptoms, alternate with non-hormonal ointments, are not used in large areas and for prevention.
Here are the drugs that are allowed to be used from an early age, applied to delicate areas: face, folds, neck, genitals:
- Afloderm - from 6 months;
- “Advantan” - from 4 months;
- “Lokoid” - from 6 months;
- “Elokom” - since 2 years.
When psoriasis is localized in children, shampoos with tar and salicylic acid are prescribed on the head: Psoril, Tana, Skin-Cap, Algopiks.
Additionally, auxiliary drugs are included in the treatment regimen:
- Sedatives (valerian, Novopassit, motherwort) reduce emotional excitability, anxiety.
- Antihistamines (Fenistil, Zirtek) help with allergies, reduce itching.
- Vitamins A, E, D, Group B regulate metabolic processes.
Specific drugs, their forms and dosage are prescribed by the attending physician based on the age, clinical form and severity of the disease. It is useful for parents to remember: a universal narrowly targeted medicine for psoriasis was not invented. What helps one child will be useless or harm another.
Folk remedies
In combination with drug therapy, recipes of alternative medicine are used:
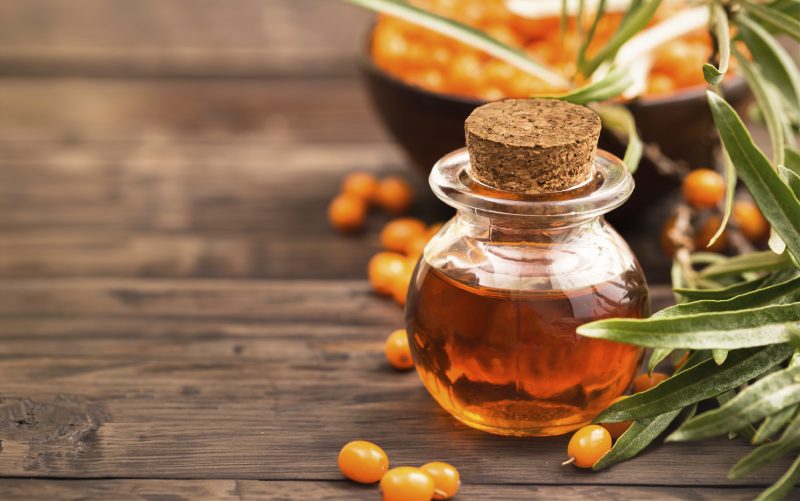
- Sea buckthorn oil. Plaques are treated, taken orally by half a teaspoon per day.
- Decoctions of chamomile, string, celandine. Add to bathtubs, make lotions.
- Fresh juice of viburnum, wild strawberry. Lubricate the rash.
- Walnuts. 0.5 kg of peeled shells are boiled in 1 liter of water for half an hour, the broth is added to the bath, the child is bathed for at least 30 minutes.
Alternative methods can not be used without consulting a doctor, so as not to harm the child.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
When the disease subsides, to prevent exacerbation of the symptoms of psoriasis in children, they are shown moderate doses of artificial or natural ultraviolet radiation:
- short stay in the sun;
- narrow-band phototherapy - is prescribed from 5 years;
- PUVA photochemotherapy - 15 years;
- excimer laser therapy - at any age.
Procedures are contraindicated in exacerbation of the disease, they are prescribed at the stationary, regressing stage or during remission.
Diet for Psoriasis
There are no scientifically based data on how a child with psoriasis can and cannot be fed.
When compiling a diet, parents are guided by the standard rules of a healthy diet and their own observations:
- The child is fed boiled, stewed dishes or steamed for him.
- Limit the amount of sweet, flour, fatty, fried.
- Drink plenty of water during the day with clean water, freshly squeezed juices, do not give soda.
- Increase the proportion of vegetables, herbs, fruits in the diet.
- Exclude any food, after which exacerbations occur.
When breastfeeding, these rules are followed by the mother.
Possible complications and predictions
With incorrect or careless treatment, the disease passes into complicated life-threatening forms:
- Psoriatic arthritis. The disease affects the muscles and cartilage, limits the mobility of the joints.
- Generalized pustular psoriasis. Vast areas of the body are covered with purulent rashes, a bacterial infection joins, intoxication of the body begins.
- Psoriatic erythroderma. Pathology covers the entire skin, thermoregulation is impaired, lymph nodes increase.
Psoriasis cannot be cured to the end, but with the right course of therapy, it is possible to alleviate the symptoms and achieve persistent remission for years.
Prevention
The only way to protect the child from the disease is to accustom him to a healthy lifestyle, since it is difficult to foresee and rule out all provoking factors.
It is important for a sick child during remission to properly care for the skin in order to prevent exacerbation:
- More often swim in warm water. Hot baths and hardening - only as directed by a doctor.
- Do not use hard washcloths or towels. To choose gels and shampoos with neutral pH, without fragrances.
- After swimming, do not wipe, but get wet, apply a moisturizer.
- Buy clothes, underwear and bedding from natural fabrics.
- Trim your nails briefly to avoid minor scratches.
- Protect yourself from sunburn, hypothermia, injury.
Psoriasis can not be completely cured, characterized by differences in the severity of symptoms. The quality of life of a child can be improved if you do not try to cope with the disease yourself at home, and pedantically follow the recommendations of a dermatologist.