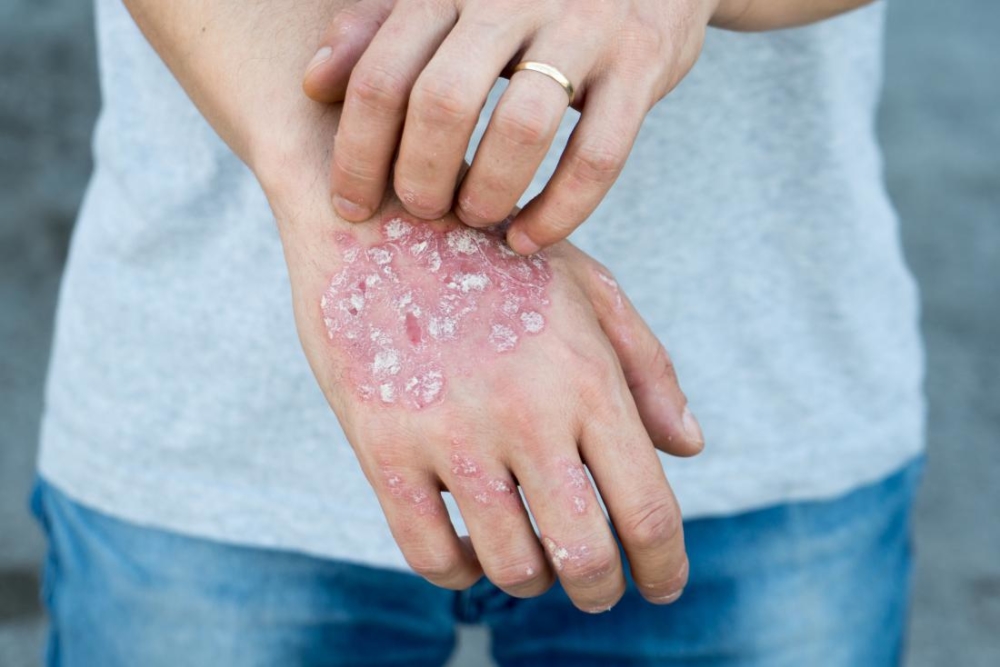
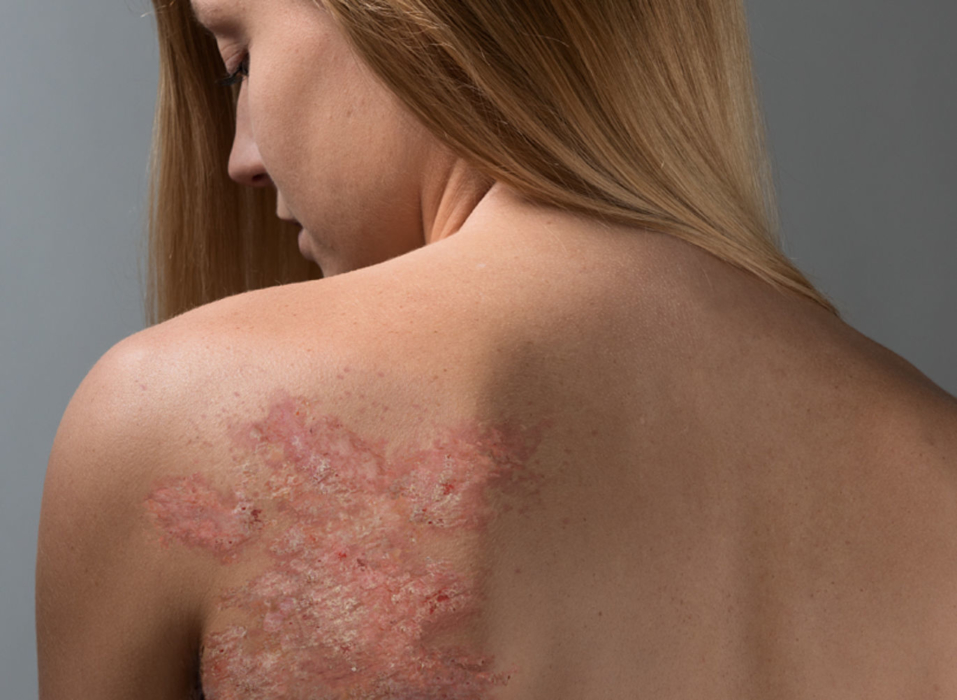
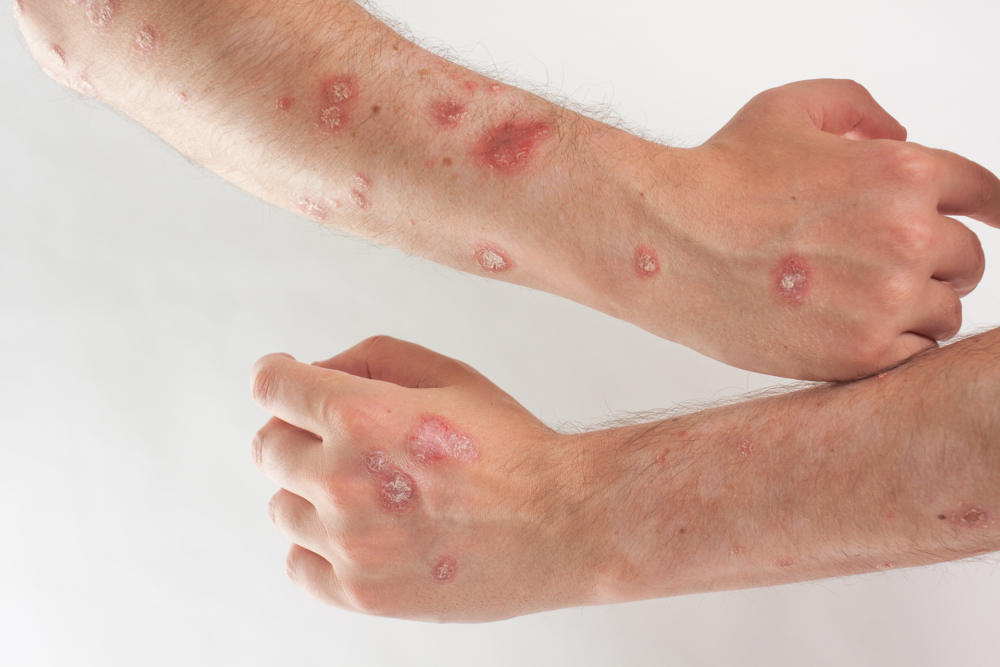
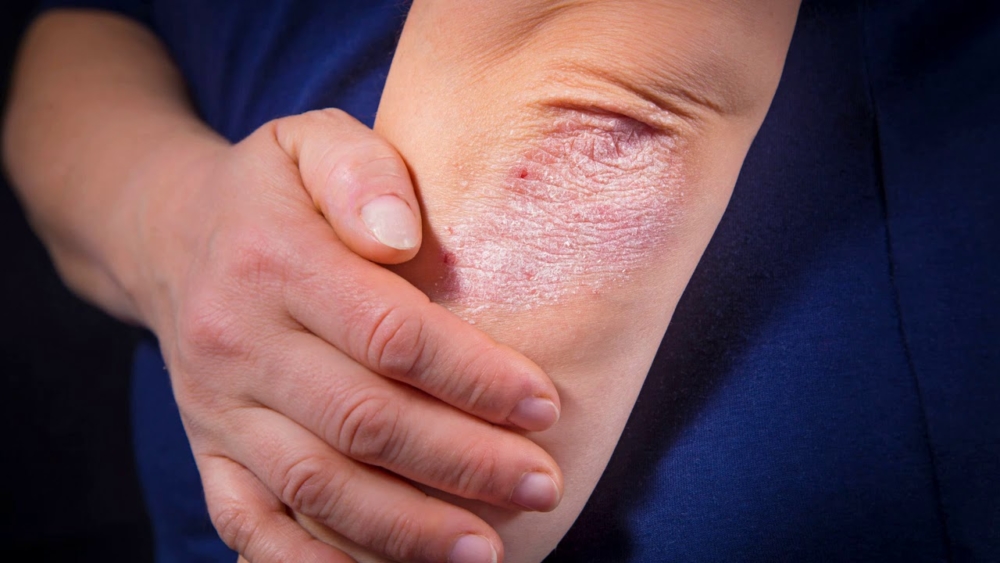
Any rashes on the body always seem suspicious and cause others to worry about the spread of infection. However, the symptoms of psoriasis are more of a cause for concern for the patient himself, since the disease is not contagious, but prone to progression. The processes at the heart of psoriasis are not yet fully understood, but doctors are sure that people with a predisposition to pathology can avoid relapses only if they follow a certain lifestyle.
Material Content:
What is psoriasis and its causes
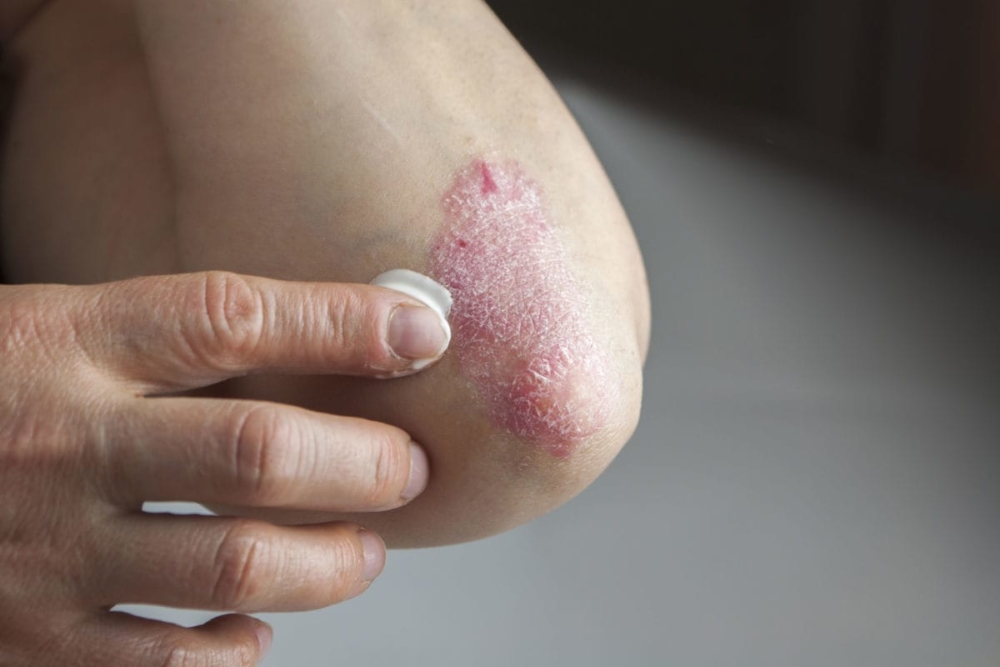
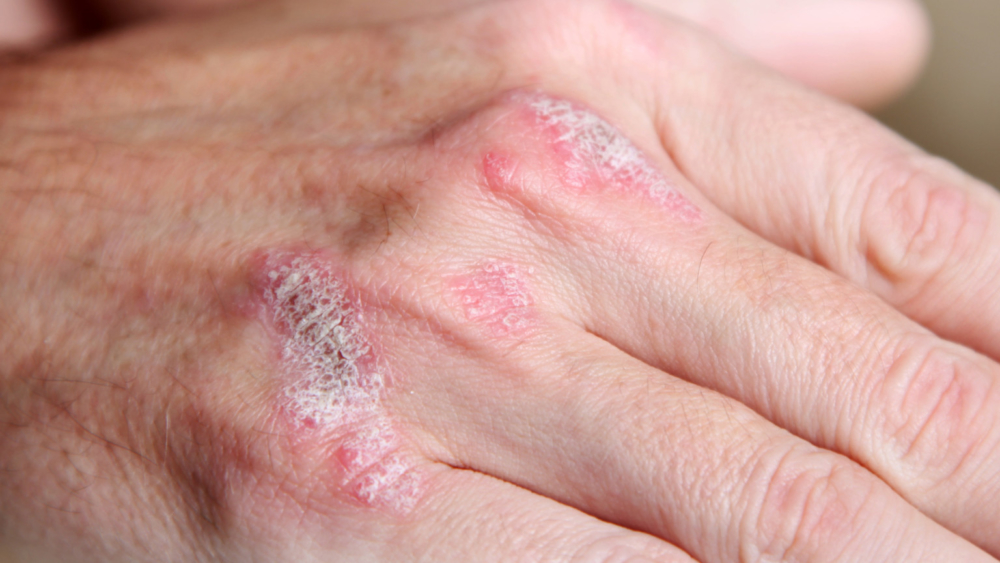
Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious disease accompanied by an itchy rash with peeling of the skin throughout the body.
The disease is characterized by a wavy nature of the course - after a therapeutic effect, remission occurs, and when provocative factors appear, a relapse occurs, and psoriasis begins again.
The development of the disease significantly affects the quality of life of the patient and can cause depression. The appearance in a society of a person with skin lesions complicates his adaptation and often affects the psychological state.
Severe manifestations of psoriasis often reduce the patient’s functionality, as they make it difficult to perform even simple everyday activities, including personal care.
According to statistics, 4% of the world's population is already affected by this disease. Moreover, the majority of cases are young people under the age of 20 years.
Why does psoriasis occur?
Scientists have been studying the disease for more than 200 years. Nevertheless, neither the causes of psoriasis, nor methods for a complete cure have yet been found.
However, scientists were able to establish the relationship of various external and internal factors with exacerbations of the disease. The following are recognized as indirect causes of psoriasis:
- physical or mental stress;
- hormonal changes due to puberty or pregnancy;
- climate change;
- a decrease in calcium and potassium in the blood test;
- skin injuries, animal bites, burns, tattoos, sometimes - injection punctures;
- infectious diseases, especially lesions with streptococci, staphylococci and fungi;
- taking medications - antidepressants, antimalarial and anticonvulsants, as well as beta-blockers;
- HIV or AIDS;
- exposure to household chemicals, cosmetics and perfumes;
- lack of nutrients in the diet, eating harmful foods, alcohol addiction;
- addiction to smoking.
In addition, it was noted that psoriasis is more often observed in women, especially against the background of a tendency to dryness and skin sensitivity.
Theoretical basis for the development of psoriasis
In search of a clue to the phenomenon of psoriasis, scientists relentlessly put forward many theories that explain the causes of the disease and its manifestations. Due to unprovenness, four hypotheses of the origin of pathology are among the most probable:
- autoimmune. The stability of inflammatory processes in the affected areas of the skin is supported by an increase in the concentration of T-lymphocytes. This means that the body perceives such areas as foreign, alien, and produces antibodies to eliminate them;
- heredity. Psoriasis can cause changes in DNA. Inherited transmission of a defective genome is manifested in a predisposition to dermatological lesions;
- endocrine dysfunction. Reducing or increasing the amount of hormones in the blood provides favorable conditions for the development of psoriasis;
- metabolic problems. Violation of the metabolic rate can cause functional disorders of the skin - changes in the processes of its maturation and weakening anti-inflammatory properties.
A particular effect on the health of the patient is exerted by the state of his nervous system. This relationship is characterized by bipolarity. On the one hand, nerve problems provoke the progress of the disease, on the other hand, manifestations of psoriasis in themselves are a provoking factor for the occurrence of anxiety and nervousness.
For a modern person, the danger of developing psoriasis remains relevant throughout life, since any weakening factors of the body or their combination can provoke skin damage.
Types and stages of the disease
According to the classification adopted in world dermatological practice, psoriasis is divided into several types, each of which differs in the severity of symptoms and the location.
Vulgar psoriasis
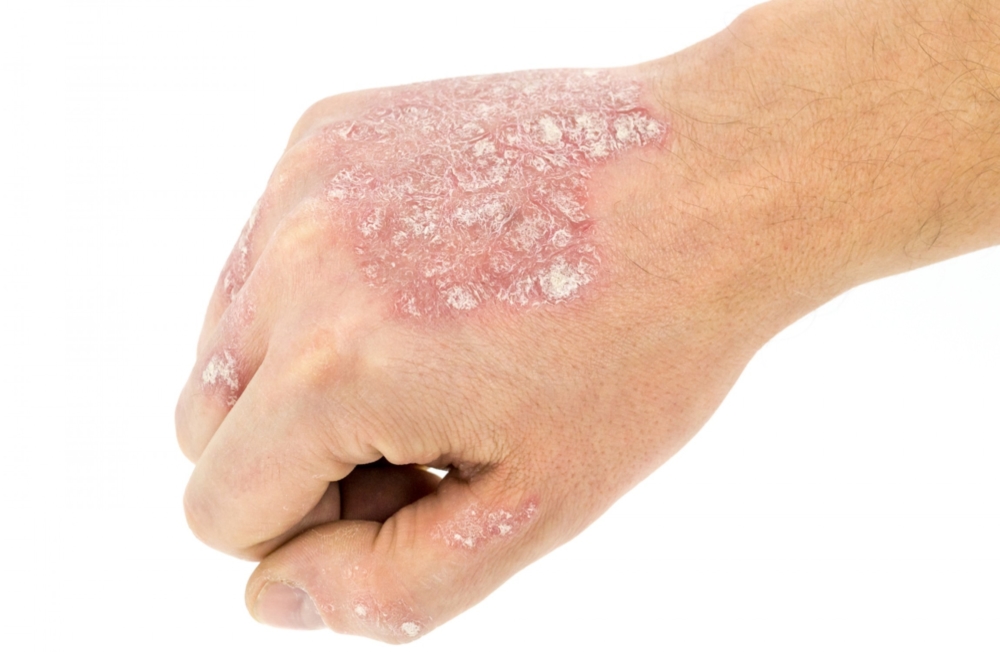
Due to the high prevalence (up to 90% of the total indicators), psoriasis of the vulgar type is often called ordinary or simple plaque-like. It is characterized by abundant rashes of small papules of bright red color with a pinkish border that clearly outlines their edges.
The affected areas are distinguished by elevation above the surface of healthy skin and a tendency to increase in size, up to a complete merger with neighboring areas with a rash.
Flexion psoriasis (reverse)
The development of reverse psoriasis affects tissues on the folds and the areas between the folds of the skin - in the groin, axillary hollows, and also under the chest.
Rashes with reverse psoriasis are on the same level with the surface of the skin and are characterized by minimal peeling.
Usually such a rash is observed in children. In adults, reverse psoriasis occurs only with diabetes.
Teardrop-shaped psoriasis
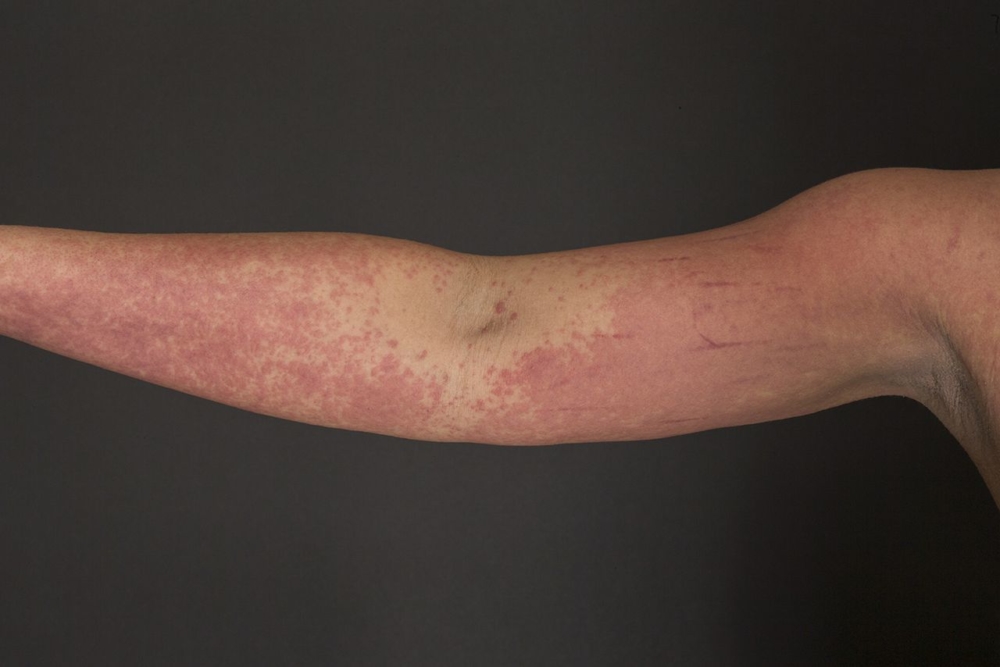
The rashes accompanying teardrop-shaped psoriasis really resemble small droplets of red, purple, or purple in shape. A drop-like rash abundantly covers large areas of the body - hips, legs, shoulders, back, and can be observed in the scalp.
Most often, teardrop-shaped psoriasis occurs against the background of streptococcal infections.
Exudative (pustular) psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis is distinguished by a severe form of the course. A characteristic feature of the pathology are weeping formations and pustules filled with exudate. The red color of the skin and the presence of swelling under the rashes indicate the intensity of inflammatory processes.
With secondary infection, pustules form at the site of pustules.
Pustular psoriasis usually develops in the distal parts of the arms and legs. But with a complex course, it can acquire a generalized character and spread over the surface of the whole body.
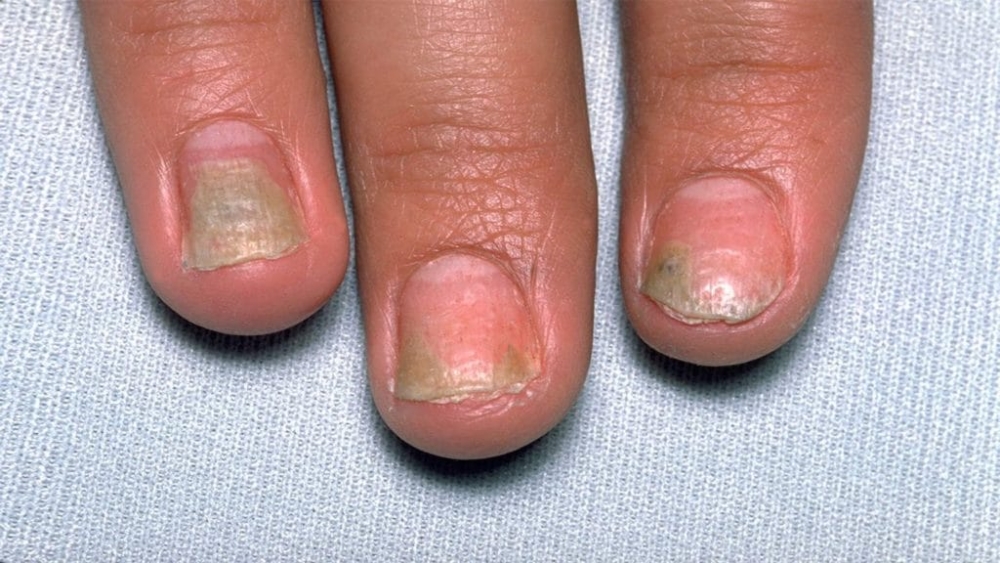
Nail psoriasis
This is one of the varieties of psoriasis with a characteristic lesion of the nails and a discoloration of their plates. The main symptoms of the pathology are stratification of the nails, the appearance of thickening of the skin around them, yellowness and spots of white or gray color, transverse lines, as well as increased fragility of the plate. Possible complete loss of the nail.
Psoriatic arthritis
This type of psoriasis is expressed in damage to the joints of the fingers, in which the phalanx swells. And it is also possible damage to the tissues of the musculoskeletal system. Severe forms of arthropathic psoriasis lead to loss of mobility and disability.
Erythroderma psoriasis
A common form of psoriasis, accompanied by inflammatory processes, edema, severe itching and detachment of large areas of the skin. Often occurs against a background of untreated vulgar psoriasis or as a result of severe stress.
As a result of intensive exfoliation, the skin loses the ability to thermoregulate and protect. In the absence of timely treatment, erythrodermic psoriasis leads to sepsis and death.
Some subspecies of the pathology can occur in the scalp (seborrheic type), palms and soles (plantar type), and mucous membranes of the oral cavity (psoriasis of the mucous membranes). Intertriginous type of disease is usually found in children, and its manifestations visually resemble diaper rash.
Stages of Psoriasis
According to the degree of damage, pathology is divided into three stages. A mild form of the course is diagnosed with damage to no more than 3% of the skin surface.
With moderate severity, up to 10% of the skin is affected. The most difficult is the severe stage, in which psoriasis covers more than 41% of the body.
Is the disease contagious
Studies by scientists confirm that psoriasis is a disease with a centuries-old past. Herodotus and Plato mentioned pathology in their writings, and traces of psoriasis were found on the mummified remains of ancient people found during archaeological excavations.
A characteristic process that accompanies exacerbation of psoriasis is considered accelerated cell division of the epidermis. Many red, scaly spots appear on the surface of the skin, causing itching. The pathological process is exacerbated by inflammation, supporting excessive cell growth.
Such manifestations do not look very attractive, but, according to doctors, the disease is not contagious and can only be inherited.
Symptoms and signs of psoriasis
Rashes are the main sign of psoriasis, similar in nature to other types of dermatological problems. However, the first signs of psoriasis often coincide:
- a feeling of tightness in certain areas of the skin is replaced by rashes in the form of papules, covered with silver scales;
- gradually, the papules merge with each other and form psoriatic red plaques rising above the skin. Their formation is accompanied by itching;
- characteristic scaly-shaped elevations primarily appear in places of closest contact with clothing - in the collar of the neck, at the level of the trouser belt, under the straps and on the bends of the arms or legs, in injured areas;
- as psoriasis develops, plaques acquire a pustular character and cause the formation of blisters and cracks;
- in a complicated form, the surface of the rashes is covered with yellowish plates, which gradually turn into crusts. When removing the crust-like plates, weeping, bleeding lesions are found.
The development of psoriasis always occurs in three phases - progressive with increased symptoms, stationary with peak indicators of intensity of manifestations, and regressive, with a general improvement in the patient's condition.
However, the duration of each stage can be reduced if the treatment is completed on time.
In the absence of adequate therapy, the cycle of exacerbations and remissions will not only be repeated, but also become more frequent. After the transition of the disease to the chronic stage, it becomes much more difficult to combat its manifestation.
Diagnostics: events
To establish a diagnosis, an experienced dermatologist often needs a sufficient visual examination of the patient and evaluates the data on the possibility of his genetic predisposition to psoriasis.
In the presence of a complex course of the disease, doctors prescribe laboratory tests:
- blood analysis. Important prerequisites for the diagnosis of psoriasis are biochemical disorders, autoimmune processes, an increase in ESR and an increase in the number of leukocytes;
- skin biopsy - analysis under a microscope of small particles of affected skin allows you to accurately determine the cause of inflammatory processes;
- histological analysis is an informative diagnostic method involving the study of tissues obtained by excision of the skin in the lesion. Used to verify the diagnosis of psoriasis.
And also for the diagnosis of pathology, a thorough examination of the affected areas is used. In this case, special attention is paid to the tendency of vessels to fragility, bleeding and the occurrence of point hemorrhages.
How to treat in adults and children
Methods of modern medicine can effectively influence psoriasis.
The most sustainable results are achieved through the use of complex therapy - medical treatment of psoriasis and physiotherapy in combination with the patient's proper nutrition and behavior in ordinary life.
The appointment of dermatologists is determined by the nature of the course of the disease, the degree of its severity, and necessarily - the individual characteristics of the patient's body.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy involves the use of drugs that reduce the intensity of symptoms and prevent the progress of psoriasis.
The appointment of non-hormonal ointments and sprays allows you to soften the skin in the lesions, suppress inflammatory processes in the initial stage of psoriasis in children and adults, and also relieve itching and soreness.
Among the most popular means of ointment with activated zinc, salicylic, heparin.
The use of local therapy ensures the cessation of skin peeling processes and the protection of sites injured by psoriasis from infections and fungi. An additional therapeutic effect is provided by creams that contribute to the regeneration of epidermal cells.
The use of corticosteroid ointments is indicated in the treatment of psoriasis on the head or in severe forms of the disease. In the presence of complicated forms of psoriasis, systemic therapy is prescribed using the following means:
- hyposensitizing effect;
- improving microcirculation;
- eliminating the effects of detoxification.
As additional therapeutic measures, psychotropic drugs are used to stabilize the patient's psycho-emotional state.
Folk remedies
The methods offered by traditional medicine can not always immediately eliminate the disease, but they can remove most of its manifestations.
Among the popular recipes of traditional healers:
- infusion made from a glass of water and a tablespoon of flax seeds. The tool is taken after standing for a day to increase the concentration of active substances;
- ointment from birch tar. Prepared by combining with sea buckthorn oil and salicylic alcohol. Apply to lesions. The time of therapeutic effect is two hours;
- compresses from crushed celery root. The vegetable gruel is applied to the affected areas, after two hours it is washed off with warm water and smeared with cream.
The result of exposure to folk recipes appears within one or two weeks, but brings pronounced relief for a long period of time.
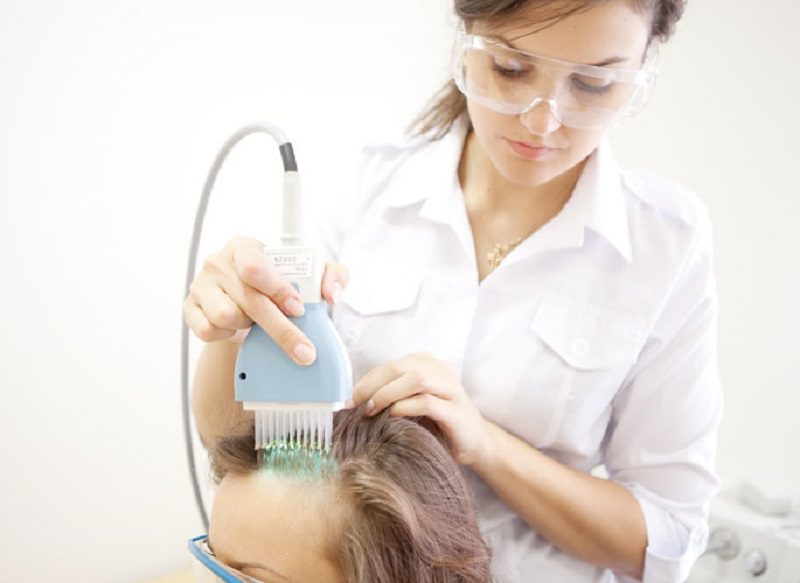
Physiotherapeutic procedures
The use of physiotherapy can significantly improve the patient's condition and speed up the healing process.
The most productive physiotherapy procedures as part of complex therapy are:
- electric sleep;
- irradiation with ultraviolet light;
- x-ray therapy;
- ultrasound;
- cryotherapy.
Each of the physiotherapeutic methods is relevant in the presence of certain indications. However, the appointment of procedures is possible only at the stage of remission.
Diet for Psoriasis
Proper nutrition is the best support of the body from the inside for any disease. With psoriasis, dermatologists are advised to exclude products from the diet that can increase the severity of its course.
Harmful are:
- spicy, fried, smoked and pickled foods;
- any kinds of sweets;
- alcohol;
- mayonnaise, mustard, ketchup.
To improve health and improve well-being, it is recommended to give preference to foods with fiber, polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamins. Among the most useful are cereals, fish, dairy products, vegetables and fruits, herbs and vegetable oils.
Possible complications and predictions
Since psoriasis is considered an incurable disease, the prognosis is classified as conditionally unfavorable.
The disease cannot be completely eliminated, but the frequency and intensity of its manifestations can be reduced, thus improving the quality of life.
Chronic pathologies suggest a slow course. The onset of symptoms signaling the onset of the acute phase indicates the effects of adverse factors.
This means that the exclusion of the causes of exposure and therapeutic measures can stop the inflammatory process and bring remission. If you ignore the signs of the disease and do not take any measures, the pathological process can take on a complex irreversible character.
In some cases, psoriasis can not only lead to disability and disability, but also cause death.
Disease prevention
To prevent exacerbations of psoriasis, the patient should adhere to certain rules. Dermatologists strongly recommend reconsidering not only habits, but also lifestyle.
It is very important to avoid the action of factors that trigger the development of psoriasis. To do this, you must:
- take a shower, not a bath. Water should not be hot, but warm;
- during hygiene procedures, use only soft sponges and washcloths, avoiding harsh products when exposed to the skin;
- choose a soap with a neutral level of acidity;
- wear loose or loose clothing made of cotton or other natural fabrics;
- avoid air-conditioned rooms;
- Before taking sun baths, seek the permission of a doctor.
Quitting smoking and walking in the fresh air are the best ways to strengthen the body's health and immune forces. In addition, spa treatment with a visit to balneological procedures is recommended for patients with psoriasis.
A healthy lifestyle and a responsible attitude to your health is the only way to avoid the consequences of the disease.