Pneumonia is considered to be one of the most unpleasant diseases of an infectious nature, as it poses a certain danger to life, and sometimes leads to disability and death. Symptoms of pneumonia in children directly depend on the type of disease, which in turn requires an individual approach to treatment.
Material Content:
- 1 Ways of infection with pneumonia and risk group
- 2 Types of pneumonia in children
- 3 Primary signs of the disease
- 4 Symptoms of pneumonia in a child
- 5 Diagnosis of the disease
- 6 Treatment of pneumonia in a child
- 7 Is it possible to treat pneumonia in children at home
- 8 Forecasts and Complications
- 9 Prevention of pneumonia
Ways of infection with pneumonia and risk group
The cause of pneumonia is bacteria, viruses, and fungi. In addition, age-related characteristics of the body and the state of the immune system influence. What pathogens cause the disease?

Among them are:
- staphylococcus;
- enterobacteria;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- pneumocysts;
- E. coli;
- legionella;
- hemophilic bacillus.
Almost always in infants, the causative agent is pneumococcus. After 5 years, mycoplasmas cause infection. In school-age children, the cause of the disease is chlamydia.
Factors that affect the development of the inflammatory process in the lungs:
- improper flu therapy;
- ARVI;
- sinusitis or bronchitis of any etiology of a chronic nature;
- hypothermia;
- household dust;
- avitaminosis;
- lack of fresh air;
- stressful situations;
- rickets;
- smoke from cigarettes (this applies to families with smokers);
- artificial nutrition for babies;
- Congenital heart defect.
Often, pneumonia becomes a complication of tonsillitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, pharyngitis, asthma.
Types of pneumonia in children
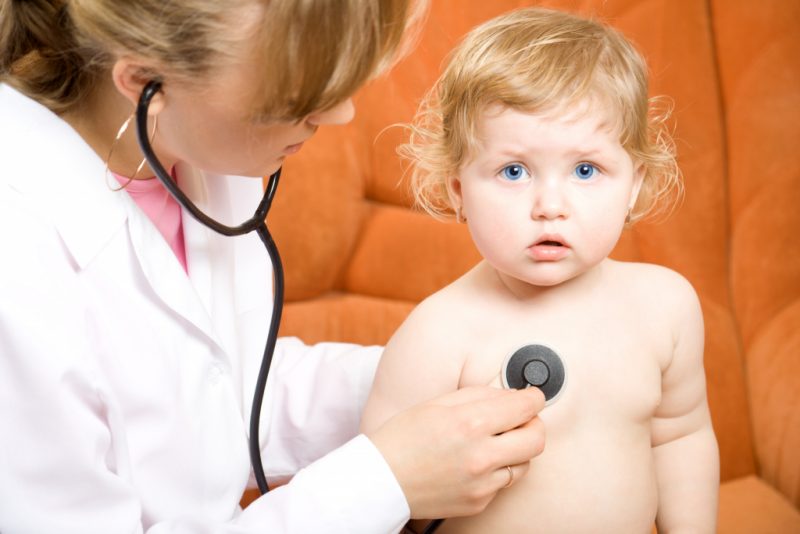
Several types of pneumonia in children are known:
- Viral pneumonia. It is considered to be the most easily tolerated form. It does not require special treatment and is able to pass by itself. Sometimes it proceeds even without temperature.
- Bacterial pneumonia. It occurs on its own, and is a consequence of a certain disease. Antibiotics may be needed to treat it.
- Fungal pneumonia It is found least of all, but it is considered one of the most dangerous. In childhood, this type of disease is a consequence of the inadequate use of antibiotics.
Read also:Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Primary signs of the disease

The first thing that should alert parents:
- after the child has practically recovered, there is a sharp deterioration in health;
- productive cough, during attacks of which sputum discharge was observed, is replaced by dry unproductive;
- symptoms of a bacterial infection are noted, for example, the skin remains pallid even during an increase in body temperature, weakness and drowsiness occur;
- shortness of breath, shortness of breath is sometimes observed even in the absence of temperature, pain in the sternum;
- the temperature can increase to an indicator of 39 ° C, and sometimes even higher; As a rule, antipyretic drugs that are acceptable for your child do not help bring it down.
Any of these symptoms should alert adults and serve as a reason to seek the advice of a specialist. The doctor will prescribe the related tests and, if necessary, may issue a referral for hospitalization.
Symptoms of pneumonia in a child
In small patients of different ages, either lobar pneumonia or acute focal pneumonia can occur. Each type of disease has its own symptomatology.

Signs of pneumonia in a child of a croupous type are characterized by:
- A strong jump in body temperature, often this figure reaches 40 degrees.
- There is weakness throughout the body, malaise, pain in the head.
- Pain in the abdomen, in some cases vomiting.
- The skin becomes white, shortness of breath appears.
- During breathing, wheezing can be felt in the chest.
- With bouts of cough, sputum with an admixture of blood may go away.
- At the beginning of the disease, there is practically no cough, but then it builds up and delivers a lot of unpleasant sensations.
Acute focal pneumonia, as a rule, is a consequence of an acute respiratory viral infection.
It has a gradual development and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Body temperature varies between 38 - 39 degrees.
- Cough becomes wet.
- There is pain in the chest area.
- The body is weakened, the skin is white.
In a child up to a year, other signs of the disease are observed, they directly depend on how the infection occurred - during the gestation of the baby, during labor, or after childbirth.
In the first case, the symptoms will appear immediately after the baby is born and will be as follows:
- pallor of the skin;
- cyanosis on the face;
- high body temperature;
- asphyxia;
- constant regurgitation;
- lethargy.
If the baby was infected during labor, then, as a rule, symptoms appear on day 11:
- body temperature rises;
- breathing becomes difficult, sometimes even groaning;
- the skin becomes pale;
- the appetite disappears, after each meal of spitting up;
- diarrhea;
- sometimes pustules appear on the skin;
- in rare cases, breathing stops.
Signs of pneumonia if infection occurs after childbirth:
- sharp appearance of a runny nose;
- increase in body temperature;
- the child often screams, refuses to eat;
- after a certain time, lethargy appears;
- respiratory failure, the appearance of tachycardia is not excluded.
Diagnosis of the disease
Even if your child has almost all of the above symptoms, this does not mean that he has pneumonia.
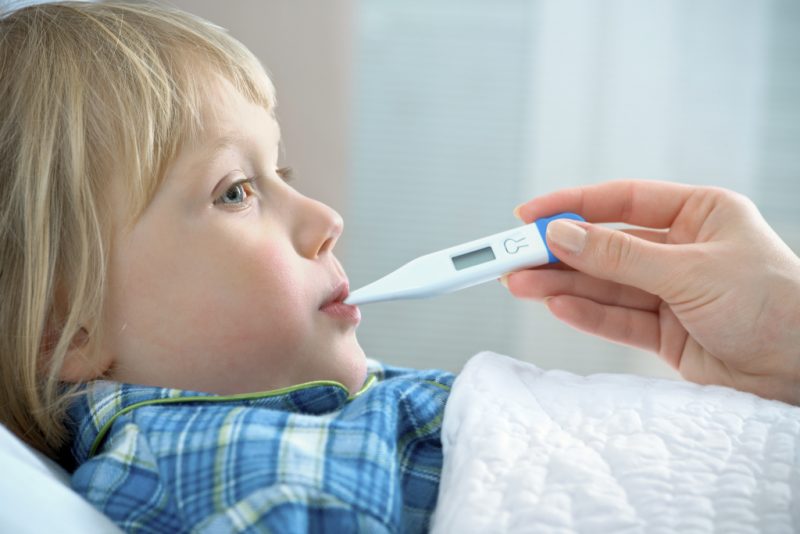
Therefore, you must remember that the signs can only cause suspicion of pneumonia, and for a more accurate diagnosis, additional diagnosis and examination of the respiratory system by a specialist will be required.
So, there are several ways that will help to recognize pneumonia in a child:
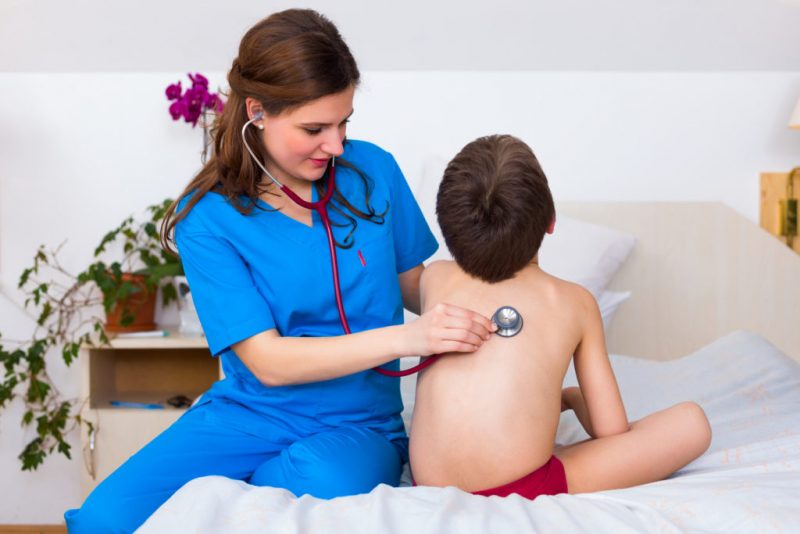
- Listening to the lungs. A good specialist can determine the presence of the disease with a stethoscope.
- X-ray image. It is advised to take a picture immediately from the front and from the side, since frontal scanning gives a clearer picture.
- The overall condition of your baby is assessed.
- Clinical blood test. It allows not only to determine the presence of the disease, but also to determine the nature of the inflammation - viral, fungal, bacterial or mixed.
Treatment of pneumonia in a child
The treatment of pneumonia must necessarily be based on antibiotics.

Parents are required to clearly comply with all the recommendations of the doctor and then the result will not be long in coming.
- Antibiotics should be taken strictly at the indicated time. If the baby needs to drink 2 tablets per day, then make sure that the interval between them is 12 hours, with 3 tablets the time interval is reduced to 8 hours. The first improvements from the prescribed remedy should be observed after 72 hours, if necessary, consult a specialist.
- If pneumonia occurs with temperature, then medications to reduce it should be used only if the thermometer shows more than 39 degrees, for children this figure may be at around 38 degrees.
- During illness, the child may refuse to eat. Forcing him to eat is not worth it, but you can’t starve either. Try to offer him lighter food at this time.
- It is necessary to drink as much liquid as possible, even the use of "Regidron" or its analogues is allowed.
- In the patient's room, arrange regular airing, do wet cleaning.
- The use of general strengthening, antihistamines is not allowed, as they can lead to various side effects.
Is it possible to treat pneumonia in children at home

Treatment of a child for pneumonia is also allowed in the home, but there are clear indications when hospitalization is still recommended:
- children under the age of 3 years;
- a child who has a severe stage of the disease.
Therefore, older children can be treated at home, but under the supervision of a specialist, and parents, in turn, must follow all the instructions of the doctors.
Forecasts and Complications
Analyzing the reviews of specialists, we can conclude that timely access to a doctor gives a favorable prognosis of pneumonia. The greatest danger the disease brings to newborns and infants. In addition, pneumonia caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus can be dangerous. But if the correct treatment is prescribed, then unpleasant complications can be avoided.

Pneumonia in children under 2 years old can go into severe form and affect other organs.
The most common complications are abscess, pleurisy, destruction of lung tissue.
Some complications can have a negative effect on other organs and cause:
- clotting problems;
- heart failure;
- pericarditis;
- meningitis;
- endocarditis;
- sepsis;
- myocarditis.
Prevention of pneumonia
These recommendations are standard not only for the prevention of pneumonia in children, but also for any catarrhal disease:
- Strengthening the immune system. A child from a young age must be tempered. It is allowed to strengthen the body with the help of immunomodulators, it is only desirable that they be of natural origin.
- Keep track of the baby’s nutrition; it should be balanced from an early age.It is advisable that the foods you eat have a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals.
- Try to immediately suppress the foci of infection that has entered the body, that is, begin timely treatment of any disease.
- Arrange daily outdoor walks for your child, regardless of temperature.
Compliance with such rules cannot completely exclude the risk of developing a disease. However, in case of inflammation, a strong body will cope with it faster and can avoid complications.