According to nephrologists, the symptoms and treatment of pyelonephritis in women are interrelated concepts, because when choosing methods of therapeutic effect, doctors always focus on the intensity and nature of the manifestations of the disease. Due to the characteristics of the anatomy, the female body is predisposed to the appearance of inflammatory processes in the kidneys. So, even a slight malaise can become chronic and cause serious health problems. That is why an important component of therapeutic measures for pyelonephritis is the relief of any signs of the disease.
Material Content:
Causes of pyelonephritis
With pyelonephritis, kidney damage by bacteria occurs, which is accompanied by inflammation of the tissues of the organ.
According to statistics, women suffer from pyelonephritis six times more often than men. This is due to the structure of the channel for urine output - in women it is wide, but short. Therefore, the infection spreads quickly through the organs and enters the kidneys, rising through the ureters.
Bacteria can spread throughout the body and through the bloodstream. However, an upward way of promotion is much more common.
Pathogenic microorganisms can be in a latent state in the human body for a long period of time and become activated only when conditions favorable for their vital functions appear.
 Among the most common pathogens of pyelonephritis are Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococci and Staphylococci. As a rule, the multiplication of pathogens occurs against the background of a weakening of the body and a decrease in its protective potential.
Among the most common pathogens of pyelonephritis are Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococci and Staphylococci. As a rule, the multiplication of pathogens occurs against the background of a weakening of the body and a decrease in its protective potential.
Thus, the main causes of pyelonephritis in women, doctors include not only the anatomical features of the urinary organs, but also factors contributing to the dysfunction of the immune system and provoking the activity of harmful bacteria:
- hypothermia;
- abnormal changes in the tissues of the bladder, urinary tract or kidneys;
- any immunodeficiency states;
- diabetes. High blood sugar contributes to the multiplication of pathogenic microorganisms;
- chronic bacterial infections;
- injuries to the tissues of the back and abdominal cavity, contributing to neurogenic dysfunction of the ureter and bladder;
- pregnancy and other processes in which stagnation of urine is possible;
- hormonal imbalance;
- surgical or instrumental, including diagnostic, interventions in the genitourinary system.
Often, inflammatory kidney disease develops against the background of age-related changes in the body.
Types of disease
The nature of the course and severity of the symptoms of pyelonephritis, the intensity of inflammation and the place of their localization are correlated with various types of disease.
Doctors distinguish two main forms of inflammatory pathologies in the kidneys - acute pyelonephritis and chronic.
The development of the acute form is accompanied by sudden and intense manifestations. In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease progresses, and pathological changes in the tissues of the organ become irreversible.
 As the infection spreads, the acute form of pyelonephritis goes through several stages of development:
As the infection spreads, the acute form of pyelonephritis goes through several stages of development:
- serous. It is characterized by the formation of multiple inflammatory foci. The kidneys swell and increase in size;
- purulent, apostematous. At the site of inflammatory foci, abscesses are formed - apostems, the growth of which is accompanied by abundant infiltration. The fusion of the apostem leads to the occurrence of carbuncles and purulent abscesses that contribute to the melting of tissues and destruction of large areas of the kidney parenchyma.
In addition, acute pyelonephritis is one-sided or two-sided - depending on whether one or both kidneys are affected.
Features of the chronic form of the disease
The appearance of chronic pyelonephritis is usually regarded as a consequence of an untreated acute form of the disease. Less often - as an independent pathological process.
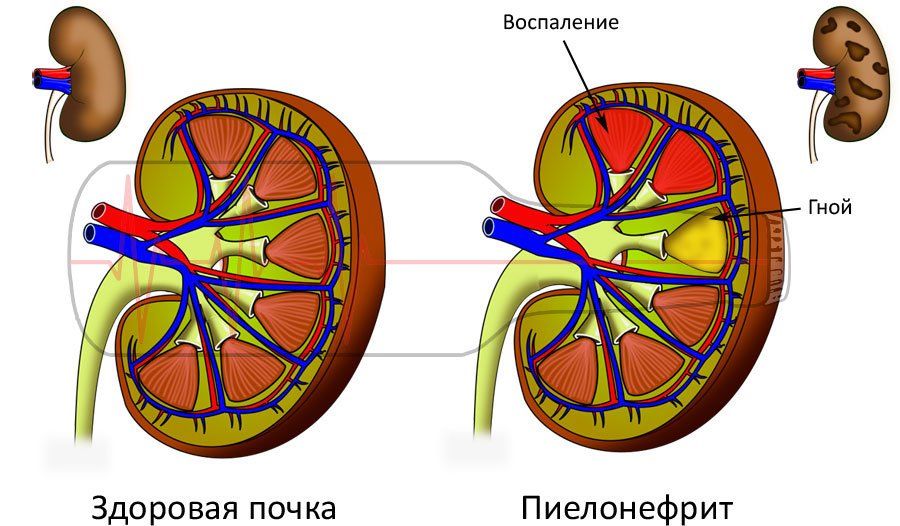 The course of chronic kidney inflammation is accompanied by mild symptoms and is predisposed to a periodic transition to the acute phase.
The course of chronic kidney inflammation is accompanied by mild symptoms and is predisposed to a periodic transition to the acute phase.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in women are determined by the form of the course of the disease and may vary.
In the acute form of inflammatory processes in the kidneys, the following manifestations are observed:
- severe chills and a sharp increase in temperature - from 38 ° C and above;
- back pain at the level of the lower ribs;
- signs of intoxication - vomiting, nausea, increased thirst;
- frequent urination.
Acute renal inflammation is often preceded by exacerbation of cystitis.
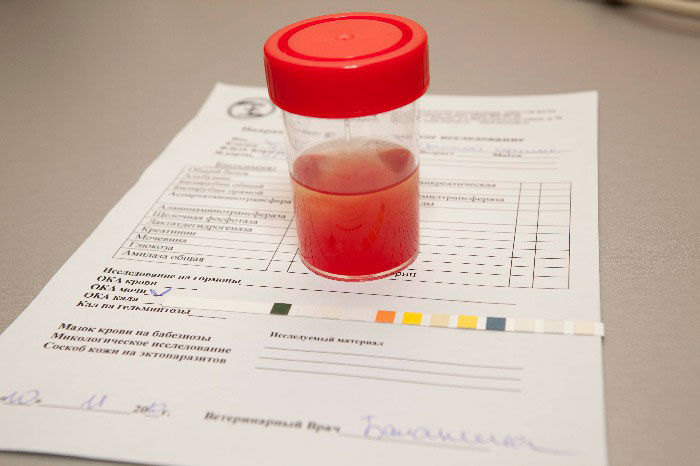
Blood may appear in the urine. It is characteristic that this symptom is observed only in women and is completely absent in men.
 Symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis in women are weak. The pathological process is accompanied by:
Symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis in women are weak. The pathological process is accompanied by:
- lethargy and increased fatigue of the patient;
- a slight increase in temperature, within 38 ° C;
- periodic pressure surges;
- frequent urination at night;
- morning swelling around the eyes;
- aching lower back pain.
An exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis is characterized by a predominance of general symptoms, so the disease is often confused with gynecological pathologies or ARVI.
Diagnosis of inflammatory kidney disease
The basis for the appointment of measures for the diagnosis of pyelonephritis is considered a consultation of a nephrologist and history taking. At this stage, doctors find out what factors could provoke the occurrence of inflammation in the kidneys of a woman:
- gynecological diseases, abortions;
- pregnancy;
- menopause;
- immunodeficiency conditions;
- the presence of infectious diseases, including a history of;
- taking antibiotics or cystostatics.
During a physical examination, the nephrologist palpates in the area of the kidneys, evaluates the color of the skin, as well as blood pressure.
 The most important component of diagnostic measures is the analysis of urine. Three different studies are practiced:
The most important component of diagnostic measures is the analysis of urine. Three different studies are practiced:
- general urine analysis. Against the background of renal inflammation, leukocytes appear in the urine, and with the development of complicated forms, red blood cells;
- bacteriological analysis of urine. The necessary measure to determine the strain and its resistance to antibacterial agents;
- Gram staining of urine is an additional procedure that allows you to accurately determine not only the type of infection, but also the characteristics of the pathogen.
Compulsory studies also include a general and biochemical blood test, which allows to establish not only the presence of inflammatory processes, but also to diagnose renal failure. If necessary, doctors can also prescribe an ultrasound of the kidneys, various types of urography, nephroscintigraphy.
The diagnosis of chronic kidney inflammation is complicated by the absence of local symptoms. Therefore, nephrologists differentiate with hypertension, amyloidosis and the chronic form of glomerulonephritis.
Features of the course during pregnancy
According to statistics, pyelonephritis in pregnant women is observed in 4% of cases. Moreover, the peak of the manifestations of the disease occurs in the second and third trimester. This situation is not accidental and is associated with changes that occur in the body of a woman when carrying a child.
The main provoking factor is the growth of the fetus and, as a consequence, an increase in the volume of the uterus. As a result of pressure on the surrounding tissues and organs, especially on the ureter, there is a slowdown in the progress of urine.
 The resulting stagnation of urine promotes the activation and reproduction of bacteria, which gradually capture the organs of the genitourinary system and are introduced into the cells of the mucous membrane of the kidneys.
The resulting stagnation of urine promotes the activation and reproduction of bacteria, which gradually capture the organs of the genitourinary system and are introduced into the cells of the mucous membrane of the kidneys.
If you start treatment at an early stage of the development of pathology during pregnancy, you can not only completely eliminate pyelonephritis, but also avoid its complications, which are a danger to the health of the fetus.
Treatment of pyelonephritis in women
Methods of treating pyelonephritis are determined by the specific state of a woman's health. The presence of gynecological problems and infections can complicate the process and provoke the transition of the disease into a chronic form.
Therefore, at the first stage of treatment, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs, the action of which is aimed at eliminating foci of infection. The choice of drugs depends on the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
The appropriateness of the use of drugs of this group during pregnancy is determined by the attending physician. The average course of antibiotic therapy is two weeks.
An equally important goal of therapy is the elimination of stagnation, an increase in the outflow of urine by taking diuretics, decoctions of berries with antiseptic properties - cranberries, rose hips, lingonberries.
 In the presence of purulent formations in the tissues of the kidneys, surgical intervention can be used. In particularly difficult cases, with the development of necrotic processes, the removal of the affected organ is prescribed.
In the presence of purulent formations in the tissues of the kidneys, surgical intervention can be used. In particularly difficult cases, with the development of necrotic processes, the removal of the affected organ is prescribed.
The chronic form of pyelonephritis is treated with reduced doses of antibacterial drugs, as well as with means that stabilize the functionality of the kidneys and improve their microcirculation.
Additionally, folk remedies are prescribed - decoctions of horsetail, bearberry, parsley.
Diet and proper nutrition
A properly organized diet is a mandatory component of therapeutic and preventive measures for inflammation of the kidneys. It is important to understand that the diet for pyelonephritis is designed to solve several problems at once:
- restore metabolism;
- normalize blood pressure;
- relieve swelling;
- stimulate the elimination of toxins and harmful compounds;
- normal kidney function;
- prevent the transition of the disease into a chronic form.
The therapeutic nutritional scheme for pyelonephritis was developed in the last century by Professor Pevzner. In medicine, this type of diet is known as Table 7.
 Slow carbohydrates, a small amount of protein, a minimum amount of fat and a regulated drinking regimen form the basis of medical nutrition. To optimize the functioning of the kidneys, it is recommended to exclude from the diet any foods containing salt, as well as fried and smoked dishes.
Slow carbohydrates, a small amount of protein, a minimum amount of fat and a regulated drinking regimen form the basis of medical nutrition. To optimize the functioning of the kidneys, it is recommended to exclude from the diet any foods containing salt, as well as fried and smoked dishes.
The priority is vegetable and milk soups, pasta, whole grains, low-fat meat, seafood and eggs. It is also recommended to include fruits and juices in the menu.
Undesirable foods in the diet are: sausages, baked goods, confectionery, fatty meat and soups based on it, cabbage, onions, mushrooms, legumes, spinach and radishes. In addition, coffee and alcohol are prohibited.
Possible complications
Timely relief of inflammation and an adequate therapeutic effect in most cases brings complete recovery. However, in the presence of purulent formations in the kidneys, complications may appear, the ignoring of which poses a threat to life.
The most dangerous complications of an acute form of pathology:
- necrotic papillitis - may be an indication for removal of the kidney;
- atrophy of the parenchyma and pyelonephritic wrinkling of the kidneys - leads to the death of organ tissues;
- abscesses, carbuncles - one of the reasons for the development of sepsis and death;
- acute renal failure.
Even after recovery, the affected kidney tissue is not able to recover in its original form. Most often, the destroyed areas are replaced by connective tissue.
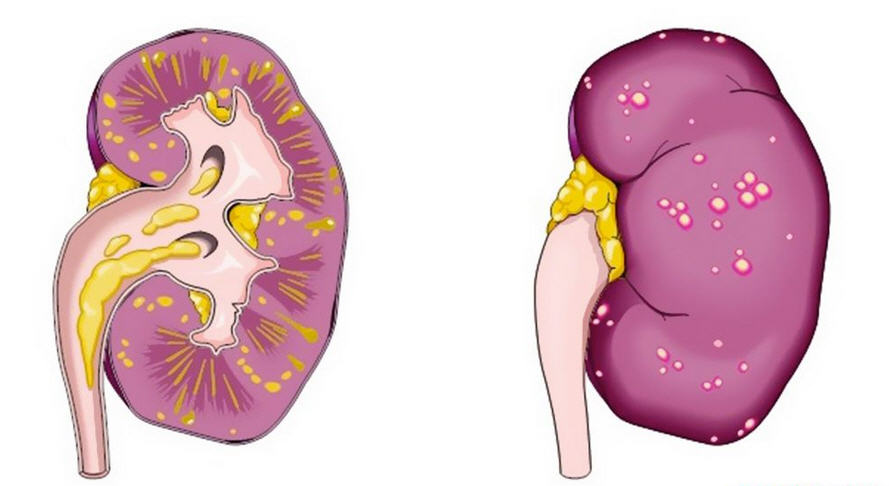 The absence of treatment in the chronic form of pyelonephritis also leads to destruction of the tissues of the affected organ. Pathological processes in this case occur slowly, but the complications caused by them are irreversible.
The absence of treatment in the chronic form of pyelonephritis also leads to destruction of the tissues of the affected organ. Pathological processes in this case occur slowly, but the complications caused by them are irreversible.
Prognosis for recovery
With the development of uncomplicated forms of unilateral pyelonephritis, even with its chronic form, the prognosis for life is considered favorable. The main thing is to optimize the functioning of the kidneys, eliminate the factors provoking the disease, undergo a full course of treatment and take measures to prevent relapse.
 The prognosis for patients with bilateral chronic pyelonephritis is less favorable. In such cases, after 10-15 years, the terminal stage occurs, in which there is a complete extinction of kidney function.
The prognosis for patients with bilateral chronic pyelonephritis is less favorable. In such cases, after 10-15 years, the terminal stage occurs, in which there is a complete extinction of kidney function.
Prevention
Despite the fact that acute pyelonephritis responds well to treatment, the risk of relapse remains relevant throughout the patient's life. Every woman who has had kidney inflammation should remember the need for preventive measures.
Among the most important precautions:
- a healthy lifestyle aimed at the overall strengthening of the body and the immune system;
- maintaining normal thermoregulation, lack of hypothermia;
- adherence to a diet and drinking regimen;
- immediate use of the toilet when urges appear;
- early detection and treatment of cystitis and other inflammatory diseases;
- personal hygiene;
- regular medical examinations.
 No matter how fragile the female body is, a reasonable and careful attitude to your health will help to avoid diseases. The main thing is to pay attention to his signals in time and not to lose optimism in any life situations.
No matter how fragile the female body is, a reasonable and careful attitude to your health will help to avoid diseases. The main thing is to pay attention to his signals in time and not to lose optimism in any life situations.












