Pyelonephritis is an infectious lesion of the kidneys, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the structures of the organ. The cause of the disease is the penetration into the renal pelvis and the propagation of pathogenic microflora there. Symptoms of pyelonephritis may vary depending on gender, age, and severity of the disease. Due to the anatomical features of the female genitourinary system, the beautiful half of humanity is sick three times more often than men.
Material Content:
Causes and signs of pyelonephritis
Causes of pyelonephritis are factors that contribute to a decrease in the strength of the immune system and the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the kidneys.
The disease can provoke:
- pathological structure of the urinary tract or kidneys;
- the ingress of aggressive microflora from the bladder or through the bloodstream;
- the presence of a focus of infection in the body;
- tumorous formations in the genitourinary system of a benign or malignant nature;
- decreased immunity;
- blockage or compression of the renal vessels, circulatory disorders;
- a history of diabetes mellitus;
- ureteral obstruction;
- genitourinary trauma;
- hypothermia.
The inflammatory process in the kidneys is often a female problem due to differences in the structure of the urethra: the urethra is 3-4 times shorter and slightly wider than that of a man.Due to this feature, bacteria can easily penetrate into the bladder and infect other organs in an ascending way. Besides, cyclic hormonal changes constantly occur in the female body, which reduce the strength of the immune response to the penetration of foreign flora.
Symptoms of Kidney Inflammation
There are two forms of the course of the disease: acute and chronic pyelonephritis. In the first case, the clinical picture is pronounced, with significant intoxication and pain. In a chronic process, the symptoms are blurred, it can be difficult to recognize the disease and make a diagnosis.
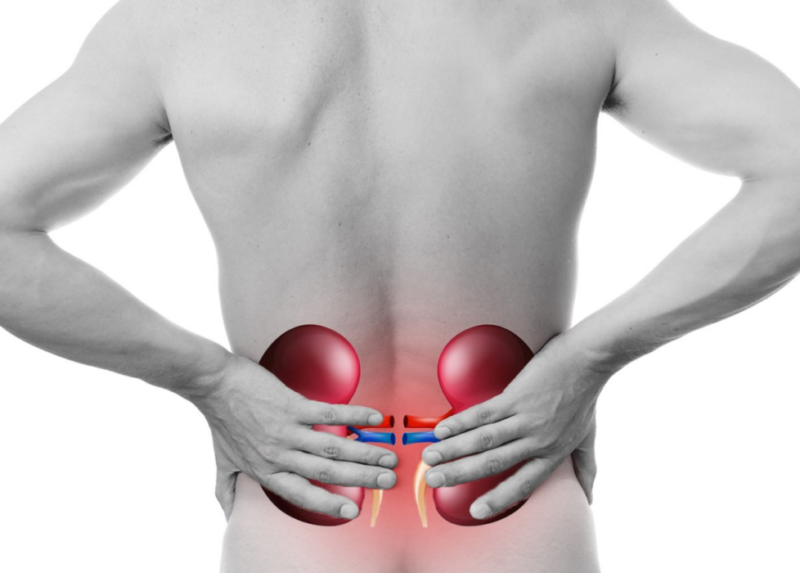
Acute patients complain of dull pain on the side of the lower back, at the site of the approximate location of the affected kidney. Body temperature rises to high values - 39-40 degrees, but quickly returns to normal after taking anti-inflammatory drugs. The daily temperature fluctuation is characteristic: hyperthermia gradually gains momentum throughout the day, reaches its maximum in the evening, and in the morning becomes physiological.
And also kidney inflammation is accompanied by signs of intoxication:
- headache;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- nausea, up to vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- malaise.
Pyelonephritis itself does not cause problems with urination, but since it often occurs simultaneously with cystitis, especially in women, dysuric symptoms are added to the manifestations. This is urinary incontinence, frequent and painful urination.
In men
The anatomical structure of the male urinary system is significantly different from the female organs, so the incidence of pyelonephritis is much lower. Obstruction of the pelvis or ureter, prostate adenoma, which interferes with the normal outflow of urine, most often causes inflammation.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in men are manifested as in a chronic process: dull back pain, mild intoxication, problems with urination. If there are stones in the kidneys, the disease may be accompanied by renal colic and the appearance of blood clots in the urine.
Among women
Symptoms of pyelonephritis in women and the treatment of the disease depend on the form of pathology. Acute inflammation is manifested by a sharp increase in temperature, serious symptoms of intoxication, pain in the affected organ. The first sign that the doctor checks is Pasternatsky’s symptom: a light tapping on the lower back on the side of the spine causes severe pain on the part of the diseased kidney.
When the process is chronic, the symptomatology weakens, disguises itself as other diseases.
During remission, such complaints are possible:
- periodic discomfort in the lumbar region;
- decreased performance, constant drowsiness;
- the appearance of morning edema;
- excretion of a small amount of urine.
Due to the short urethra, acute pyelonephritis in women is often combined with inflammation of the bladder - cystitis.
Therefore, to the clinical picture are added:
- uncomfortable sensations during and after going to the toilet;
- frequent urination;
- inability to completely empty the bladder;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen.
In children
Pyelonephritis in children is characterized by a latent course and can only be manifested by an increase in body temperature against the background of a satisfactory state of health. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient immediately undergo a general analysis of blood and urine.
At an older age, children may complain of chills, nausea, back pain, headache. The child becomes inactive, sleepy, refuses food.
Diagnosis of an infectious disease
If you suspect the presence of pyelonephritis, you should contact your family doctor: he will collect an anamnesis, prescribe additional examinations and select rational therapy.
Initial diagnostic methods include:
- urinalysis - reveals an increased concentration of protein, a decrease in the density of urine and a large number of immune blood cells (white blood cells), salt impurities;
- blood test - detects signs of inflammation in the body (many white blood cells, rapid erythrocyte sedimentation);
- urine for sterility - bacterial inoculation is needed to accurately determine the pathogen and the selection of an antibiotic, to which the pathogenic microorganism is most sensitive;
- urine according to Nechiporenko - allows you to accurately determine the concentration of blood elements and cylinders in 1 ml of fluid. With inflammation, all these indicators are overestimated;
- ultrasound examination - determines the expansion of the renal pelvis, obstruction of the ducts, the presence of stones or sand.
In severe pyelonephritis or suspected complications, doctors resort to more complex and costly diagnostic methods - contrast radiography of the urinary tract and kidneys, computed or magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment methods
A urologist or nephrologist is involved in the treatment of the disease. Therapy can take place both in the hospital and at home. Severe cases in adults, as well as acute pyelonephritis in children, always require hospitalization. The main method of treatment is conservative using antibacterial drugs, the duration of the course is from 5 to 10 days. It will take more time to get rid of the chronic process, up to several months.
Drugs and antibiotics
Inflammation of the kidneys is treated with antibiotics, at the beginning of the disease, medications are prescribed almost at random. When determining the pathogen, a drug is selected to which it is most sensitive.
Most commonly used:
- penicillin row;
- cephalosporins;
- sulfa drugs;
- aminoglycosides;
- carbapenems.
In addition to pathogenetic, supportive therapy is also prescribed, which includes the intake of diuretics and anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants and synthetic vitamins.
Folk remedies
Along with traditional treatment, you can resort to methods of alternative therapy. The use of decoctions, infusions and tinctures based on the correct medicinal herbs promotes the outflow of urine, improves blood circulation, and increases the body's immune defense. In addition, most medicinal plants have an anti-inflammatory effect, and are also able to dull the pain.
When pyelonephritis is recommended to use funds from the following components:
- bearberry;
- birch leaves;
- peppermint;
- yarrow;
- calendula
- cranberries;
- lingonberries;
- rose hips.
About the use of alternative recipes, you must inform the attending physician so that he takes this into account when choosing medicines.
Diet for pyelonephritis
Dietary nutrition for pyelonephritis plays an important role in the success of treatment.
The severity of the restrictions depends on the degree of kidney damage and the presence of concomitant complications.
In any case, you need:
- practically eliminate the use of salt, reducing its amount to 5 g per day;
- completely abandon alcoholic drinks, soda and coffee;
- reduce the consumption of fatty meat and fish;
- exclude rich broths, protein foods, canned food, smoked dishes, spicy and mushrooms;
- eat more vegetables and fruits.
In the absence of edema, you need to drink more fluid in order to quickly clear the kidneys of pathogens and their metabolic products.
Consequences and complications of the disease
If the patient’s body is weakened, he seeks medical help too late or ignores the prescribed treatment, there is a high risk of pyelonephritis complications:
- acute renal failure - develops only with simultaneous damage to both organs;
- chronic failure - is the final outcome of prolonged ignoring of the symptoms of the disease and refusal of treatment;
- the formation of sand and stones in the kidneys and bladder;
- kidney abscess
- pyonephrosis - filling the renal pelvis with purulent contents;
- persistent increase in blood pressure of renal origin.
To avoid complications, you need to see a doctor at the first sign and clearly adhere to all his instructions.
Preventative measures
To avoid the development of acute pyelonephritis or reinfection, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- avoid hypothermia;
- timely treat any infectious lesions;
- observe intimate hygiene;
- drink enough water;
- use the toilet on demand, and not endure to the last.
People who have already experienced pyelonephritis should periodically have a urinalysis and take a course of uroseptics. This will help prevent the recurrence of the disease.