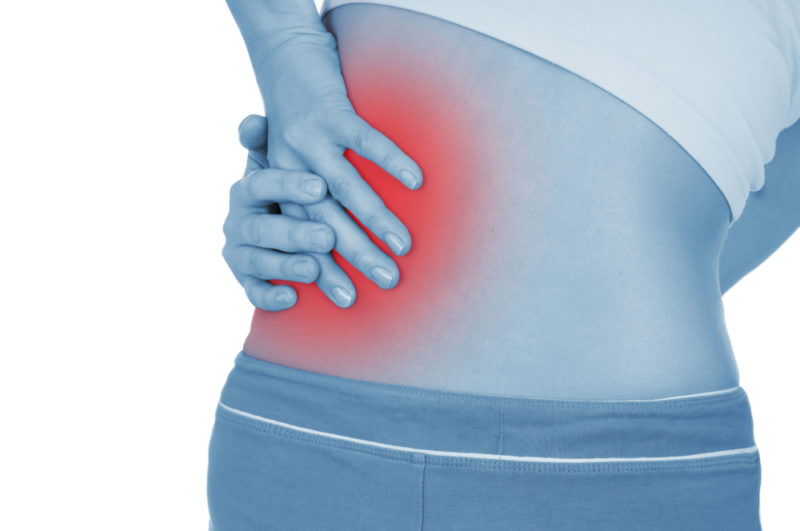
Infectious lesions of the kidneys can cause severe inflammatory processes that provoke the development of complications. Pyelonephritis is especially dangerous during pregnancy, since the additional burden on organs in combination with antibiotic therapy can affect the health of the fetus.
You can avoid the risk if you prevent the onset of the disease in advance, recognize its symptoms in time and take the necessary therapeutic measures.
Material Content:
- 1 Reasons and mechanism of development
- 2 Pyelonephritis development factors
- 3 Types of disease
- 4 Symptoms of pyelonephritis during pregnancy
- 5 Which doctor should I contact, diagnostics
- 6 Features of diagnostic measures
- 7 Treatment of inflammatory kidney disease
- 8 The specificity of the diet for pyelonephritis
- 9 Consequences for the child
- 10 Prevention
Reasons and mechanism of development
Inflammation of the kidney tissue or pyelonephritis occurs as a result of damage to a bacterial infection. The main pathogens of the disease include such pathogenic microorganisms as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterococci and staphylococci.
However, in the vast majority of cases (90% of the total), kidney inflammation develops after penetration into the organ of E. coli. All of these bacteria are conditionally pathogenic, since they can be in the body for a long time without causing health problems.
Infection enters the body in different ways - through the blood, through the urinary tract or the lumen of the ureter. However, favorable conditions are needed to activate the pathogens.Such prerequisites are formed in the body of a woman expecting a baby.
The immune system weakens already in the early stages, the load on the kidneys during the formation of the fetus increases. During the development of the child, the uterus increases in size and puts pressure on the surrounding tissue.
As a result of this process, the channel through which urine flows is pinched, causing it to stagnate. For bacteria, such events in the ureter are an ideal medium for reproduction. And due to the structural features of the genitourinary system in women, the development of infection occurs much faster than in men.
That is why pregnant women suffer from pyelonephritis several times more often than a strong half of humanity.
Pyelonephritis development factors
Along with pregnancy, additional factors provoking the occurrence of pyelonephritis are:
- abnormal structure of the kidneys and urogenital organs;
- hypothermia;
- urolithiasis disease;
- chronic bacterial infections, even those common as tonsillitis and tonsillitis;
- diabetes;
- surgical interventions in the field of pelvic organs;
- any immunodeficiency conditions;
- stagnation of urine;
- injuries of the back and peritoneum.
As the bacterial organism invades the cells of the organ, inflammation in the renal tissues intensifies, the intensity of which depends on the number of pathogens and their activity.
The stronger the lesion, the less chance of tissue repair, since the damaged kidney parenchyma is no longer regenerated, but replaced by scar tissue, which leads to impaired renal structure.
Types of disease
According to the type of course and the nature of the lesions, kidney inflammation in pregnant women is divided into several types.
Gestational pyelonephritis
The occurrence of gestational pyelonephritis is characteristic only of expectant mothers.
The development of pathology is preceded by changes in the female body:
- in the first trimester. An increase in the level of hormones reduces the tone of the muscles of the ureter and affects the functionality of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys;
- in the second trimester. Due to the increase in the uterus and increased pressure on the urethra, its tone decreases, the nutrition of tissues and urodynamics of the kidneys are disturbed, stagnation of urine occurs. Thus, favorable conditions for the life of bacteria are created;
- in the third trimester, hormonal changes reach their peak. Therefore, this period is considered the most critical for the occurrence of infectious inflammation of the kidneys.
The form of the course of gestational pyelonephritis is acute and chronic.
Acute pyelonephritis
Typically, acute pyelonephritis develops very quickly and is accompanied by fever and pain at the lower back.
The acute form is characterized by impaired intercellular metabolism and damage to interstitial tissue. With repeated exacerbation, it can go into a purulent form.
And also the acute form of exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis during pregnancy.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis during pregnancy
The manifestations of the inflammatory process in the kidneys differ in degree of intensity, depending on the form of the course of the disease. The most pronounced signs are observed in acute pathology.
The disease occurs suddenly and is accompanied by:
- chills;
- raising the temperature to 40 ° C;
- a feeling of pain in the lower back and when urinating;
- changes in the characteristics of urine - volume, color, degree of transparency;
- nausea
- general weakness;
- headaches.
Over time, the symptoms of pyelonephritis in women change during pregnancy. In the first trimester, lower back pain is more pronounced and can be given to the lower abdomen. In the second and third trimesters, the intensity of the pain decreases, but difficulty urinating progresses.
Most often, primary (acute) and secondary (repeated exacerbation) pyelonephritis occurs in the second trimester.Exacerbations of the chronic form of pyelonephritis in the third trimester are rare.
Which doctor should I contact, diagnostics
Most pregnant women with signs of pyelonephritis do not know which doctor to seek help from - a gynecologist conducting a pregnancy, or a urologist who specializes in diseases of the urinary system.
The standard algorithm of actions in such cases involves a visit to a gynecologist, then a therapist, nephrologist or urologist. You can independently turn directly to a nephrologist to save time and save strength.
Features of diagnostic measures
The patient's complaints about problems with urination are the first signal about the development of pathological processes in the urinary system. To determine local symptoms, doctors evaluate the degree of muscle tension and the presence of pain in the lumbar region.
And since such processes cannot be started, gynecologists immediately prescribe the main diagnostic procedure to detect pyelonephritis - the delivery of a urinalysis.
The presence of leukocytes and protein inclusions testifies to inflammatory processes in the kidneys in the results of urine analysis. Protein in the urine is another alarming sign, indicating not only inflammatory, but also purulent manifestations in the urinary system.
Other diagnostic methods for pyelonephritis:
- blood test - general and biochemical;
- study of urine sediment and its bacteriological composition;
- Gram urine stain analysis;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys - to clarify the diagnosis;
- radiography;
- radionuclide methods, CT and MRI are less commonly used.
Signs of pathological processes in the kidneys are: an increase in ESR and the number of leukocytes, an increase in the size of the organ and a decrease in mobility. Bacteriological analysis of urine allows not only to identify the causative agent of pyelonephritis, but also to establish the degree of its resistance to the effects of antibiotics.
Treatment of inflammatory kidney disease
Methods of treating pyelonephritis in pregnant women are determined solely by the individual characteristics of the patients.
Before making an appointment, the doctor conducts the following activities:
- establishes factors complicating the course of the disease;
- specifies the type of pathogen bacterium and checks its sensitivity to antibacterial agents;
- assesses the condition and functionality of the ureter;
- analyzes the functional potential of the kidneys.
The choice of drugs for the treatment of pyelonephritis in pregnant women is complicated by considerations of maintaining the health of the child. Therefore, in the early stages, antibiotic therapy is prescribed only as an exception.
During this period, the formation of the most important physiological systems of the child occurs, in connection with which any influence from the outside can provoke the development of anomalies.
Starting from the second trimester and up to childbirth, it is possible to use antibiotics of the second and third generation cephalosporins.
Additional therapeutic measures include positional therapy, which provides for sleep on the left side and daily stay in the knee-elbow position for 10 minutes. This method allows you to remove the load from the ureter and improve the outflow of urine.
And herbal medicine is also welcomed - taking decoctions of nettle, oats, birch leaves and lingonberries. The traditionally used diuretic herbs - yarrow, parsley or juniper berries during pregnancy are not recommended.
The specificity of the diet for pyelonephritis
An important aspect of exposure to the body in order to support the urinary system is the organization of proper nutrition.
The diet of women with pyelonephritis includes:
- intake of sufficient water;
- the use of fruit drinks from cranberries and cranberries;
- rejection of spicy foods, pickled products and coffee;
- an increase in the diet of seafood, chicken, vegetables and fruits;
- limiting the amount of salt used.
Alcohol and smoking are completely eliminated.
A patient is considered healthy if a triple urine test showed the absence of pathological changes in its composition.
Consequences for the child
Pyelonephritis during pregnancy can cause premature birth. In addition, the development of pathology is fraught with dangerous consequences for the child.
Among the most likely complications of fetal health:
- infectious lesion;
- hypoxia;
- inflammatory processes of internal organs;
- abnormal development of organs;
- disturbance of nutrition and blood circulation.
Children in mothers with patients with pyelonephritis are born weak, with insufficient weight and growth, prone to frequent diseases.
In order to preserve pregnancy and protect the child from the effects of inflammatory processes, timely treatment and strict implementation of all the doctor's recommendations are necessary.
Prevention
By the prevention of pyelonephritis is meant not only the prevention of its development, but also the prevention of relapse of the disease.
To maintain kidney health:
- avoid hypothermia - dress warmly, do not go barefoot;
- maintain a drinking regimen. The optimal amount of fluid consumed per day is 1.5–2 liters;
- regularly undergo an examination to identify infectious or inflammatory foci in the tissues of the body;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, stop smoking, reduce alcohol consumption to a minimum;
- adhere to a diet recommended for pyelonephritis;
- visit the toilet immediately when the urge appears, avoiding stagnation of urine;
- observe personal hygiene;
- reduce the intensity of sexual activity.
Like many infectious diseases, pyelonephritis occurs against a background of decreased immunity. Therefore, the main task of a woman planning a pregnancy is to take all measures to maximize the strengthening and support of her health.