Paratonsillitis is called acute inflammation of the tissues that surround the palatine membrane. Almost always, the disease is unilateral, but it is also not necessary to exclude bilateral inflammation. The last stage leads to the formation of a cavity filled with pus near the tonsils - paratonsillar abscess.
Material Content:
Causes of paratonsillitis
An acute inflammatory disease can occur as a result of the action of pathogens such as streptococci, staphylococci, hemophilic bacillus. As practice shows, all varieties of angina have the same bacterial picture, phlegmonous, as a rule, is considered a complication. The main reason for the development of the disease is a prolonged weakening of the immune system.
Among other reasons, it is worth highlighting:
- chronic inflammatory or infectious diseases;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- endocrine system diseases, including diabetes;
- loose lymphoid tissue;
- chemotherapy;
- mechanical, thermal or chemical injuries;
- radiation therapy.
The presence of these factors increases the likelihood of an ailment.
Symptoms and signs
In most cases, acute paratonsillitis appears a few days after the disappearance of the underlying disease. In a person, the general condition can sharply worsen and unilateral pains in the throat area appear. All this happens against the backdrop of a general recovery.
Other symptoms of paratonsillitis include:
- severe headaches;
- a whitish or yellowish tinge that occurs both on and near the tonsils;
- a temperature jump of up to 40 degrees, which already indicates a serious inflammatory process;
- the phlegmon does not show clear contours;
- difficulty swallowing;
- pain can occur in the ear region from the side where the inflammatory abscess forms;
- loss of voice;
- an unpleasant odor appears from the oral cavity;
- hyperemia and swelling of the tissues of the soft palate;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck;
- swelling of the cervical-facial region.
One-sided pain in the throat is so strong that a person is forced to take a certain position in order to alleviate his condition at least a little. Opening the mouth also causes pain, and eating and water is almost impossible.
Diagnostic measures
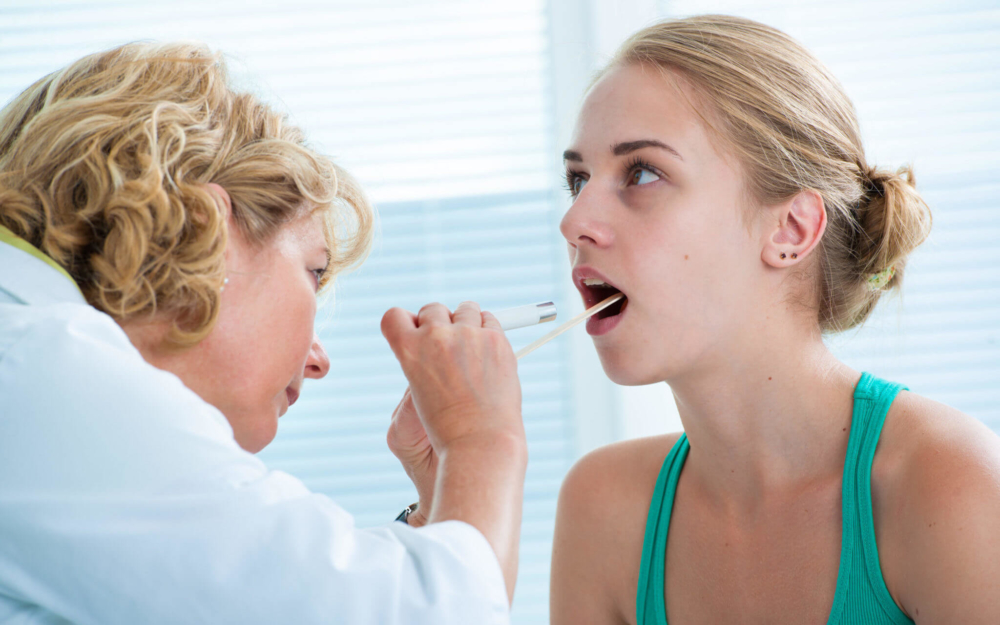
In order to diagnose the disease, an experienced otolaryngologist will not take much time. Most often, for a diagnosis, an examination of the affected palatine tonsil, as well as collecting anamnesis data, is enough. Ideally, a complete diagnosis of phlegmonous tonsillitis consists of several stages:
- Interrogation of the patient. The doctor must pay attention to acute sore throats, recent, the presence of chronic tonsillitis. It also examines how the previous treatment was carried out.
- Physical examination - there may be a slight tilt of the head towards the inflamed tonsil. Lymph nodes increase in volume, while there is a painful sensation.
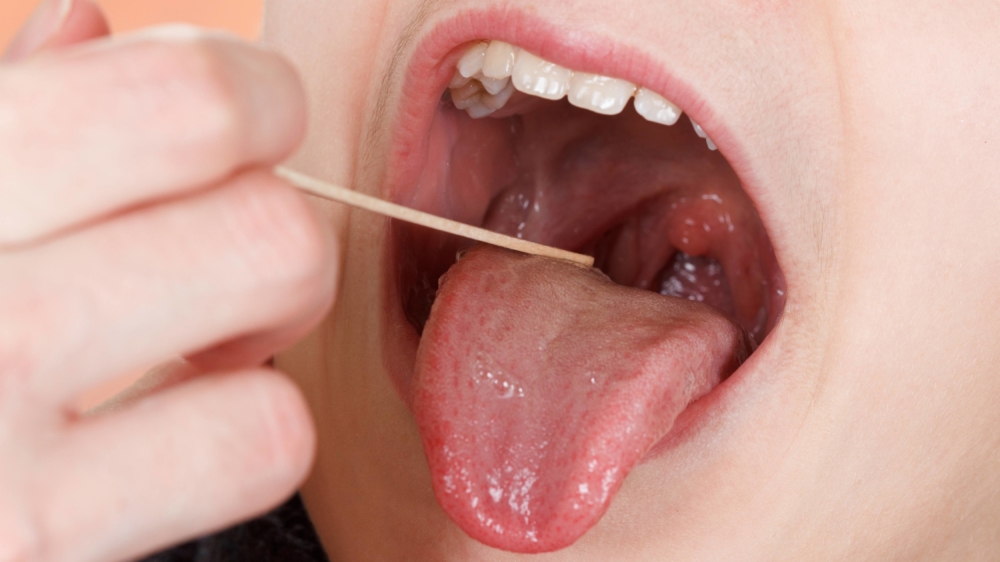
- Pharyngoscopy - visually it is possible to determine hyperemia and diffuse swelling of the throat tissues. The palatine tonsil increases in size and shifts to the midline. A plaque forms on top. It can be dirty gray or yellow, it can be removed using a special spatula.
- Laboratory research. A general blood test is done, a bacterial examination of a smear from the throat is performed. With the help of the latter, the resistance of bacteria to an antibiotic is checked.
Treatment of acute inflammatory disease
Treatment of paratonsillitis can not do without taking medications, in addition, during the development of the disease, a sparing regimen is required. Regardless of age, the patient should refrain from any physical exertion and spend most of the time at rest. It is also necessary to abandon fatty and salty.
An antibiotic is required to treat phlegmonous tonsillitis. To choose the right medicines, you need to conduct a tank-sowing. Most often, the disease is treated with Cefepim, Amoxiclav, Sparfloxacin, Flemoclav, Azithromycin, Cefixime.
Additionally, local preparations can be used - Bioparox, for rinsing the throat, Iodinol, Miramistin, Furacilin, Lugol are suitable.
To disinfect the mucous membrane, it is worth using Faringosept, Hexalysis, Neo-angin, Gramitsidin. With the help of Strepsils or Flurbiprofen, they soften the throat and slightly relieve inflammation. Symptoms are taken with antipyretics.
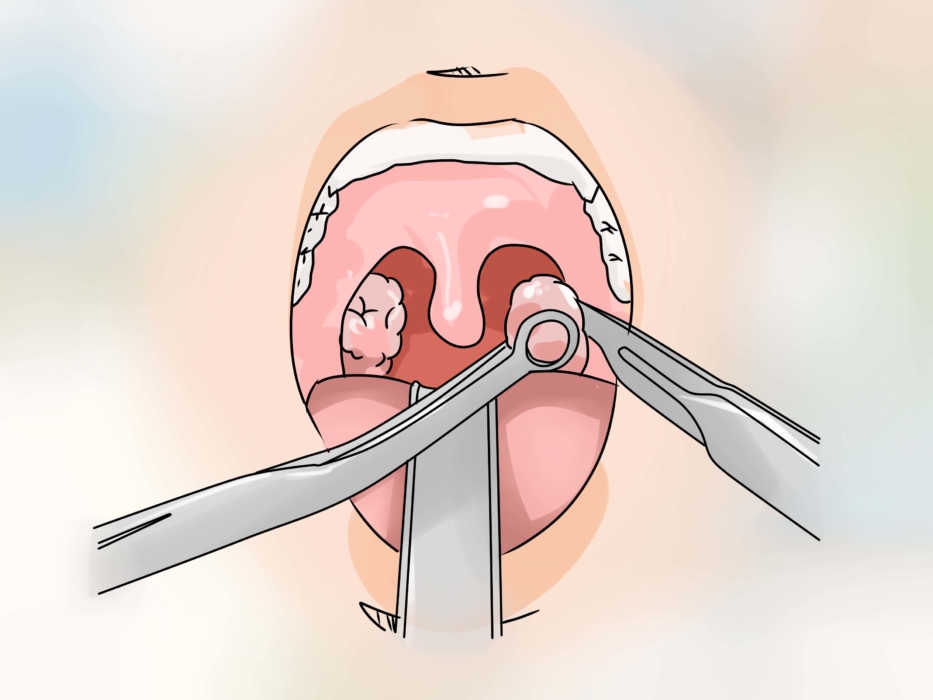
Sometimes an autopsy is required, which is necessary only in a hospital. Experts do not recommend waiting for the spontaneous expiration of pus. After opening, the inflamed cavity is thoroughly washed and drainage is established, the task of which is to ensure the exit of pus.
Possible complications
Treatment of the disease must begin with the onset of the very first symptoms, otherwise complications of angina can have the most unpleasant consequences:
- Bacterial inflammation of the meninges.
- After opening the abscess, a fistula may form.
- Otitis suppurative character.
- Laryngeal edema.
- Inflammation of the nasal cavity.
- Infections of nearby tissues and muscles.
- Bleeding from vessels located near the mucous membranes.
The result of angina can be blood poisoning, infectious damage to the heart muscle, osteomyelitis, polyarteritis.
Prevention
Any upper respiratory tract infection must be treated promptly. Try in every possible way to strengthen the immune system. Follow basic oral hygiene practices.
To get rid of the foci of inflammation, try to treat all chronic diseases and infections. And also in time to heal the teeth affected by caries. For sore throats, treat your sore throat regularly.