One of the forms of dermatological pathologies, also called urticaria, is considered acute urticaria. In general, the term “urticaria” is combined and combines several varieties of this disease. However, the acute form is considered the most serious and fast-flowing.
Material Content:
Description of acute urticaria
In recent years, medical complaints of patients with urticaria or urticaria rash have become more frequent in medical practice. It is characteristic that this disease is observed in almost 25% of the population. 5% of children of preschool and school age suffer from the symptoms of this pathology.
Acute urticaria in children is monitored more often than in adults: in children under 2 years of age, this form is diagnosed in 90% of cases. As a patient grows up, the disease often flows into a chronic form.
Note! It is believed that children under 6 months of age do not suffer from urticaria. However, in pediatrics, the admission of patients in the first months of life with symptoms of urticaria was monitored. All these cases were combined by a curious fact - the pathology was provoked exclusively by food allergens.
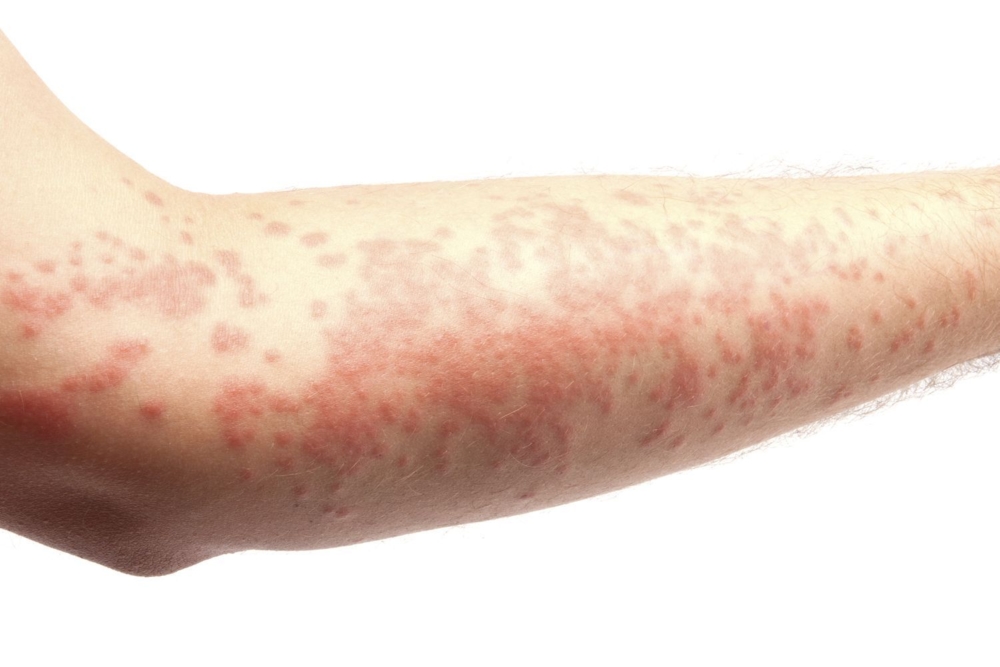
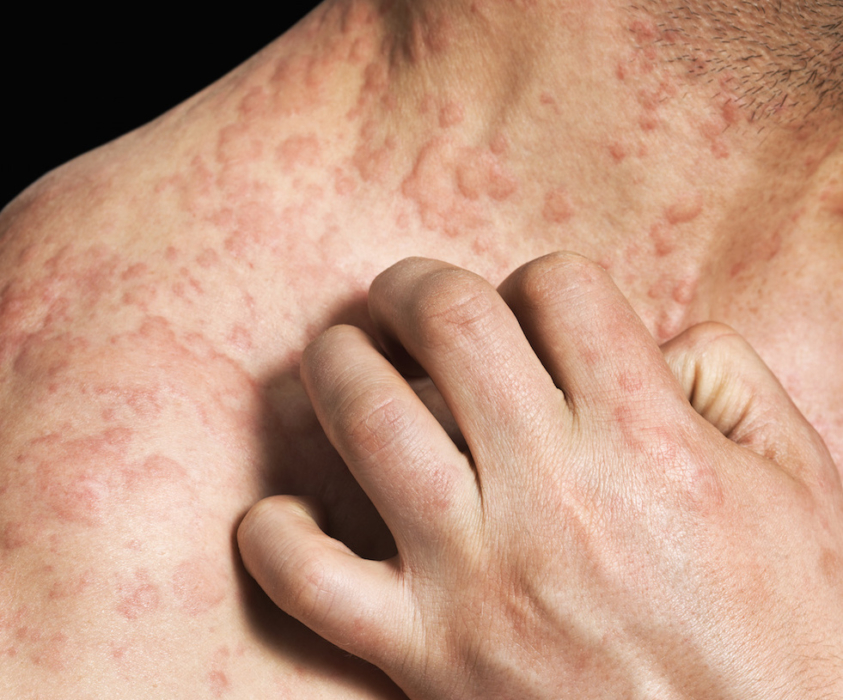
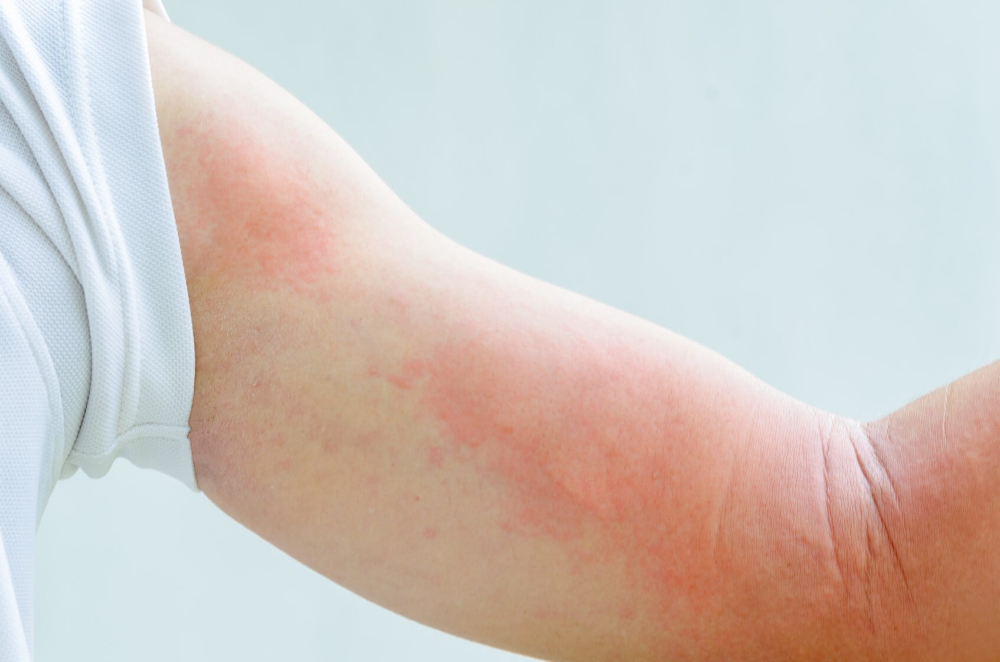
The main manifestation of urticaria is considered to be the instant occurrence of blisters (during the day). This symptom can also quickly disappear.
Most often, people prone to atrophic diseases are affected.
Causes in children and adults
The main causes of acute urticaria in children include:
- Food allergies. In this case, allergen products are citrus fruits, wheat, seafood, milk, eggs, honey, food additives.
- Medications: penicillin antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and anticonvulsants, B vitamins.
- Viral infections provoked by the causative agents of herpes, hepatitis.
- Bacteria: mycoplasmas, chlamydia, etc.
- Parasites: helminths, protozoa
- The poison of some insects - bees, wasps.
Also, the cause of the development of urticaria can be household allergens or pollen from plants.
Symptoms and manifestations
How to determine that the child suffered from acute urticaria? It is enough to observe the rash that appears on the surface of the skin. If the vesicles disappeared as suddenly as they appeared, this is most likely an acute form of the disease. This kind of urticaria can last at most 6 weeks. If after this time the alarming symptoms have not disappeared, the disease becomes chronic.
The main symptom by which urticaria can be recognized is an allergic skin rash accompanied by itching. Rashes are represented by white or pale pinkish blisters surrounded by reddened skin. The size of the rash can be small and large, merge into a single red spot.
Additional signs of urticaria are:
- hyperthermia (up to 39 ° C);
- stomach ache;
- gastrointestinal tract disorders;
- headache;
- hemorrhagic syndrome
On a note! In almost half of cases, acute urticaria is combined with Quincke's edema. In especially severe cases, damage to the membranes of the brain or heart muscle can be monitored.
Diagnosis of the disease
Urticaria should be differentiated from scabies and eczema due to the similarity of the clinical manifestations of these two pathologies.
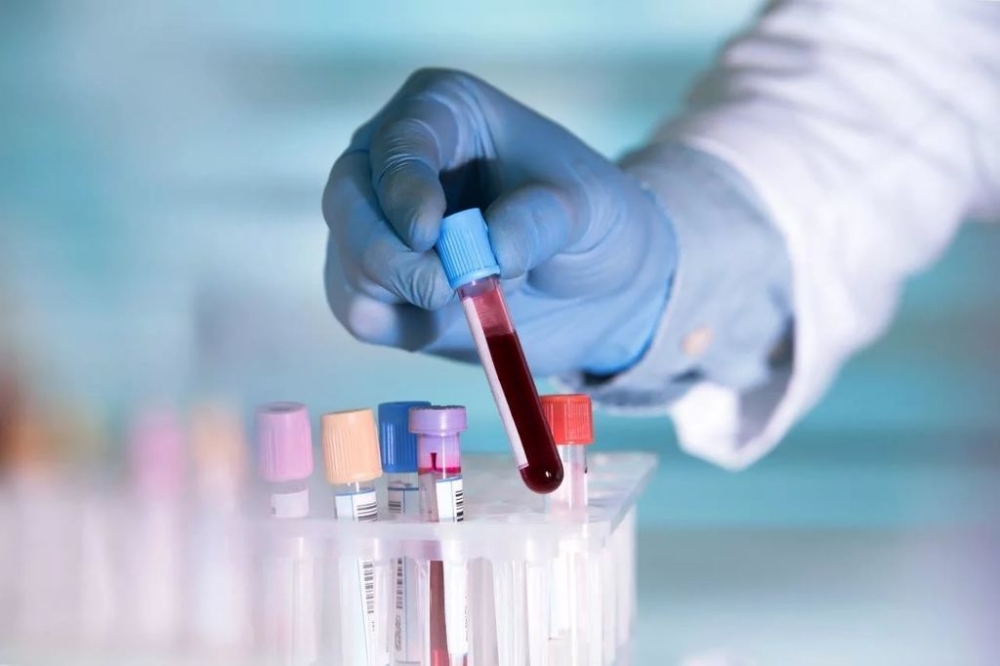
The main methods for diagnosing the disease are:
- Inspection of the patient by a specialist. A characteristic rash is the main symptom of urticaria.
- Allergological tests. They help to identify a type of allergen that provoked a skin disease.
Sometimes urticaria can act as a secondary disease against the background of the main pathologies (kidneys and gastrointestinal tract, etc.). In such cases, the diagnosis should be more detailed and include:
- blood chemistry;
- general analysis of blood, urine;
- blood test for syphilis, hepatitis;
- screening for parasites.
Additional methods for diagnosing secondary urticaria include ultrasound of the internal organs, an electrocardiogram, and an x-ray.
Treatment methods
The basis for the treatment of acute urticaria lies in the cessation of contact with the allergen. Urticaria, provoked by an acute food allergy, requires urgent gastric lavage. In addition, enterosorbents are recommended for the patient to finally remove traces of the allergen from the body (Filtrum, activated carbon, Enterosgel). If the disease was triggered by an insect bite, you need to immediately remove the poison from the body and apply cold for 15 minutes.
The next step is the introduction of antihistamines or glucocorticosteroids. Most often, for this purpose, first-generation anti-allergic drugs (Suprastin, Fenkarol, Fenistil) are used, taken from the age dosage.
Taking antihistamines continues after stopping the manifestation of allergies. After eliminating the symptoms of acute urticaria, you should definitely follow a diet for the next 2-3 weeks.
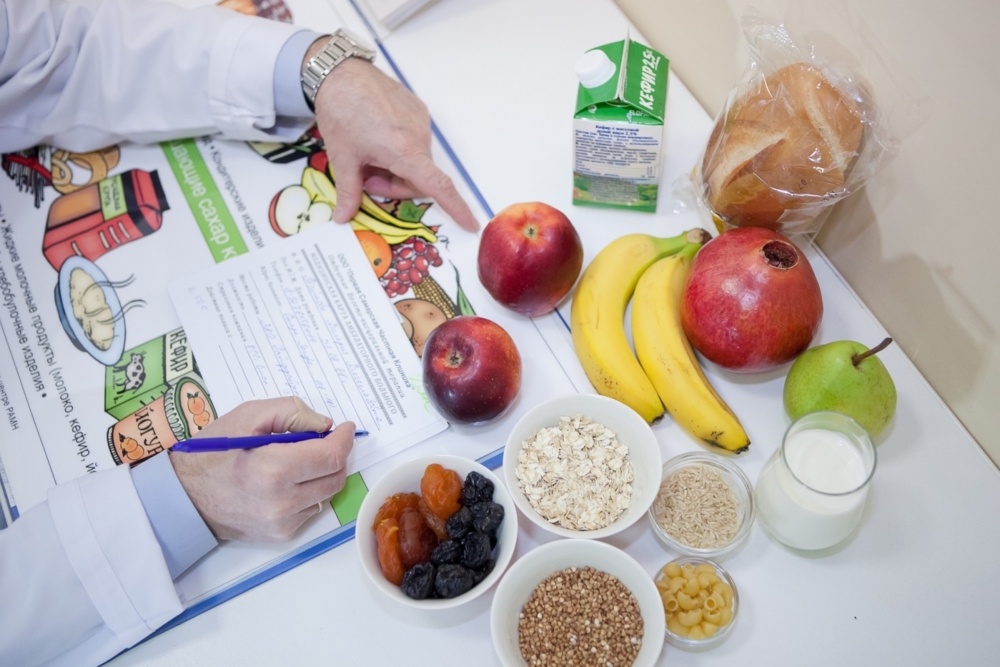
Dietary Tips
A hypoallergenic diet for urticaria is indicated for patients if an allergic rash was triggered by a reaction to food. In such cases, all foods suitable for the definition of allergens should be excluded from the diet. Even if it is not known what exactly the urticaria was triggered by, it is worth to be safe and limit the consumption of all suspicious products.
So, patients suffering from an acute rash are prohibited:
- citrus;
- red fruits and berries;
- seafood and fish;
- nuts
- eggs
- spicy vegetables (radish, horseradish, radish);
- chocolate, coffee;
- honey, sugar, jam, sweet pastries (all sweets in principle, especially industrial);
- mayonnaise, ketchup;
- juices;
- mushrooms;
- cheese;
- alcohol.
You should also for some time abandon fried, fatty foods, foods containing preservatives, spices and flavorings in the composition.
The products that are allowed in the process of following a hypoallergenic diet include:
- meat (boiled beef, turkey, chicken);
- soups on vegetable broth;
- vegetable oil;
- cereals (rice, oatmeal, buckwheat);
- dairy products;
- vegetables and fruits (except prohibited);
- dried fruit compote, tea;
- white bread (dried).
The doctor must tell the patient the exact time to follow such a diet. If the bubbles formed on the skin gradually pass, you can add fruits, vegetables, low-fat fish and more to the menu.
Forecast and Prevention
There are frequent cases when manifestations of acute urticaria are monitored in patients once in a lifetime. However, such luck is not inherent in everyone, and allergies can transform into a chronic form. In this case, spontaneous remissions account for almost half of all cases of urticaria.
Manifestations of skin rash are an unpleasant but not fatal symptom. Anaphylactic reactions accompanying the acute form of urticaria present a much greater danger. Swelling of the larynx and mucous membranes can lead to the development of irreversible processes that threaten not only the health but also the life of the patient.
Prevention of acute urticaria in young patients susceptible to this disease is as follows:
- dieting;
- normalization of the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract;
- excluding contact with allergens.
Urticaria is a type of dermatitis accompanied by the formation of a skin rash. The acute form of the disease affects children infrequently, but it can harm the health of the child. The main danger of urtikaria lies in its insidious companion - Quincke's edema, often leading to the tragic end of pathology.