Determining the creatinine norm in the blood is considered an important laboratory method for diagnosing the condition of the kidneys. A healthy excretory system almost completely removes this compound from the body. The occurrence of the pathological process provokes its delay, causing deviations of the indicators.
Material Content:
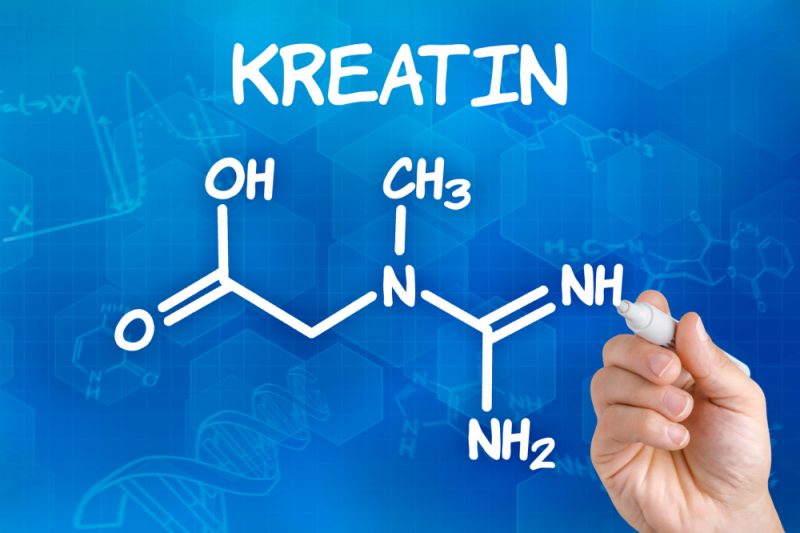
What is creatinine?
Creatinine is the final chemical element that is formed due to the complex biochemistry of nitrogen metabolism in muscle tissues. The production of this element occurs in liver cells from creatine, which is delivered to the muscle myocytes, where as a result of complex biosynthesis it is converted to creatine phosphate.
Further, this compound is decomposed into creatinine and phosphate, followed by the release of energy for muscle contractions. Subsequently, the element is transported to the kidneys and almost all is excreted in the urine. The remaining minor part is fixed at the corresponding value and is considered the best option in a blood test.
The norm in men, women and children
The optimal levels of creatinine in the blood can be called a variable, they depend on a number of indicators, such as:
- age qualification - element norms fluctuate throughout a person’s life and depend on many factors. Blood creatinine in children from birth to age 18 will vary, and in an adult it is higher than in a small child;
- gender - the norm of creatinine in blood serum in men will be more than in women. This difference is due to differences in the physiology of the male and female body, their hormonal levels.In addition, energy consumption in the stronger sex is higher than in women;
- complexion - asthenic or athletic build with a certain amount of muscle mass also affects the level of creatinine;
- preferred food selection;
- the presence of 1 kidney.
Normally, creatinine in men will be slightly higher compared to women. This difference is due to the presence of a more significant amount of muscle mass. And in childhood it will be even lower.
As the boy grows up, the indicators of this organic compound approach the values corresponding to adult men, and their norm corresponds to the following parameters.
| Newborns | 35-95 μmol / L |
| Children up to a year | 15-33 |
| From year to 12 years | 30-65 |
| 13 to 18 years old | 50-110 |
| Men up to 50 years old | 83-115 |
| After 60 years | 70-105 |
Exceeding these parameters indicates abnormal processes in the excretory system. In patients with insufficiency in the form of a chronic course, the indicator of a chemical element in the blood can go beyond the upper limit of the norm. Such a malfunction in the normal excretion of this substance indicates the progression of the disease.
The blood creatinine rate in women will be slightly lower compared to men. This is due to the presence of less muscle mass. The balance of this organic compound is played by sports, various diets, and the woman's age. Digital data on the creatinine norm in the analysis of blood in females correspond to the following parameters.
| Up to a year | 55-99 μmol / L |
| Up to 5 years | 31-52 |
| 5 to 12 years old | 34-60 |
| 12 to 16 years old | 48-70 |
| From 16 to 20 years | 51-81 |
| After 20 years | 50-97 |
| After 50 years | 55-88 |
| After 60 years | 60-89 |
These optimal blood creatinine values are average. When determining these parameters, various factors are taken into account that can reduce or increase it. Data assessment is carried out taking into account the characteristics of the body and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Diagnostic measures
Laboratory tests for creatinine in the blood are done under the following circumstances:
- to assess the filtration qualities of the kidneys;
- in the study of biochemical analysis of blood and kidney samples;
- to determine the onset of hemodialysis in renal patients.
To obtain the result of a laboratory analysis for creatinine, venous blood is examined, before which it is necessary to conduct preparation in compliance with certain rules.
The list includes:
- limitation of physical stress for 48 hours before laboratory analysis;
- exclusion from drinking alcohol, strong tea and coffee, protein foods 24 hours before blood donation;
- a ban on taking medication 2 days before the analysis;
- dinner ends at 6 p.m. on the eve of the visit to the laboratory;
- during rest, only mineral water without gas is allowed.
Blood for creatinine is given on an empty stomach. Diagnosis of renal failure is carried out using the Reberg test, which allows you to determine the glomerular filtration rate. It makes it possible to differentiate between functional and organic damage to the kidneys. For a more accurate diagnosis of renal pathology, the simultaneous delivery of blood and daily urine is practiced.
Important! Self-medication with a deviation from the optimal values of the creatinine content in the blood is not allowed, since improper actions can contribute to aggravation of the renal pathological process.
Reasons for the decline and increase
Deviation from the norm of creatinine is possible due to various factors. Not always these changes in indicators indicate a negative process in the kidneys. Sometimes the concentration of this element is higher or lower than the usual level with a certain lifestyle.
Professional athletes with significant muscle mass, ballet dancers who follow a diet, vegetarians who do not consume animal protein, may have physiological deviations from the norm of creatinine.With the exclusion of the factors provoking this process, it is quickly restored to optimal levels.
If the concentration of creatinine in the blood is increased, then this may indicate the presence of various negative processes in the body, such as:
- renal failure, in any form;
- cardiovascular pathology, contributing to the development of hypoxia in the excretory system, which leads to a decrease in its functional activity;
- volumetric processes of a malignant nature;
- thyroid disease with a violation of its function;
- diabetes;
- traumatic muscle damage of a different nature;
- extraction of one kidney;
- dehydration of the body, resulting in a thickening of the blood.
The pathology that provoked an increased content of creatinine in the blood must be diagnosed and treated, since the lack of therapeutic measures can aggravate the course of the disease.
Sometimes laboratory tests show creatinine below normal.
This condition also has its reasons, which are:
- pregnancy within 1-2 trimesters;
- anemia;
- rigid diets;
- starvation;
- muscle atrophy on the background of a stroke;
- leukemia;
- a sharp decrease in muscle mass until the development of cachexia, which can be observed with cancer of the stomach or anorexia.
The decrease in value is accompanied by the development of asthenia, manifested in weakness, periodic headaches, dizziness, and reduced working capacity. To relieve pathological symptoms and improve the well-being of the patient with both high and low rates, certain measures must be taken.
How to normalize creatinine
If the cause of the change in the normal value of creatinine in the blood is determined, its correction is required.
In the condition associated with functional abnormalities, the following measures are recommended:
- nutrition control, that is, a balanced intake of protein foods with the exception of salt;
- compliance with the water regime;
- correction of physical activity.
A slight inconsistency with the norm can be corrected with traditional medicine in the form of herbal drinks or rice broth. But the use of these funds is possible only after the recommendation of a doctor.
When identifying the presence of a pathological process that provoked a change in creatinine parameters, drug treatment is used, which includes the following drugs:
- Ketosteril;
- Chitosan;
- Lespeflan.
High blood creatinine values are an indication for hemodialysis in decompensated renal failure or severe intoxication of the body. Tracking these important parameters of the compound allows you to monitor the treatment and condition of the urinary system of the body.