Higher functions of nervous activity are contained in a relatively new area of the brain. The name of this structure in Latin means "new bark" - the neocortex. Consider its structure and role in human life.
Material Content:
What is a neocortex in humans
This area of the brain is also called isocortex. The prefix "isos" - "equal" - means the same thickness of this cortex, formed by six neural layers. The total length of the neocortex is much larger than the area it occupies. Therefore, it forms numerous convolutions and furrows. In numerical terms the size of the membrane covering one hemisphere is 220,000 square meters. mm Most of the bark is in the concave part.
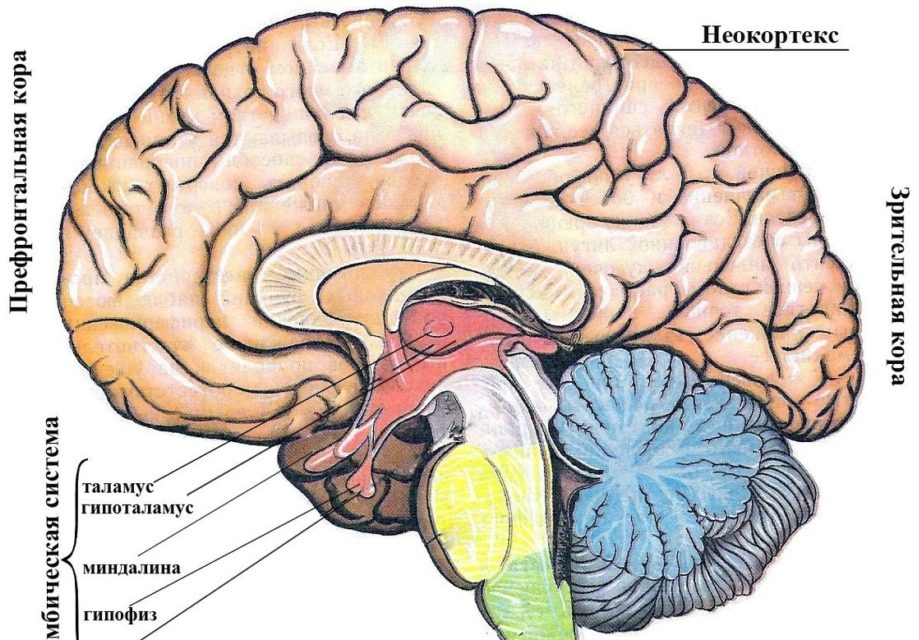
Structure and function
The new cortex includes two types of neurons:
- insertion - 20% of the total;
- pyramidal - 80% of the total.
This structure consists of layers of neurons that extend horizontally. The type of relationship between them varies. Connecting vertically, they form cortex columns. Outwardly, the cortex resembles an intricate labyrinth consisting of many grooves and convolutions. The largest furrows divide it into lobes. Each lobar part performs the specific functions of the neocortex for motion control or recognition of signals from the senses.
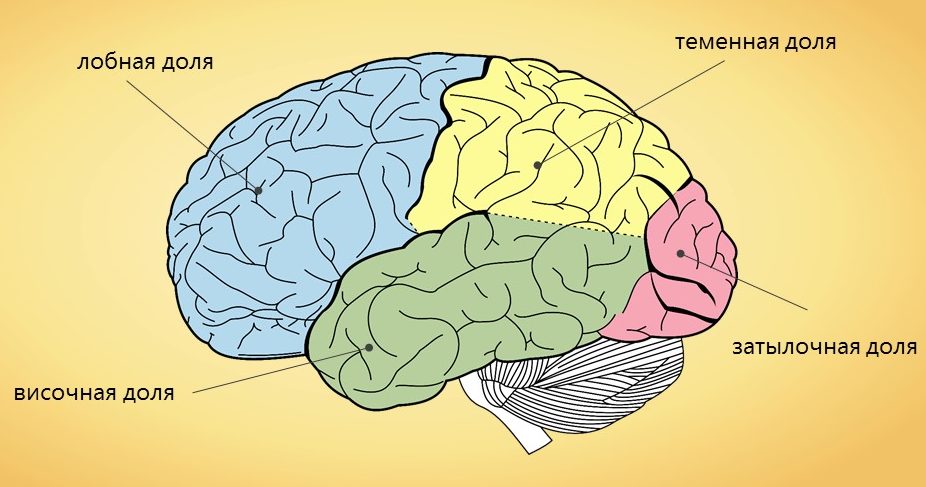
- The frontal lobe "specializes" in controlled movements.
- The parietal lobe reads information about sensory perception (pain, touch).
- The temporal lobe is responsible for the signals received from the hearing organs.
- In the occipital lobe are the visual centers.
However, for all these processes, the so-called primary cortex is responsible, which makes up about 5% of the entire neocortex. The remaining area of the cortex plays a secondary role, summarizing the data. It is called the associative or secondary part. For example, the associative centers of the occipital lobe collect disparate visual information into one complete image. Separate fractions summarize information received from several zones of the association, and in fact are a tertiary bark. The integration of data at this level served as the beginning of such higher nervous activity as speech. Its centers contain the temporal and frontal lobes in the left hemisphere.
What is the new cerebral cortex responsible for?
This area is responsible for sensory perception and thinking. In humans, speech is added to higher nervous activity. Also, neural connections formed in the new cortex are associated with the development of fine motor skills and voluntary movements.
The frontal lobe plays a special role in the following areas of mental activity:
- planning;
- logics;
- creative approach to solving problems;
- recognition of subtle irony and sarcasm;
- perception of other people's emotions;
- attention retention;
- suppression of involuntary impulses.
It is noteworthy that damage to this part of the brain does not significantly affect the intelligence and mental abilities of a person. But his behavior is undergoing noticeable changes. Thus, violation of the lower part of the frontal cortex leads to unreasonable cordiality, a lack of criticality to one’s own actions, sloppiness, loss of a sense of humor and a strange inappropriate laugh. The patient may exhibit increased activity that does not have a specific focus.
 An interesting fact: the appointment of some fields of the frontal lobes has not been identified. They do not respond to electrical impulses. And their absence does not affect anything. This is especially true for the right hemisphere. But the bilateral removal of a significant area of these fields already causes noticeable mental disorders.
An interesting fact: the appointment of some fields of the frontal lobes has not been identified. They do not respond to electrical impulses. And their absence does not affect anything. This is especially true for the right hemisphere. But the bilateral removal of a significant area of these fields already causes noticeable mental disorders.
The centers of perception of sensory information that form efferent impulses are localized mainly in the cortex. Whereas the associative zones that are associated with higher nervous activity interact and work as a single mechanism.
How Neocortex Is Interconnected With Sexual Love
The connection between the new cortex and sexual desire is characterized by a term such as "neocortical inhibition." This process means the inverse relationship of the emotional part of the brain (limbic system) and the neocortex. The higher the intelligence and the more information coming from the senses, the less the influence of natural instincts.
This interdependence leads to the need to consciously include the needs originally inherent in nature. Biological aspects fade into the background, giving way to mental functions.
 Problems with the reproductive system in women can be associated with the phenomenon of neocortical inhibition. In this case, there is a subconscious blockage of the very possibility of conception during intercourse.
Problems with the reproductive system in women can be associated with the phenomenon of neocortical inhibition. In this case, there is a subconscious blockage of the very possibility of conception during intercourse.
Interaction with the limbic system
The new cortex is closely connected with the limbic structure - the emotional center of the brain. This allows people to maintain qualities such as compassion, selflessness, selflessness, as well as the ability to love and appreciate the beautiful. In other words, thanks to this connection, a person will never turn into a "insensitive machine" for thought processes and calculations.
In addition, the emotional perception of various life events helps to better navigate when making decisions in the future. The rational brain works only with dry facts and figures. But only the centers of the limbic system are able to turn on intuition or the “inner voice”, based on experienced experiences, memories of which are clearly recorded in these structures of the brain.
The development of a new cortex in humans
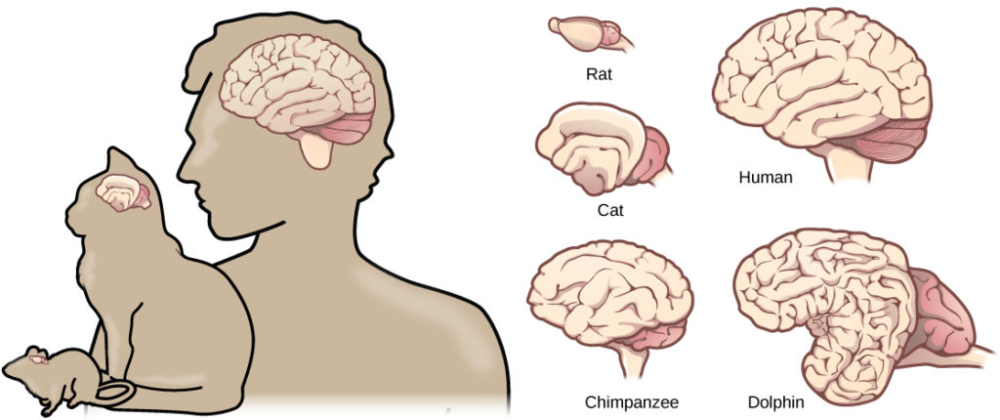
About 100 millionyears ago, the mammalian brain made a sharp leap in development, marked by the appearance of a new superstructure over the existing cortical base (cortex). During this evolution, animals gained indisputable advantages over previous species (reptiles).
The size of neocortex of different animals is significantly different. To evaluate it, an encephalization coefficient was introduced. This indicator reflects the level of intelligence and is equal to the difference obtained by subtracting the mass of the brain from the total body mass. For clarity, you can take the following data:
- the average coefficient of an adult is 6.9;
- the average white-fronted capuchin is 4.9;
- the value of intelligence of bottlenose dolphin is 5.3.
 A recent scientific study involving 28 species of mammals involving 143 people from different age groups established an obvious correlation between the development of neocortex in humans and more than 400 gene families. The genetic categories considered included genes that participated in the following:
A recent scientific study involving 28 species of mammals involving 143 people from different age groups established an obvious correlation between the development of neocortex in humans and more than 400 gene families. The genetic categories considered included genes that participated in the following:
- intercellular signaling;
- chemotaxis;
- creating an immune response;
- negative regulation of endopeptidase activity, etc.
All the categories mentioned before did not compare with the formation of the neocortex. According to the scientific community, the results, in addition to the general contribution to the study of the development of the new cortex, will help in understanding the structure and mechanisms of higher mental functions and related pathologies.
Neocortex is the most amazing area of the brain. Her study is ongoing. Neurobiologists have yet to find answers to many questions related to the features of its functioning and origin.