Some neurological diseases are difficult not only to treatment, but also to diagnosis. To determine the symptoms of the disease and find a way to eliminate muscle weakness, doctors have to carefully analyze the symptoms and causes of myasthenia gravis.
Material Content:
What is myasthenia gravis
The feeling of fatigue that occurs after physical exertion is familiar to many and is perceived quite naturally. But when the weakness becomes constant and does not decrease even after a night's rest, anxiety begins to overcome the patient.
And not in vain, since muscle fatigue is a characteristic sign of myasthenia gravis. And the main symptom of the disease is considered abnormal muscle weakness with a tendency to slow progress.
How does myasthenia gravis occur and what is it, it is important to understand on time. This is the best way to avoid provoking factors and prevent the development of severe pathological processes. And even in this case, the disease recedes in only 80% of patients, because the success of therapy depends not only on the professional qualifications of the doctor, but also on the patient's conscious attitude to his health.
In Latin, the name of the disease sounds like "myasthenia gravis," which means "muscle weakness." The first description of the disease (an autoimmune neuromuscular disease) dates back to the 17th century. Since then, giant steps have been taken in studying the nature of muscle dysfunction, but scientists have not been able to determine the exact causes of the process.
One of the known prerequisites for the development of pathology is dysfunction of the immune system, because myasthenia gravis belongs to the category of autoimmune diseases.
According to statistics, in recent years, the number of people suffering from myasthenia gravis has increased, and women aged 20 to 40 years predominate on this list.
Reasons and mechanism of development
The development of myasthenia occurs against the background of a violation of the immune system, which suddenly begins to perceive the body's tissues as foreign. It is believed that this mechanism is triggered by genes that, until a certain point, were in a sleeping state.
The reason for the activation of sleeping genes can be any stressful situation in the body:
- viral infections;
- nervous shocks;
- gene mutations that upset the balance of the immune system;
- pregnancy, childbirth, cesarean section;
- hormonal changes;
- a sharp change in climate when moving to another country;
- taking anticholinesterase drugs.
The mechanism of the development of the disease is associated with complete or partial blocking of the muscles and their innervating compounds. Antibodies produced by the immune system inhibit the functioning of the nerve receptors of acetylcholine, which provide neural connections.
As a result of the aggression of immunoglobulins, the following changes occur:
- the number of acetylcholine receptors decreases;
- the quality of information transfer in nerve cells decreases;
- the postsynaptic membrane is destroyed, which is responsible for the sensitivity of cells and the amplification of nerve impulses;
- signaling to the neuromuscular tissue stops.
In addition, the progress of pathology causes changes in the biochemical processes of the neuromuscular fibers, which leads to dysfunction of the brain regions responsible for the production of immune cells and the functionality of the endocrine system.
Types of disease
Myasthenia gravis is congenital, acquired, and neonatal. In the first type, muscle damage is genetically determined, which is extremely rare.
Acquired myasthenia gravis is one of the most common ailments. This disease develops as a result of an immunity reaction in the form of the formation of immunoglobulins to the transmission of nerve impulses in muscle tissue. An additional provoking factor in the occurrence of myasthenia may be thymoma - a thymus tumor.
The development of the neonatal type is possible in infants to whom the disease has passed from a sick mother. Weak activity and inactivity of the fetus is noticeable with ultrasound of pregnant women. There are frequent cases when such children died a short time after birth.
Symptoms of myasthenia gravis
Three main forms of manifestation of myasthenia are distinguished - ophthalmic, bulbar and generalized. Each of these types of ailment is manifested by different symptoms and the nature of the lesions.
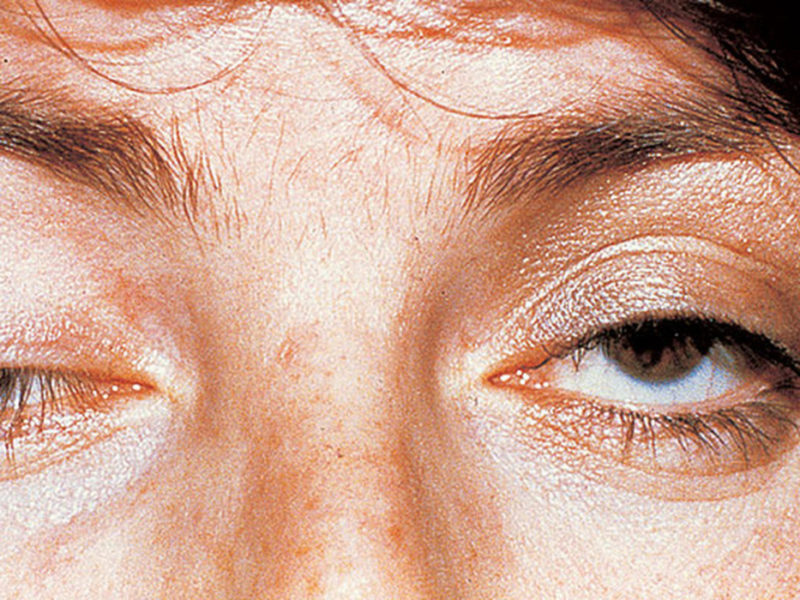
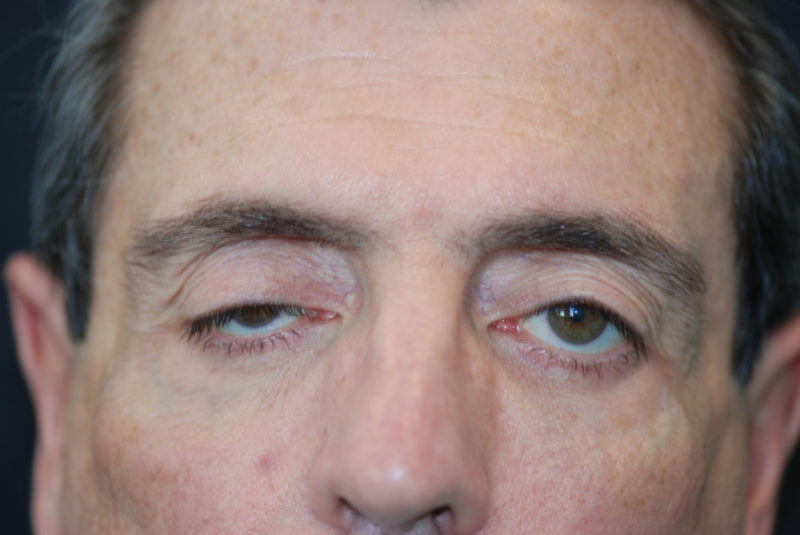
With the ocular form of myasthenia, weakening of the muscles responsible for the movement of the eyeball is observed. In this case, there is double vision and drooping of the eyelids.
Bulbar form
The bulbar form of the disease is accompanied by damage to the cranial nerves.
A characteristic sign is bulbar paralysis, having the following symptoms:
- violation of the innervation of the speech apparatus, problems with speech, diction;
- violation of the process of chewing and swallowing, a decrease in the motor potential of the muscles of the tongue and nasopharynx up to their atrophy;
- respiratory distress;
Patients with bulbar myasthenia cannot pronounce words distinctly, speech slows down, and the voice becomes nasal. In severe cases of the disease, the bulbar syndrome can cause non-life-related dysfunctions of the heart system.
Generalized form of myasthenia gravis
The generalized form of myasthenia gravis is the most complex in nature, since it captures several muscle groups at once. The onset of the pathology is subtle, the symptoms are dynamic, so the severity of manifestations during the day can vary several times or even be absent.
The development of a generalized form of myasthenia gravis occurs in stages. The first phase of the disease is characterized by the manifestation of symptoms of the ocular form - drooping eyelids and blurred vision, especially towards evening.
As the progress of the generalized form progresses, pathological changes capture new muscle groups. At this stage, symptoms characteristic of bulbar myasthenia appear: a change in timbre and sound power of the voice, difficulties with chewing food and swallowing even liquid foods.
Further development of the disease is characterized by an increase in weakness throughout the body. The muscles of the arms and legs lose their strength so much that it becomes difficult for the patient to make even the simplest movements - sit on or stand off the chair, climb the stairs, raise your arms, turn your head.
Myasthenic crisis
Like many autoimmune diseases, myasthenia gravis can occur not only in acute or chronic form, but also acquire an aggressive and even malignant character of development.
Neurologists regard cases of sudden and rapid deterioration of neural connections in muscle fibers as myasthenic crisis, a life-threatening condition in which severe respiratory and bulbar disorders occur.
According to the etiological type, myasthenic crisis is classified as bulbar, cholinergic and mixed.
Bulbar myasthenic crisis is manifested by pronounced bilateral dysfunction of the hyoid, vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves and respiratory muscles, as well as an increase in skeletal muscle weakness.
With a long absence of load, the muscles atrophy, and a decrease in the motor activity of the chest provokes the development of respiratory failure. Therefore, such patients are subject to immediate hospitalization in the intensive care unit and intensive therapeutic treatment, including lung ventilation.
Cholinergic crisis occurs with an overdose of anticholinesterase drugs. It is characterized by the generalization of processes with the capture of facial and chewing muscles, as well as muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle.
The symptomatology of the pathology is similar to the course of the bulbar crisis, but differs in the severity of vegetative disorders:
- increased salivation;
- intense secretion of bronchial mucus;
- sweating;
- dyspepsia
- vomiting
- rapid intestinal motility;
- loose stools;
- abdominal pains;
- hypotension.
And also a cholinergic crisis may be accompanied by narrowing of the pupils, convulsions and loss of consciousness of the patient.
Mixed myasthenic crisis belongs to the category of the most severe conditions, because it combines the clinical characteristics of bulbar and cholinergic crises.
Its malignant form is possible against the background of a thymus tumor.
Diagnostic measures
The diagnosis of myasthenia gravis is often difficult. Often, the patient who complains of a feeling of constant fatigue, therapists recommend more rest and taking vitamins.
But it is especially difficult to determine the development of myasthenia gravis in the elderly, as muscle weakness can be regarded as one of the symptoms of other age-related diseases.
Diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis is in the competence of neurologists and neurosurgeons. And even a specialist can not always immediately determine the type of disease, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, special tests and tests are prescribed to differentiate the pathology.
To state the exact cause of the disease with suspected myasthenia gravis, the following methods are used:
- clinical examination, history;
- proserin test - the effect of prozerin effectively relieves the symptoms of myasthenia gravis, thereby confirming the existing disease;
- study of blood composition for the presence of immunoglobulins;
- blood test to determine hormones of the endocrine gland;
- electromyography - the study of the functional potential of the neuromuscular system;
- computed tomography of the thymus gland.
A few decades ago, such diagnostic techniques were not yet available, therefore, in 40% of cases, myasthenia gravis ended in death. The possibilities of modern medicine exclude the development of complications, provided that therapy is started on time.
How to treat a disease
Improving the well-being of the patient with myasthenia gravis is achieved only against the background of correction of neuromuscular impulses. To restore disturbed processes, acetylcholine and drugs that suppress anticholinesterase are prescribed. And glucocorticoids are used to regulate the immunological disorder.
With an insufficient treatment effect, additional therapeutic measures are used - intravenous administration of a large dosage of methylprednisolone.
In addition, the appointment of potassium-sparing agents, including a diet with a high content of dried apricots, bananas and raisins, is considered an important stage in the treatment of myasthenia.
In the treatment of a generalized form of pathology, the use of surgical intervention in the thymus gland is permissible.
To restore the health of elderly patients, cytostatic therapy and blood purification are used.
Prevention of myasthenia gravis and its complications
Compliance with preventive measures is the basis for preventing the development of myasthenia gravis and possible relapses. Many disease-provoking factors are present in the lives of most people.
Forecast
Myasthenia gravis is considered a chronic ailment; therefore, the degree of prognosis is determined by the patient’s discipline. Subject to all medical recommendations and regular observation by a neurologist, patients achieve not only remission, but also recovery, while maintaining the possibility of a full life.