Among the drugs of the glucocorticoid type, methylprednisolone is indispensable. He has a large list of indications, which is associated with multidirectional action. The release in several dosage forms allows you to use it both for emergency care and for planned long-term treatment.
Material Content:
- 1 Release forms and composition
- 2 Pharmacological properties
- 3 What is methylprednisolone prescribed for?
- 4 Instructions for use and dosage
- 5 During pregnancy and breastfeeding
- 6 Interaction with other medicines
- 7 Compatibility of Methylprednisolone with Alcohol
- 8 Contraindications, side effects and overdose
- 9 Glucocorticosteroid analogues
Release forms and composition
Methylprednisolone is a steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It can be found under the trade name Metipred.
The medicine is available in several forms, depending on the purpose:
- Tablets containing 4 mg of methylprednisolone, as well as 16 g of additional components, are packed in 30 or 100 pieces in containers or glass vials;
- powder for injection into muscle and vein - 250 mg of methylprednisolone in the form of sodium succinate, as well as sodium hydroxide as an additional substance, are in 1 bottle of 4 ml
- ointment in the form of methylprednisolone aceponate with a concentration of 0.5% per tube, the size of which is 10 or 15 mg;
- powder for injection around the joint, into its cavity, bag or muscle - is produced in the form of methylprednisolone acetate, used to treat pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
The choice of dosage form is carried out depending on the disease, the desired dosage and the purpose of the drug. As an emergency, methylprednisolone is injected, and tablets are prescribed for planned treatment. For topical use, an ointment that acts when applied to the skin is suitable.
Pharmacological properties
Since methylprednisolone is a glucocorticoid drug, it has anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, anti-shock and immune suppressing effects. The tool affects the composition of ribosomal proteins through exposure to messenger RNA cells. As a result, its functions and reactions change.
The suppression of inflammation is due to an increase in the synthesis of lipocortins, which inhibit phospholipase A2 and reduce the production of specific mediators. The drug strengthens the membrane of lysosomal components, which prevents the release of enzymes from them. It also acts on capillaries, reducing their permeability, which prevents the accumulation of exudate.
The antiallergic effect is manifested due to the suppression of the release of specific mediators, as well as a decrease in the number of basophils in the blood. This also explains the immunosuppressive effect. There is a decrease in the concentration of T and B lymphocytes and mast cells. As a result, the formation of antibodies, which are responsible for the body's response to the penetration of foreign objects, is inhibited.
Methylprednisolone increases the need for muscle cells in proteins, which increases its production in the liver. And the amount of fat also increases, because it specifically accumulates in the head, neck and belt of the upper extremities. Due to the effect on metabolic processes, the amount of glucose in the blood rises and its synthesis is enhanced. Mineralization changes in bones, calcium is washed out.
Methylprednisolone salts form active metabolites in the blood. They are able to pass through the blood-brain and uterine-placental barriers, as well as into the mother’s milk. The half-life of the drug takes from 12 to 36 hours.
What is methylprednisolone prescribed for?
The instructions for use for the drug indicate a list of diagnoses in which treatment with this agent is possible.
These include:
- unconfirmed pulmonary tuberculosis;
- multiple myeloma;
- unspecified pathologies of connective tissue of a systemic nature;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- lung or bronchial cancer;
- infectious gastroenteritis or diarrhea (bacterial or dysenteric origin);
- leukemia of unspecified etiology;
- meningitis with tuberculosis;
- mycosis of unspecified etiology;
- red cell aplasia of an acquired nature of unspecified genesis;
- hemolytic anemia of autoimmune origin;
- trichinosis;
- non-Hodgkin type lymph, unspecified;
- agranulocytosis;
- increased concentration of calcium in the blood;
- aplastic anemia of constitutional origin;
- acute leukemia, not specified by cells;
- pulmonary sarcoidosis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura of idiopathic type;
- subacute thyroiditis;
- pathology of the adrenal glands of a specified nature;
- secondary thrombocytopenia;
- keratitis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- primary adrenal cortical insufficiency and unspecified;
- laryngeal edema;
- pemphigus;
- iridocyclitis, including unspecified;
- inflammation of the optic nerve;
- conjunctivitis of the acute course of the atopic species and unspecified etiology;
- myasthenia gravis and other pathologies of the neuromuscular junction;
- ulceration on the cornea;
- unclassified lipodystrophy;
- choreoretinal inflammation, including unspecified etiology;
- berryliosis;
- atopic, unspecified contact, exfoliative or seborrheic dermatitis;
- endophthalmitis;
- asthma;
- fever of rheumatic origin with or without heart damage;
- ulcerative colitis;
- psoriasis, including with joint damage;
- allergic and vasomotor rhinitis;
- bullous lesion of unspecified genesis;
- pneumonitis due to the action of a liquid or solid;
- simple lichen chronic course;
- increase the number of eosinophils in the lungs;
- colitis and gastroenteritis of non-infectious origin;
- lichen planus;
- chronic hepatitis;
- keloid type scar;
- unspecified bursopathy;
- ribbon-like form of nesting baldness;
- arthritis of juvenile, gouty, or rheumatoid nature;
- unspecified enthesopathy;
- idiopathic gout;
- granulomatosis of fatty tissue and skin;
- spondylitis of the ankylosing type;
- unspecified tendosynovitis and synovitis;
- systemic or discoid lupus erythematosus;
- polymyositis;
- rheumatism of unspecified genesis;
- tissue or organ transplantation;
- serum reactions;
- shock of unspecified anaphylactic, cardiogenic, traumatic or burn nature;
- surgical intervention;
- nausea and vomiting during treatment with cytostatics;
- unspecified arthrosis;
- pathology of the tendon and synovial membrane;
- complications after a blood transfusion, infusion, or drug injection;
- edema of unspecified origin;
- adrenal gland hyperplasia of congenital origin;
- collagenoses;
- unspecified allergic reactions;
- non-purulent thyroiditis;
- epicondylitis;
- negative reactions after treatment with certain drugs;
- Leffler's syndrome;
- osteoarthritis after an injury;
- erythroblastopenia;
- Crohn's disease;
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
- anaphylaxis;
- iritis;
- tendon cysts and aponeurosis.
Methylprednisolone has a large number of indications, because the dose of the drug is selected individually for each case and patient. In this case, not only the diagnosis is taken into account, but also the age, general condition and the need for emergency assistance. Since the medicine is potent, you should not take it without consulting a specialist.
Instructions for use and dosage
Methylprednisolone tablets are used as routine therapy, which can last a long time. They should be consumed immediately after or during meals. To facilitate passage through the digestive tract and faster dissolution, it is recommended to drink the drug with 2-3 sips of water.
The medicine is taken 1 time per day at a small dosage, from 2 to 4 doses - at high, the bulk of the substance consumed falls in the morning. In some cases, a double amount of the drug is prescribed, but 1 time in 2 days. This is due to the rhythm of hormonal secretion of the adrenal glands.
The average dosage for treatment with tablets is in the range of 4–48 mg per day. But with some pathologies, it increases to 200 mg (multiple sclerosis), 1000 mg (cerebral edema) and 7 mg / kg of weight (condition after transplantation of organs and tissues). In the absence of positive dynamics in the patient, the medication is canceled and an analog of methylprednisolone is selected.
Dosage for children is determined by the weight of the patient. In case of insufficiency of the adrenal glands, it is 0.18 mg per 1 kg of body weight, and in other cases, from 0.42 to 1.67 mg / kg for 3 times. If the treatment lasts a long time, the medicine is canceled gradually, reducing the amount by 1 mg / day for 1-2 weeks.
The solution for the administration of the drug in the form of injections is diluted with special water, which is in the package with the medicine. In urgent cases, the use of 30 mg per 1 kg of weight intravenously for 30 minutes of infusion is indicated. Methylprednisolone can be reused after 4-6 hours. The total duration of therapy should not exceed 2 days.
Attention! For planned treatment with injections, an application regimen is developed individually for each patient.
The dosage for children should not be less than 0.5 mg per 1 kg of weight per day.If the initial amount of the drug is not more than 250 mg, the minimum administration time is 5 minutes. If this norm is exceeded, the duration increases to half an hour.
Methylprednisolone ointment is applied topically to the affected area. The skin in these areas should not be damaged. Since with such use the drug does not penetrate the blood, dosage calculations are not carried out, and treatment is continued until the symptoms disappear completely.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
Glucocorticosteroids are able to penetrate the uteroplacental barrier. Therefore, their use during the period of bearing a child is possible only according to strict indications. After the birth of children whose mothers were treated during pregnancy, they are examined by ultrasound on the level of development of the adrenal glands.
Attention! Since the drug passes into breast milk, it is not recommended to use it during feeding.
If treatment cannot be postponed, the child should be transferred to food with an adapted milk mixture. After completing therapy, the mother can continue breastfeeding in a natural way. To maintain lactation, it is recommended to continue pumping throughout the treatment period.
Interaction with other medicines
Since the drug is considered highly active, it can affect other drugs.
Methylprednisolone interacts with several groups:
- inducers of liver enzymes, phenytoin, diphenhydramine, rifampicin, phenobarbital, mitotan and drugs that inhibit the work of adrenal cortical cells - reduce the severity of the therapeutic effect;
- cyclosporine - increases the risk of side effects, ensures the accumulation of substances in the blood;
- acetylsalicylic acid, somatotropin, drugs for diabetes, vaccines - loses its characteristic properties and is more quickly excreted from the body;
- anticoagulants - the risk of bleeding from the digestive tract increases;
- paracetamol - increases the toxic effect on the liver;
- antacids - reduce the degree of absorption of the drug;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - increase the risk of ulcers and bleeding from the digestive tract;
- cardiac glycosides - can cause arrhythmia;
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and amphotericin B - reduce the amount of potassium in the blood, can provoke osteoporosis and heart failure;
- Sodium-containing agents - increase the risk of edema and high blood pressure.
In some cases, dosage adjustment helps to avoid unpleasant consequences from the interaction of drugs. The treatment regimen for multicomponent therapy should be selected by the doctor. This will balance the effects of drugs on each other and reduce the risks of complications.
Compatibility of Methylprednisolone with Alcohol
The drug is not recommended to be taken simultaneously with alcoholic beverages. This will increase the toxic effect of ethanol on the patient's liver, which can cause damage or impaired function. In this case, the absorption of the active substance from the digestive tract is reduced, which reduces the effectiveness of therapy. The local use of methylprednisolone in the form of an ointment can be combined with moderate alcohol consumption, since there is no systemic effect.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
Methylprednisolone is a group of drugs that have a significant effect on all organ systems. Therefore, it can not be used for all groups of patients.
Among the contraindications for use include:
- allergy to one of the components of the drug;
- infectious diseases of chronic and acute course, including HIV and tuberculosis;
- prematurity;
- heart failure with congestion;
- pathology of the coagulation system;
- high blood pressure;
- joint prosthesis;
- fresh myocardial infarction;
- recent vaccination;
- serious pathologies of the kidneys or liver;
- lymphoma due to BCG vaccination;
- intestinal anastomosis;
- polio, excluding bulbar-encephalic type;
- esophagitis;
- pathology of the psyche;
- peptic ulcer of latent or acute course;
- hypothyroidism;
- gastritis;
- myasthenia gravis;
- diabetes;
- severe osteoporosis;
- glaucoma.
In the presence of one of the contraindications, the drug cannot be prescribed. Otherwise, the development of side effects is possible.
These include:
- Metabolic disorders - edema, hypernatremia, fluid retention, weight gain, hypokalemia with signs of alkalosis, pathological nitrogen balance.
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels - increased pressure, arrhythmias, congestion in the pulmonary circle, thrombophilia, a rare pulse.
- Endocrine diseases - atrophic changes in the cortical layer of the adrenal glands, the appearance of glucose in the urine, Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome, pathological menstruation, insufficiency of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, stunted growth, a drop in glucose tolerance, problems with potency, steroid type diabetes, hirsutism, increased need for drugs that lower blood glucose in patients with diabetes.
- Allergic manifestations - anaphylaxis, urticaria, bronchospasm.
- Disorders of the digestive tract - vomiting, the formation of a peptic ulcer and its perforation with the development of bleeding, nausea, inflammation of the pancreas, ulcerative esophagitis, flatulence.
- Musculoskeletal system pathologies - osteoporosis, muscle weakness, abnormal fractures, steroid type myopathy, weight loss, compression type spinal fractures, tendon ruptures, aseptic necrosis of the femoral and humerus epiphysis.
- Skin diseases - atrophy of the epidermis, dermis and fatty tissue, candidiasis, delayed restoration of integrity, striae, pyoderma, petechiae, steroid-type acne, ecchymosis, pigmentation disorder.
- Disorders in the nervous system - mental pathologies, headaches, exophthalmos, increased pressure inside the skull or eye, dizziness, pseudotumor of the brain, convulsive syndrome.
- Common pathologies - decreased immunity, sterile abscess, numbness and burning at the injection site, paresthesia, scars at the injection site.
The severity and frequency of adverse events associated with the duration of the course and the amount of the prescribed drug. If the latter is not observed, overdose symptoms develop.
These include:
- protein in the urine;
- increase in pressure;
- swelling;
- drop in glomerular filtration.
If signs of an overdose are detected, appropriate treatment is prescribed. Long-term use of a large amount of the drug may require hormone replacement therapy to restore adrenal function. Abruptly remove methylprednisolone is not recommended even with an overdose to avoid the effect of withdrawal.
Glucocorticosteroid analogues
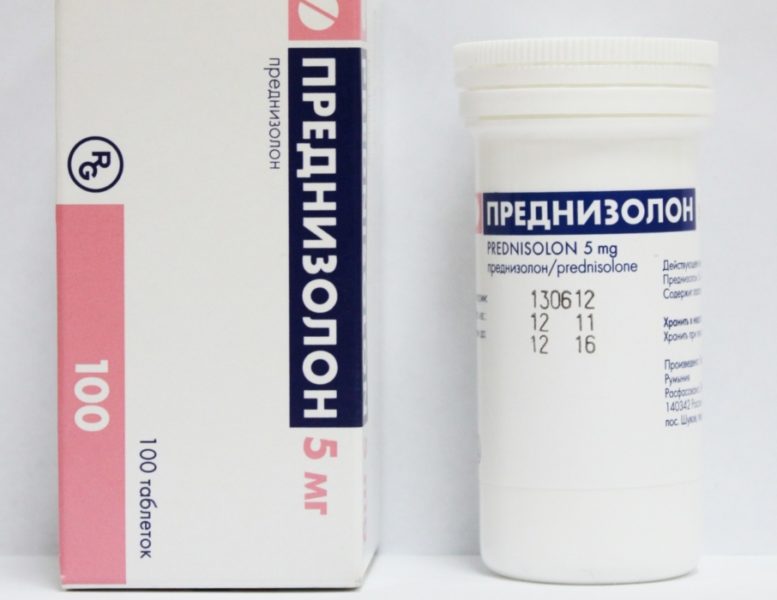
As an analogue to the drug, prednisone is used. It is available in 5 mg tablets in a package of 100 pieces. The medicine also exists in the form of a solution for injection, in 1 ml of which contains 30 mg of the active component. For topical use, there is 0.5% ointment and 0.5% drops for the eyes. Due to the difference in glucocorticoid concentration, it is not recommended to replace one with another without consulting a doctor, since this can provoke an overdose or the development of side effects.
Methylprednisolone has a large spectrum of action and high performance. But its dosage should be selected individually for each patient, the risk of side effects is so great. The medication is used both urgently and plannedly, which makes it universal, allowing, allowing to smoothly complete the therapy.