Meningitis is a serious disease, which in most cases develops acutely and requires urgent treatment. Procrastination in this case is fraught not only with formidable complications, but also with death. Everyone should know the symptoms of meningitis in adults so as not to miss the time and start treatment quickly.
Material Content:
Causes of Adult Meningitis
The meningitis or inflammation of the meninges in the vast majority of cases is an infectious disease. Its development occurs when pathogens appear in the tissues of the membranes and begin to rapidly multiply. It is they who become the cause of inflammation. And if most diseases are caused by one virus or bacterium, then meningitis is an exception. It can develop due to the ingress of viruses, bacteria, and even fungi into the tissues of the meninges.
Most often, the cause of the development of the disease is an infection that already exists in the body, the causative agents of which reach the brain with a blood stream. The human immunity is weakened, he could not cope with them, and the disease took a severe and life-threatening course.
Weakened immunity is the cause of meningitis of a fungal nature. The disease is more likely to affect children and the elderly.
The main viruses that cause viral meningitis are:
- enteroviruses;
- influenza and herpes viruses;
- Coxsackie viruses;
- paramyxoviruses - causative agents of measles and mumps (mumps);
- togaviruses are the causative agents of rubella.
If in the human body there is a foci of suppuration (infected burn, pneumonia, tonsillitis), the microorganisms that caused them can cause bacterial meningitis.
It:
- staphylococci;
- pneumococci;
- streptococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
But the most common cause of bacterial meningitis (up to 70% of all cases) is meningococcus. It was they who led to repeated epidemics of this disease. The carrier of meningococci is a person, infection occurs by airborne droplets.
But this bacterium, getting on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, does not always behave aggressively. Often, it does not manifest itself in any way and, in the absence of chronic diseases of the nose or throat, is safely eliminated without treatment after 2-3 weeks. Otherwise, meningococcus can cause a disease similar in symptoms to the common cold - meningococcal nasopharyngitis. If for some reason the body is weakened, meningococci are spread throughout the body and can cause inflammation of various localization. But the most common target is the brain.
Disease classification
Doctors classify meningitis by origin:
- primary - it occurs without an intermediate focus of infection;
- secondary is a consequence of an existing disease.
According to the pathogens that caused it:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- protozoal - caused by the simplest unicellular microorganisms - amoeba, toxoplasma, malarial plasmodium;
- fungal.
In severity, from mild to severe.
Meningitis can be serous and purulent. Doctors distinguish the disease by the rate of progression:
- lightning fast;
- sharp;
- subacute;
- chronic
Classification allows not only to recognize the disease on time, but also to approach its treatment differentially.
How to recognize an ailment by the first signs
The first signs of meningitis in each case may vary. But the most severe headache always comes to the fore, for the most part it is accompanied by a rapid rise in temperature to high numbers. At this stage, the disease can still be confused with the flu or another infection that occurs with similar symptoms. But literally after several hours, and sometimes almost immediately, repeated vomiting appears, which does not bring relief to the patient.
Tension and pain in the occipital muscles joins, forcing the patient to take a characteristic posture with legs bent at the knees tucked up to the stomach, his head thrown back and his back arched. The symptoms of Kernig and Brudzinsky indicate irritation of the meninges. Even the presence of some of these symptoms is a reason to call an ambulance.
The earlier treatment for meningitis is started, the better the prognosis and the lesser the risk of complications
How to recognize meningitis? This will help knowledge of the various symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms and clinical presentation
Symptoms of meningitis depend on its origin, the pathogen by which it is caused, and the rate of progression of the disease.
With meningitis of a viral nature
The incubation period of this disease is short - from 2-4 days. It begins with a high temperature, intoxication is strongly expressed. Other symptoms of viral meningitis also appear soon: stomach and throat hurts, cough, runny nose.
Then, and sometimes from the very beginning of the disease, meningeal syndrome joins them. It manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- very severe headache that does not go away;
- repeated vomiting, sometimes a fountain;
- a drowsy and lethargic patient can become restless and very agitated;
- skin sensitivity increases;
- harsh sounds and bright lights are difficult to tolerate.
Symptoms of irritation of the meninges and manifestations of increased intracranial pressure appear. The occipital muscles are tense and painful.When the temperature drops, it may rise again.
Manifestations of serous meningitis
Serous meningitis is usually a childhood illness. In adults, it is rare. The most common cause is viruses. In adults, it may have a tuberculous etiology. Fungal serous meningitis occurs in patients with AIDS. There are aseptic forms due to tumors or cysts of the brain.
The clinical picture of serous meningitis makes it possible to distinguish a rather long, from 3 to 18 days, incubation period, during which the patient feels unwell, the temperature is subfebrile. The acute phase of the disease begins with a rise in temperature to 40 degrees, a severe headache and intoxication. Symptoms of ARVI may be observed: rhinitis, dry cough. Meningeal syndrome is moderate, with a predominance of intracranial hypertension. Sometimes there is double vision, strabismus, difficulty swallowing. All this suggests damage to the cranial nerves. The fever may have a two-hump shape - after a drop in temperature, a new rise is observed in a few days.
Meningococcal meningitis
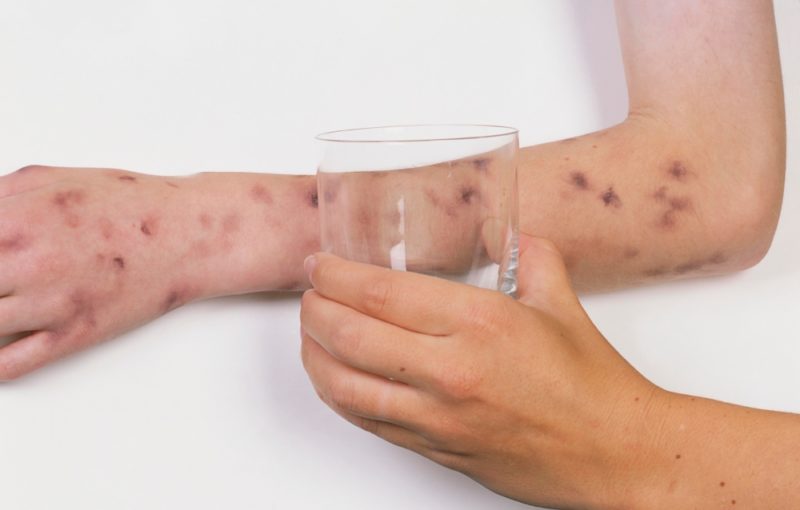
Meningococcal meningitis is also severe. Its main feature is a rash - erythematous or measles. It appears on the first day of illness and lasts no longer than 2 days, disappearing spontaneously.
As the disease develops, and often it proceeds rapidly, the endotoxin released during the death of meningococci leads to a violation of microcirculation in the vessels, increasing the permeability of their walls. The rash takes on the character of spider veins, and sometimes bruises that rise above the skin. Necrosis occurs in their center, and long-lasting non-healing ulcers form.
There is a danger of internal bleeding. There are all other symptoms of inflammation and irritation of the meninges. Severe intoxication leads to disruption of the heart and respiratory system. Convulsions join, the patient may fall into a coma.
If meningococcus enters the bloodstream, meningococcal sepsis occurs, which is called meningococcemia. This disease can be fatal in a few hours.
Purulent meningitis
It is rarely primary. Most often this is a consequence of the penetration of the pathogen into the cerebrospinal fluid from an already existing purulent focus. The first symptom of the disease is a sharp deterioration, accompanied by chills and fever. Meningeal syndrome is accompanied by disorders of the heart: bradycardia or tachycardia. The course of purulent meningitis can be both acute and chronic.
Diagnostics
In the first hours of the disease, meningitis is difficult to diagnose. But with the advent of meningeal syndrome, there is no doubt. The clinic of meningitis in this case is well defined. An additional and very informative diagnostic technique is a lumbar puncture, which is performed immediately after the patient enters the department.
Doctors evaluate leaky cerebrospinal fluid according to the following indicators:
- pressure;
- transparency and color;
- the absence or presence of a fibrin film;
- concentration of protein, glucose and chlorides.
Cytosis is carried out - the calculation of the number of blood cells, and a cytogram - an analysis of their qualitative composition.
Additionally, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- general and biochemical blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- bacteriological crops for the detection of the causative agent of the disease;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging, encephalo- and electromyography.
Adult Meningitis Treatment
An individual treatment plan is drawn up depending on the etiology of meningitis, the condition and age of the patient.
It is carried out comprehensively:
- antibacterial drugs are prescribed intramuscularly, and in severe cases, and into the spinal canal;
- with the viral nature of meningitis - antiviral agents;
- anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs;
- anticonvulsant and normalizing intracranial pressure drugs;
- immunomodulators.
Mandatory detoxification measures are carried out.
Complications and Predictions
Even with the current state of medicine, mortality from meningitis is high and amounts to about 10%. This figure strongly depends on the etiology of the disease and its severity, as well as the prognosis. If viral meningitis ends in recovery in the vast majority of cases, then with respect to purulent or tuberculous process, the prognosis is always ambiguous.
Complications after the disease occur in 30% of cases. Most often this is asthenic syndrome, which disappears after about a year.
But there may be more serious complications:
- impaired intelligence;
- paresis and paralysis;
- visual and hearing disorders up to blindness and deafness;
- hydrocephalus;
- increased convulsive readiness;
- ischemic stroke.
Prevention
Most forms of the disease are transmitted by airborne droplets, so the preventative measures are the same as with a common cold:
- always clean hands;
- well washed vegetables and fruits;
- restriction of contacts with patients;
- hygiene at home.
Strengthening immunity also plays a significant role in prevention. Vaccinations exist for some forms of the disease. And if the disease catches up, you need to treat it immediately.