One of the most formidable liver diseases is cirrhosis. Late detection and untimely treatment of this disease leads to serious consequences, so it is very important to know how the disease manifests itself and how to avoid it. Read about the symptoms, prevention and treatment of cirrhosis in this article.
Material Content:
What is liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease. It is a substitution of the connective or fibrous organ tissue. Fibrous nodes appear in the liver, pathological tissue grows throughout the organ parenchyma. Unfortunately, these changes are irreversible, therefore cirrhosis of the liver is incurable.
Stages of the disease, classification
The disease has several stages. Each of them has certain changes in the organ parenchyma.
There are 4 stages of the disease:
- Stage of compensation. In the liver, an inflammatory process begins, accompanied by necrosis of parts of its tissues. As a rule, changes are not accompanied by specific symptoms.
- Stage of subcompensation. At this stage, the inflammation progresses, there is a replacement of the functional connective tissue. The first symptoms of the disease appear, but the liver can still function normally. Further, the pathological tissue grows, the organ becomes denser and palpated. At this stage, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites) is possible.With cirrhosis with ascites, a significant protrusion of the abdomen on the right is characteristic.
- Stage of decompensation. At this stage, hepatic coma, pneumonia, blood poisoning, venous thrombosis, malignant tumors can develop. Possible causeless nosebleeds.
- Terminal stage. The size of the liver decreases several times, the spleen, on the contrary, increases. The brain is affected. The patient is in a coma. Most often, a fatal outcome occurs.
There are several classifications of cirrhosis of the liver, depending on the causes and characteristics of the course of the disease.
In the etiological systematics, the following types of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- viral;
- drug;
- toxic;
- congenital;
- stagnant (caused by such phenomena in the cardiovascular system);
- alimentary (often develops due to malnutrition);
- secondary biliary (develops due to prolonged blockage of the biliary tract).
When the cause of the disease has not been established, the concept of cryptogenic cirrhosis of the liver is used. Primary biliary cirrhosis is also distinguished. It has an autoimmune origin.
Based on the size of fibrous nodes and other morphological features, the following forms of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- small-knotted (the diameter of the formations is less than 3 mm), more common with alcoholism, blockage of the bile ducts, circulatory disorders;
- coarse-knotted (the size of the nodes is more than 3 mm);
- septal (characterized by the appearance of a kind of septum (septum) from the connective tissue);
- mixed (both large and small nodes are observed).
There is also the so-called Child-Pugh classification. According to this evaluation method, each class of the disease corresponds to a certain number of points, which are assigned taking into account certain parameters characterizing the course of the disease.
In accordance with this method of systematization, 3 classes of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- A - compensated cirrhosis. Patients with cirrhosis of this class have the most favorable prognosis. Their life expectancy is up to 20 years, survival after surgery is about 90%.
- In - subcompensated. Patients have a chance to live up to 10 years, survival rate after surgical measures - 70%.
- C - decompensated. The life expectancy of patients is 1-3 years, survivors after surgery - 18%.
This classification takes into account such indicators as the concentration of bilirubin and albumin in the blood, prothrombin time, the presence / absence and degree of ascites, brain damage.
Causes of development, symptoms of the disease
The leading cause of cirrhosis is alcoholism. In people who have been abusing alcohol for 5–10 years, cirrhosis is diagnosed in 35% of cases. More often it is found in men than in women. This is due to the greater prevalence of alcoholism among the stronger sex.
Other causes of pathology are:
- hepatitis B, C, D;
- long-term use of drugs that have a hepatotoxic effect (methotrexate, isoniazid and others);
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels, accompanied by stagnation of blood;
- autoimmune hepatitis (a condition in which immunity attacks healthy cells of the body, taking them for pathogens);
- genetic disorders (hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease);
- bacterial and parasitic diseases (brucellosis, opisthorchiasis, toxoplasmosis and others);
- narrowing of the bile ducts, stagnation of bile.
At the very beginning, the ailment is often asymptomatic. Its non-specific signs (minor digestive disorders, lethargy) are often attributed to malnutrition and chronic fatigue.
As the disease progresses, the following symptoms of liver cirrhosis join:
- soreness in the right side;
- a feeling of heaviness in the stomach (even after eating a small amount of food);
- itching of the skin;
- high body temperature;
- signs of disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (flatulence, impaired stool, etc.);
- nosebleeds;
- yellowness of the skin;
- ascites;
- specific changes in the shape of the fingers (“drumsticks”) and nails (“watch glasses”);
- vascular "stars";
- weight loss;
- redness of the palms;
- possibly swelling of the mammary glands in men.
Many of these symptoms are characteristic not only for cirrhosis, but also for some other liver diseases.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a doctor - gastroenterologist or hepatologist. The first stage of the examination is the survey and examination of the patient.
Further, laboratory and hardware research methods are used:
- general blood test (cirrhosis is characterized by a decrease in the number of leukocytes and platelets, a low level of hemoglobin);
- biochemical analysis of blood (revealed elevated levels of bilirubin, salts, high activity of liver enzymes, etc.);
- Ultrasound and computed tomography of the abdominal organs;
- MRI of the liver;
- Dopplerometric examination of the vessels of the liver.
The final diagnosis is made after a biopsy, which is necessary to assess changes at the cellular level, determine the cause of the disease and determine the treatment regimen.
Treatment of cirrhosis
Since cirrhosis is an incurable disease, therapy is necessary to improve the quality of life of the patient, increase its duration and prevent complications. An important component of therapy is a diet for cirrhosis. Based on the characteristics of the course of the disease, a special table is recommended for patients. The use of alcohol is strictly prohibited.
For treatment, medical and surgical methods are used. As an addition to the main therapy, folk remedies can be used. An important role is played by clinical nutrition. The diet should be balanced. In case of a high risk of renal failure, protein food should be limited, with ascites - salt.
The best medications
With cirrhosis, various combinations of medications can be used. In the first stage, drug therapy is not required. The patient is shown vitamins, diet and a healthy lifestyle. These measures can significantly slow down the progression of the disease.
At later stages, several main groups of drugs are used:
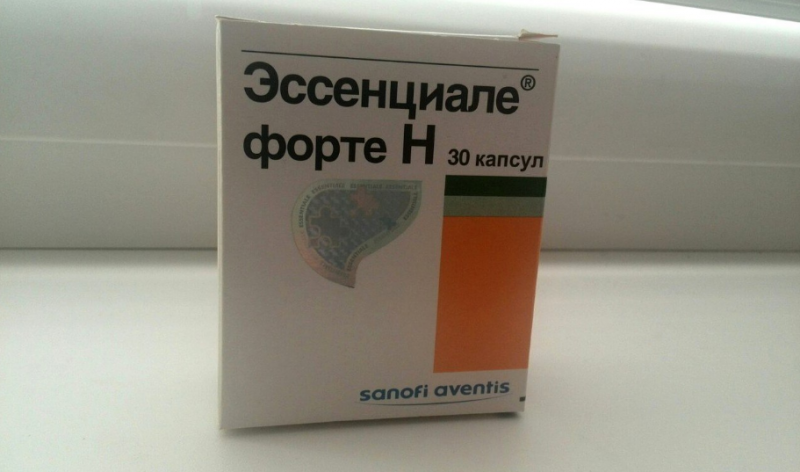
- hepatoprotectors (Essential Forte N, Essliver, hepatoprotectors of animal and plant origin);
- interferons (in case of viral cirrhosis);
- glucocorticosteroids (prednisone);
- detoxification;
- vitamins (preparations containing B, A, C, E vitamins, lipoic acid);
- diuretics (furosemide).
Many medicines used for cirrhosis have a complex effect. Below are the most effective and often prescribed drugs that provide several therapeutic effects at once.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid ("Ursosan"). Bile acid with the properties of hepatoprotector and immunomodulator. It has a choleretic effect, contributes to the destruction of cholesterol stones.
- Ornithine ("Hepa Merz"). Amino acid that has hepatoprotective and detoxification effects. Reduces the concentration of ammonia in the blood.
- Ademethionine ("Heptral"). Restores liver cells, has anti-fibrosing, detoxifying effect.
And also with cirrhosis, medications necessary for treating complications, relieving symptoms and eliminating the factors that triggered the disease (painkillers, enzymes and others) can be prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
With cirrhosis, as with many other liver disorders, physiotherapy is contraindicated. Such treatment does not have a positive effect on the disease, but exacerbates its course. The method in some cases can be prescribed for inactive forms of hepatitis.
Surgical intervention
With severe ascites against cirrhosis, the abdominal wall is punctured and the accumulated fluid is removed. This is a relatively safe and effective operation.
With portal hypertension syndrome (increased pressure in the portal vein system) against the background of cirrhosis, collateral vessels are bypassed. The operation consists in creating an alternative blood flow bypassing the affected areas of the vessels.
A cardinal method for eliminating cirrhosis is a transplant of a donor organ. The operation is performed for people with rapidly progressing disease, liver failure and extensive liver damage.
Folk remedies
As an addition to the main treatment, traditional medicine methods can be used. It is important to remember that cirrhosis is a dangerous disease, so you can use these drugs only with the permission of a doctor. Below are several methods of alternative medicine for the treatment of this pathology.
- Norman Walker Vegetable Juices. Naturopath from the United States, whose product is named, a well-known expert in the field of medicinal properties of vegetable juices. With cirrhosis, he proposed the following combinations: juice of carrots, cucumbers and beets are mixed in a proportion of 10: 3: 3; juice of carrots and spinach are combined in a proportion of 10: 6; 2 tablespoons of black radish are added to carrot juice. Any of the above mixtures is drunk in an amount of at least 600 ml per day for several approaches.
- Milk thistle meal. The powder is taken orally by half a teaspoon up to 5-6 times a day, washed down with water.
- Turmeric. For treatment, 5 g of crushed plants are added to a glass of warm water. Use half a glass twice a day before meals.
- Oats Two glasses of grains are poured with boiling water and left for 2 hours, then they are drunk like tea.
- Propolis tincture. The first 10 days in 10 ml of drinking water add 10 drops of liquid, drink once a day. Then every day they increase the number of drops by one until a maximum of 50 drops is reached. Then, the dosage is similarly reduced dropwise per day.
Treatment with folk remedies in combination with the main therapy contributes to a significant improvement in the patient's condition.
Consequences and forecast
The most serious consequence of cirrhosis is acute liver failure, which requires immediate medical attention. The chronic course of the disease without appropriate therapy leads to hepatic coma and death of the patient.
In addition, with cirrhosis of the liver, the following complications often occur:
- ascites;
- portal hypertension;
- renal failure;
- oncological diseases of the liver;
- complications due to the joined infection.
With the early detection of cirrhosis, compliance with all the doctor's prescriptions and elimination of the causes of the disease, the prognosis is relatively favorable. Alcoholic cirrhosis with the regular use of alcohol progresses rapidly and leads to dangerous complications. In ascites, the predicted survival is 3 to 5 years.
Preventative measures
Measures to prevent the occurrence of cirrhosis are quite simple:
- limited alcohol consumption;
- timely and effective treatment of liver diseases, including viral hepatitis;
- proper nutrition;
- moving lifestyle.
In addition, medication should be avoided without a doctor's prescription and exposure to toxic substances on the body.
Despite the fact that even the most effective drugs cannot completely cure cirrhosis, it is quite possible to slow its progression and prevent the development of formidable complications thanks to early diagnosis. Therefore, it is extremely important to contact specialists in a timely manner.