Cardiac pathology is the most common problem among patients of both adult and childhood. One of them is atrial fibrillation, the treatment of which requires constant monitoring of the activity of the heart muscle. Arrhythmia can develop under the influence of both external and internal factors.
Material Content:
The causes of the disease
With atrial fibrillation, there is a violation of the contractile activity of the heart muscle, that is, atrial fibrillation with increased heart rate up to 400 beats per minute.
Such a failure of the heart rhythm may be the result of the presence of cardiac or cardiac pathology:
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiosclerosis;
- heart defects of a congenital or rheumatic nature;
- myocarditis, that is, the inflammatory process of the lining of the heart muscle;
- arterial hypertension;
- severe heart failure.
- cardiomyopathy
Often, heart disease develops due to extracardiac causes, that is, caused by a pathological process in the internal organs:
- endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis);
- severe neuropsychic stress;
- intoxication with alcoholic beverages, cardiac glycosides;
- heart muscle surgery;
- diseases of viral etiology;
- organ diseases due to central nervous system disorders.
Arrhythmia of an idiopathic form is sometimes diagnosed, the nature of which cannot be determined.
Atrial fibrillation
According to the clinic of manifestations, a pathological violation of arrhythmia is divided into the following types:
- paroxysmal form - a characteristic feature of this paroxysm is its sudden onset. The duration of the attack can last up to 5-7 days. But most often its duration is no more than 24 hours. Such a violation of cardiac activity can stop on its own;
- persistent form - the duration of the attack can be more than 7 days, paroxysm is removed only with medications;
- chronic form - a characteristic feature of this type of pathology is its duration without the result of the action of medications.
The paroxysmal and persistent form of cardiac pathology, having first appeared, has the property of repeating itself in the future. A chronic or persistent form of atrial fibrillation can lead to a sharp increase in chronic circulatory failure.
Developing paroxysm differs in the number of ventricular contractions in the following form:
- bradysystolic type - a decrease in heart rate to 60 beats per minute;
- normosystolic - preservation of the pulse in the range from 60 to 90 beats per minute;
- tachysystolic - the number of heart contractions exceeds 90 beats per minute.
Violation of the rhythm of the heart muscle can manifest itself as extrasystole, a characteristic feature of which is its extraordinary contraction.
Symptoms and signs
The clinical symptoms of the pathology of cardiac arrhythmias are manifested depending on its shape, on the state of the heart muscle, as well as on the emotional mood of the patient.
The most common manifestations of cardiac pathology are:
- a strong heartbeat, accompanied by shortness of breath, interruptions and pain in the chest area on the left, aggravated by physical exertion. This symptomatology is characteristic of a tachysystolic form of arrhythmia, which is most severe for patients;
- sudden development and termination of an attack of a strong heartbeat with pulse beats up to 140-220 per minute. This manifestation of the pathology of rhythmic contractions of the heart is characteristic of paroxysmal tachycardia;
- high pulse rates may be manifested by weakness, dizziness, sweating, a fear of death, or fainting. In some cases, paroxysm is accompanied by polyuria, that is, the discharge of a large amount of light urine;
- very high pulse values can provoke the development of Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome, when, due to severe hypoxia of the brain, loss of consciousness occurs, accompanied by a convulsive syndrome;
- the appearance of a sensation of a push or fading in the left half of the chest, which is characteristic of extrasystole;
- the appearance of weakness, darkening in the eyes, dizziness, up to the development of a fainting state, are characteristic of a brady systolic type of cardiac pathology.
The restoration of the corresponding rhythm of the heart muscle almost immediately gives the disappearance of the clinical manifestations of the disease with the restoration of the normal state. If atrial fibrillation by its nature has a constant rhythm disturbance, patients after some time cease to notice it.
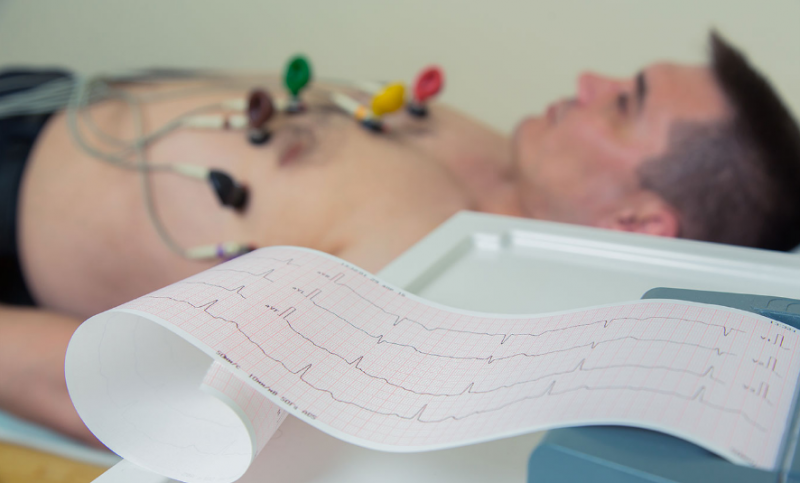
Diagnosis of heart rhythm disturbances
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is possible even with an objective examination of the patient, when rhythm disturbances, changes in filling and pulse voltage are detected. When listening to the heart muscle, irregular heart sounds and their volume are detected.
To clarify or confirm the diagnosis, the following instrumental studies are carried out:
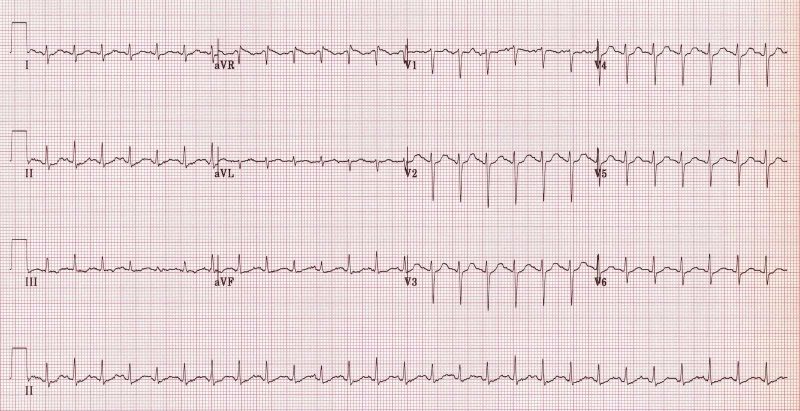
- ECG;
- daily ECG monitoring to determine the form of atrial fibrillation;
- echocardiography for an objective assessment of the state of the heart muscle;
- according to the MRI of the heart;
- transesophageal ECG according to indications, especially when planning implantation of a pacemaker.
A complete examination of the function of the heart muscle allows you to determine the type of atrial fibrillation and prescribe a good treatment.
Heart Disease Treatment Methods
Therapeutic measures for atrial fibrillation solve the following problems:
- restoration of rhythmic contractions of the body;
- support the normal activity of the heart muscle;
- prevention of repeated paroxysms;
- preventive therapy aimed at eliminating the formation of blood clots.
In most cases, the treatment of arrhythmia is carried out conservatively, that is, by prescribing medications. With severe manifestations of cardiac pathology and the absence of the effect of conservative therapy, surgical treatment is possible according to indications.
Drug treatment
To stop the manifestations of atrial fibrillation, conservative treatment with the following medications is carried out:
- to stop paroxysms - Novocainamide (orally or intravenously), Quinidine, Propafenone (inside) under the control of pressure and ECG;
- to reduce heart rate - Verapamil, Propanolol, Digoxin;
- to prevent the formation of blood clots - Warfarin;
- to prevent repeated paroxysms and stabilize the rhythmic contractions of the heart - Amiodarone, Propafenone;
If atrial fibrillation has a chronic form of the course, drug treatment with drugs involves their constant intake.
In this case, the following means are shown:
- adrenoblockers - Atenolol, Metoprolol;
- calcium antagonists - Verapamil, Diltiazem, Digoxin;
- for the prevention of blood clots - Warfarin under the control of the analysis of the blood coagulation system.
A prerequisite in the treatment of pathology is the therapy of the main pathological process that caused a violation of the heart rhythm.
In older patients, heart failure symptoms are much more common, including atrial fibrillation (AF). The treatment of atrial fibrillation in elderly patients requires a certain approach, since there is a restriction in the administration of certain medications due to various diseases of the internal organs.
In this case, the selection of antiarrhythmic drugs is carried out necessarily taking into account the age and individual characteristics of the body.
Important! The appearance of cardiac arrhythmias requires the obligatory consultation of a cardiologist to determine the form of atrial fibrillation and the appointment of quality therapy. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, since serious complications are possible that pose a threat to life.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment methods are used when conservative therapy does not give the expected result or atrial fibrillation becomes severe.
Surgery involves the following methods:
- pacemaker;
- implantation of a cardioverter - defibrillator;
- catheter radiofrequency ablation.
The surgical method of treating rhythm disturbances is determined by the doctor after a complete examination of the patient in a hospital setting. In most cases, surgery gives a good result in terms of significantly improving the patient's condition and improving his quality of life
Rehabilitation of patients after treatment
After restoring the rhythm of the heart muscle, the patient must undergo a rehabilitation course, which includes the following activities:
- decrease in physical activity;
- elimination of stressful situations;
- maintenance drug therapy;
- moderate physical activity.
Of great importance in the rehabilitation period belongs to proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
A prerequisite for recovery after treatment is a diet that recommends:
- dietary correction with increased consumption of potassium-rich foods (dried apricots, apricots, baked potatoes);
- decreased intake of salt, animal fats;
- low-fat varieties of dietary meat and fish, preferably marine, rich in omega-3 should predominate in the diet;
- the use of confectionery and sweets is minimized.
Compliance with all the doctor's recommendations will allow the patient to smoothly undergo rehabilitation and improve overall health.
Folk remedies
You can treat atrial fibrillation by supplementing with folk remedies that will help reduce or stop the symptoms of the disease, such as weakness, shortness of breath, periodic dizziness, heart pain. In addition, alternative recipes, as an aid, can be used to thin the blood.
The most popular and giving a positive effect are the following decoctions:
- from berries of hawthorn;
- from viburnum berries;
- from rosehip berries;
- infusion of calendula and mint flowers;
- infusion of hawthorn and horse chestnut in a ratio of 1: 1.
Infusions of herbal medicines are prepared in the proportion of 1 tablespoon of raw materials per glass of boiling water, followed by infusion for 2-4 hours, preferably in a thermos. Used natural remedies for a quarter cup 2-3 times a day.
Broths are prepared by boiling, in the same proportion of berries over low heat for 15 minutes. After cooling, the products are ready for use.
Traditional medicine is used only on the recommendation of a cardiologist in combination with the main therapy for rhythm disturbance.
Possible complications and prognosis
A cardiac pathology such as atrial fibrillation can cause serious complications. If it was caused by heart defects, severe myocardial infarction or widespread cardiosclerosis, rapid progression of heart failure of varying severity is possible.
Thromboembolism, which leads to a violation of cerebral circulation or the development of myocardial infarction, is of great danger. In this case, the prognosis for life is poor, since such complications often lead patients to disability.
If the myocardial ventricles are in satisfactory condition, and there is no pronounced cardiac pathology, the prognosis for life is relatively favorable, provided that antiarrhythmic tablets and drugs that reduce the formation of blood clots are constantly taken.
Prevention
To avoid such a serious disease as atrial fibrillation, the following measures must be taken to prevent the occurrence of the disease:
- conduct timely therapy of pathology, which can provoke a violation of the heart rhythm. This is primarily the treatment of arterial hypertension, as well as manifestations of heart failure;
- undergo clinical examinations in a clinic with a control ECG. In the presence of atrial fibrillation, preventive treatment is mandatory under the supervision of a specialist;
- eliminate bad habits;
- engage in physical education, including swimming, cycling, and include daily walking.
Compliance with preventive measures will improve the general condition of the body and prevent the development of cardiac arrhythmias. And if cardiac pathology already occurs, the strict implementation of the recommendations of a specialist will help the patient avoid serious health complications and improve the quality of life.