Hepatitis C treatment consists of several important aspects: diet and lifestyle, medications, ongoing monitoring by a hepatologist. The disease is characterized by a protracted course, without timely treatment, acute forms quickly turn into chronic. Interestingly, some people are able to recover on their own. However, they do not even suspect the presence of any pathology. This is due to the special gene responsible for the body’s immune response - it is present in about 20% of the world's population.
Material Content:
What is hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious pathology that occurs due to an invasion of the RNA virus in the body. The target of the disease are hepatocytes - liver cells, therefore this organ is the first to suffer. The virus is dangerous in its ability to constantly change. 6 genotypes and a larger number of subtypes are known. Several types of the pathogen can simultaneously enter the human body, due to which the disease progresses faster and proceeds in a severe form.
The main routes of infection are parenteral (through blood) and instrumental (skin damage by infected equipment). And there is also a small risk (about 5%) with unprotected intercourse with a patient or a carrier of the virus. Transmission from a sick mother to a child is possible when the baby passes the birth canal, as well as while caring for the newborn.However, subject to medical prescriptions, the percentage of infection is small - no more than 3-10%.
Once in the body, the pathogen with blood flow reaches the liver and settles in its cells. The immune system detects a foreign agent and aggressively attacks it, but hepatocyte also kills with the virus.
At the beginning of the disease, the liver constantly regenerates and replaces damaged cells with new ones, but with the progression of hepatitis, the organ ceases to have time to be updated.
The resulting gaps are filled with connective tissue, which cannot fulfill the function of hepatocytes - fibrosis develops.
If the process is not stopped at this stage and let the scars cover more area and destroy the hepatic lobules, a defeat of the whole organism occurs:
- the vessels of the liver overlap, the blood can no longer fully enter the body, therefore it is delayed in the veins of the digestive tract, bleeding may develop;
- harmful substances are not filtered by the liver, but continue to circulate in the bloodstream, resulting in severe intoxication;
- clotting disorders occur.
Without proper treatment, severe renal failure occurs and death occurs. In addition, a fatal outcome is possible at earlier stages from bleeding, most often from the veins of the esophagus.
Forms and stages of the virus
Hepatitis C drugs are selected according to the type and stage of the disease.
During the pathology, three forms are distinguished:
- fulminant - rare, characterized by rapid multiplication of the virus and the onset of cirrhosis;
- acute - occurs when the pathogen first enters the body, is most often asymptomatic, sometimes with jaundice, and eventually becomes chronic;
- chronic - lasts for years (5-10-20 years), provokes irreversible changes in the liver.
And the fourth option is also possible - virus carrying. The body of the carrier does not suffer, hepatitis does not attack its organs, but a person is able to infect others.
In the process of development, the disease goes through several stages, meanwhile, the clinical picture is often blurred, the virus "gets stuck" at one stage or misses some stage.
Therefore, periods can be distinguished far from always:
- incubation - there are no symptoms, the body does not react in any way to the invasion of the pathogen;
- pre-icteric stage - resembles the signs of a cold, soreness and heaviness in the liver can be felt;
- jaundice - signs of liver damage, deterioration of health;
- transition to a chronic form;
- liver failure.
It happens that after a period of incubation, the body is cured on its own - without a diet, medication or a special regimen. Chronic hepatitis C can develop at any stage of the disease.
Who is at risk
Hepatitis C transmission occurs by contact with the patient’s blood; the disease is not transmitted by other means.
The following persons are at increased risk:
- injecting drug users due to the reuse of disposable needles;
- medical workers who come in contact with human biological fluids (nurses, surgeons, obstetricians, etc.);
- citizens living with a patient with non-compliance with hygiene standards;
- promiscuous women and men;
- donors and recipients;
- people in need of frequent injections.
And you can also get infected by a dentist, hairdresser, manicure, tattoo parlor and other places where reusable tools are used and contact with blood is possible. To avoid unpleasant consequences, you need to choose salons and clinics where they maximize the use of disposable equipment, and reusable carefully sterilized.
Symptoms of the disease
Knowing the risk of infection, you need to carefully listen to your body so as not to miss the symptoms of the acute phase of viral hepatitis, which often resemble a common cold:
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- an increase in body temperature, often to subfebrile;
- upset gastrointestinal tract - nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite;
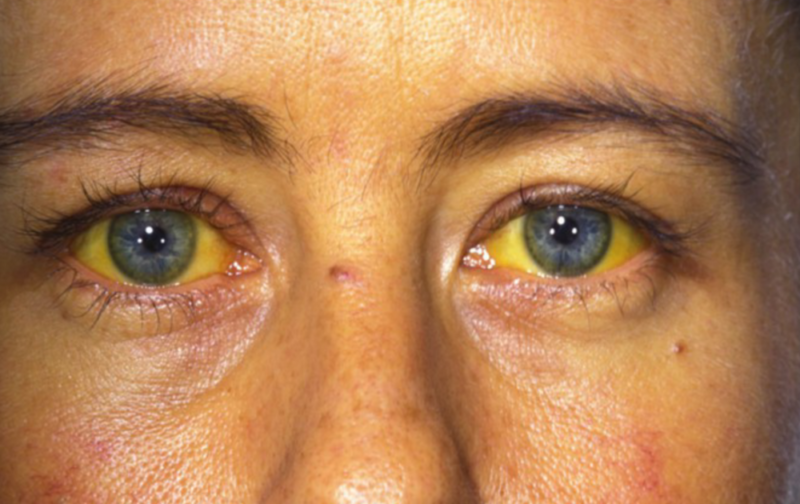
- yellowing of the sclera of the eyes, skin - rarely occurs;
- joint pain
- the appearance of skin itching, accompanied by jaundice.
Unfortunately, in most cases, the acute period proceeds with almost no symptoms, and the disease becomes chronic.
Symptoms of chronic hepatitis C for a long time do not make themselves felt, the pathology begins to appear only after sufficient liver damage:
- heaviness on the right side, pain after eating;
- weight loss;
- decreased performance;
- increased need for rest.
With the further development of the disease, the blood ceases to clear itself of non-useful substances, and the brain is the first to react to intoxication. The patient becomes apathetic, lethargic, too irritable, complains of insomnia. Perhaps the development of severe depression, which does not respond well to standard medication. Due to uncharacteristic symptoms, few people realize that the problem is in the liver, and hepatitis develops further.
With severe damage to the filter organ, the clinical picture becomes more expressive, appear:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- stable yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes;
- persistent pain;
- swelling of the legs, ascites - an increase in the abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid in it;
- regular digestive tract disorders;
- expansion of veins in the esophagus.
The patient's urine becomes like dark beer, and the stool, on the contrary, discolors and looks almost white. In severe renal failure, brain damage occurs - hallucinations, loss of consciousness, impaired coordination.
Diagnostic measures
If viral hepatitis is suspected, the patient should consult a doctor. The hepatologist is involved in the treatment of the chronic form of the disease, and the infectionist is involved in the acute.
To confirm the diagnosis, they resort to such additional studies:
- blood biochemistry - shows the concentration of liver enzymes in the blood and bilirubin;
- analysis for the presence of antibodies to infection in the blood serum;
- PCR - determination of virus particles and their number;
- ultrasound diagnosis of the liver and other organs of the peritoneum;
- biopsy of the affected organ.
In some cases, hepatitis is detected even before the onset of the first symptoms, for example, during a physical examination at work or during pregnancy.
A positive antibody test does not always mean that the disease is developing at the moment, there are other reasons:
- previous infection - the body overcame the pathogen and retained antibodies to it;
- false positive result due to ignoring the rules for passing the analysis.
After identifying specific antibodies, a deeper examination is necessary to determine the virus RNA in the blood and its concentration.
The modern treatment regimen for hepatitis C
Treatment for viral hepatitis C is carried out in courses and lasts several months. During this time, the patient regularly takes pills and injections, visits a doctor and passes tests. Interruption of therapy without the knowledge of the attending specialist is categorically impossible, as this can contribute to serious consequences.
In addition to the use of medicines, the patient is recommended to observe a special regimen:
- minimize exposure to the sun;
- increase the amount of fluid you drink up to 3 liters per day;
- It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol and smoke;
- do not drink any medicine without the knowledge of a doctor;
- stick to a diet;
- Do not physically overstrain the body.
Patients with a large body weight need to lose weight, gradually abandon the usual food.
As a drug therapy, several antiviral drugs are used at once: sofosbuvir with daclatasvir or ledipasvir. The course of treatment is at least 3 months.At the same time, the patient is credited with means to protect the liver - hepatoprotectors, as well as detoxification of the body.
With a mild course of hepatitis, you can resort to cheaper treatment. It is carried out using a well-known old drug - ribavirin in combination with interferons.
Folk remedies for the virus
To help the body cleanse itself of toxins and protect healthy hepatocytes, you can resort to alternative medicine recipes.
Well cleaned blood and liver decoctions of such plants:
- sage;
- oats;
- bird highlander;
- horsetail;
- St. John's wort
- tansy;
- burdock;
- burdock;
- lovage.
These herbs can be brewed individually or assembled. The regular use of prepared formulations will saturate the body with useful trace elements and vitamins, increase immunity and protect liver cells. Medicinal plants have a choleretic effect, and are also able to reduce the intensity of pain in the hypochondrium.
Treatment with folk remedies does not affect the cause of the disease - the virus, so it can only act as an adjunct therapy.
Non-traditional methods can be used only after consultation and permission of the attending physician, otherwise, there is a risk only to aggravate the patient's condition.
Diet for HCV
For successful treatment of viral hepatitis, the patient will need to radically change his lifestyle. First of all, refuse any alcohol and tobacco products. And also by all means adhere to the prescribed diet.
Dietary nutrition is aimed at protecting the liver and normalizing its work, improving the excretion of bile.
Following simple rules, the patient can significantly reduce the burden on the digestive system:
- refuse all fried and salty, smoked meats and canned foods;
- replace fatty meat and fish with dietary analogues;
- reduce the consumption of sweets, especially chocolate, and muffin;
- Do not drink soda, shop juices, strong coffee or tea;
- Do not eat sour fruits, legumes and greens.
You need to eat often (5-6 times), but in small portions. It is advisable to give preference to food that is cooked or steamed. If there is no severe edema, you need to drink plenty of water (over 2 liters per day).
Life expectancy with disease
With timely detection of the virus and the correct treatment for hepatitis C, you can get rid of it forever. If the disease did not manage to destroy a large number of liver cells, then the life expectancy of the patient does not differ from healthy people.
In the absence of the required therapy, the patient’s existence depends on many factors: state of health, hepatocyte regeneration rate, level of immune response, pathogen genotype, presence of negative effects on the body. Hepatitis C is called a “silent killer”, because it is capable of not making itself felt for 10-15 years, but only multiplying and damaging the liver. Someone can live with the disease for many years and not even guess about it, and someone dies away in just a few weeks.
Proper treatment guarantees the extension and improvement of the quality of life, and with a timely start - a complete cure.
Preventive measures
A specific vaccine against the virus has not yet been invented, therefore, the prevention of hepatitis C is to reduce the risk of infection, for which it is worth adhering to certain rules:
- Do not visit dubious beauty salons, clinics and tattoo studios;
- use only disposable syringes, needles, systems and other instruments in contact with blood;
- adhere to the rules of personal safety at the workplace (doctors, nurses);
- use condoms as contraception during casual sexual intercourse;
- do not use other people's shaving machines, toothbrushes and other personal hygiene items;
- refuse to visit asocial places.
To avoid the simultaneous infection of several types of virus at once, it is recommended to be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.In this case, when the pathogen invades, the body will already have a set of ready-made antibodies, which will help it quickly deal with the disease.