Laryngotracheitis is a bacterial or viral disease that affects the state of the organs of the nasopharynx. A progressive illness is fraught with negative consequences, in particular, temporary loss of voice. How is laryngotracheitis diagnosed in children, and is it treatable?
Material Content:
Causes of laryngotracheitis
Often diagnosed with the so-called laryngotracheitis of viral etiology, which accompany the following diseases:
- rubella;
- ARVI;
- chickenpox;
- scarlet fever.
Bacterial etiology of laryngotracheitis is provoked by chlamydia or mycoplasma, staphilo-, strepto- or pneumococcal infections.
A number of factors favor the development of ENT pathology:
- chronic ailments (hepatitis, tuberculosis, pyelonephritis, diabetes, etc.);
- stagnant processes in the respiratory system;
- continuous oral breathing, impaired nasal, sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis;
- air indicators (too cold / hot, dry / wet);
- negative parameters of the air mixture in the production (dusty air, irritating components in it, etc.);
- hypothermia;
- smoking (in particular, passive);
- excessive voice or respiratory tract.
Infection occurs through inhalation of air. However, a good state of immunity reduces the risk of the disease.
Symptoms and signs in children
Symptoms of laryngotracheitis in children are runny nose, discomfort when swallowing, hyperthermia, sore throat, etc.
Acute stenosing laryngotracheitis (false croup) is easily recognized by a dry, barking cough, which provokes a narrowing of the lumen of the larynx to a minimum.Often it is monitored in the morning and at night, is able to be paroxysmal in nature and literally shake the patient's body. These attacks are provoked by laughter, crying, inhaling, etc. The amount of sputum excreted is small, but the development of the disease makes the discharge plentiful, fluid, with impurities of pus and mucus. Sputum volume is gradually increasing. An additional symptom of pathology is a hoarse voice.
Acute laryngotracheitis sometimes provokes lymphadenitis, which leads to soreness of the lymph nodes in the neck, their increase. The patient's breathing becomes noisy, dry or wet rales can be monitored.
Chronic laryngotracheitis provokes vocal disturbance (dysphonia), pain behind the sternum and larynx, cough. Husky can be insignificant (manifest only at night or in the daytime), or constant.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of laryngotracheitis is carried out by a number of methods:
- History taking, listening to patient complaints.
- Examination of the patient's oral cavity, listening to the respiratory tract.
- Sputum microscopy.
- Bacteriological culture of smears of the throat of the mouth and nose, sputum.
- X-ray, CT (indicated for bronchopulmonary complications).
Laryngotracheitis is differentiated with pneumonia, diphtheria, asthma. The presence of a foreign body in the trachea should also be excluded.
Disease treatment
Treatment of laryngotracheitis in children is medication (at home) or outpatient. In the absence of concomitant stenosis of the larynx, the patient does not need hospitalization. The most dangerous condition is considered false croup. With a similar diagnosis, mandatory hospitalization is indicated. However, parents should familiarize themselves with the basic rules for first aid for a child who has acute stenotic laryngotracheitis.
Urgent Care
There are 4 stages of stenosis, each of them requires competent pre-medical care.
The first is characterized by an increase in signs of respiratory failure.
The main actions of parents:
- Provide the patient with fresh air.
- Apply mustard plasters on the calves of the legs, foot baths are acceptable (detailed recommendations are relevant only in the absence of hyperthermia).
- Provide a warm drink (the child should drink in small sips).
- It is permissible to administer intramuscularly 2% papaverine (0.15 g of the drug per year of a child's life).
- When tracking allergies, administer antihistamines.
In the second phrase, signs of respiratory failure are monitored not only during exercise, but also at rest.
The procedures carried out in the first phase should be added:
- Intramuscular administration of prednisone (2 mg per 1 kg of patient body weight).
- Mandatory hospitalization. After the arrival of doctors, they should be informed of previous activities.
In addition to respiratory failure in a child with a third stage of laryngotracheitis, CNS problems (excessive agitation or, on the contrary, inhibition) are monitored.
The latter is marked by hypoxic coma. The risk of death is great. It is permissible to administer 0.1% epinephrine (0.01 ml / kg body weight) with an interval of 5 minutes.
2, 3 and 4 stages of the disease require emergency hospitalization of the child.
Medications
Features of the choice of medicines depend on the types of disease:
- treatment of viral laryngotracheitis involves the management of antiviral agents ("Proteflazid", "Interferon");
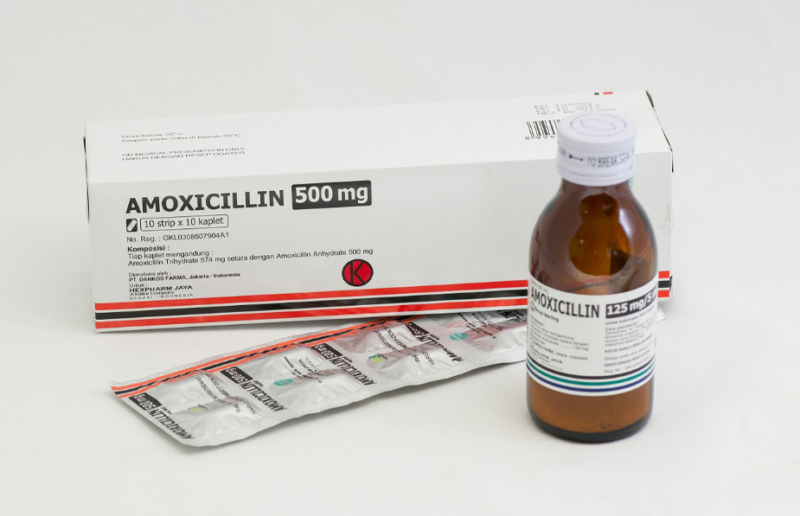
- the bacterial type of the disease is treated with antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Cefuroxime) and may be accompanied by antipyretic and antitussive medications;
- chronic laryngotracheitis is treated with immunomodulating medications (Broncho-munal, Likopid), physiotherapy (electrophoresis, inductothermy, massage) is appropriate;
- with stenosing laryngitis at an early stage, Erespal, Fusafungin (Bioparox) are prescribed.
Treatment of barking cough is accompanied by the introduction of mucolytics by inhalation.However, in the absence of a nebulizer, these drugs can be taken orally.
Note. Many ENT diseases suggest the use of steam inhalation as a therapeutic agent. Laryngotracheitis is not on the list of these diseases.
Traditional steam inhalation does not improve, but will aggravate the clinical picture, causing an exacerbation of the inflammatory process and swelling of the larynx. Only inhalations with a nebulizer with the drug recommended by the doctor are allowed (“Eufillin”, “Ambrobene”, “Lazolvan”, etc.)
If treatment with drugs is ineffective, surgery is recommended. The latter is relevant when there is a threat of development of laryngeal tumors and involves excision of excess tissues of the vocal cords and the larynx itself, removal of cysts. Similar manipulations are performed by microsurgical technique.
A good addition to the therapy of ENT diseases will be room humidification, because laryngotracheitis is often a consequence of the dryness of the inhaled air. In this regard, it will be useful to purchase an air humidifier. Another option is to place a damp cloth on a hot battery. Also, patients can take baths (in the absence of temperature) and inhale the evaporating air.
Possible complications and prognosis
The prognosis of acute laryngotracheitis is often favorable. The chances of recovery with stenotic laryngotracheitis are high exclusively with timely therapy. Delayed treatment is often ineffective. The risk of death in such cases increases, especially in the terminal, final stage.
Prevention of laryngotracheitis
Prevention of laryngotracheitis is based on general strengthening measures, namely:
- systematic sports and outdoor games;
- good nutrition;
- observing the rules of personal hygiene;
- hardening of children;
- intake of vitamins;
- vaccination against influenza.
The child should be protected from hypothermia, make sure that he does not breathe through the mouth. It is also recommended to avoid crowded places during the period of increased incidence of influenza.
Laryngotracheitis is a disease whose complications are extremely dangerous for children. The acute form of the disease - false croup - can lead to a tragic outcome of the pathology. Prevention of ENT diseases and their timely treatment will minimize all possible risks of pathology.