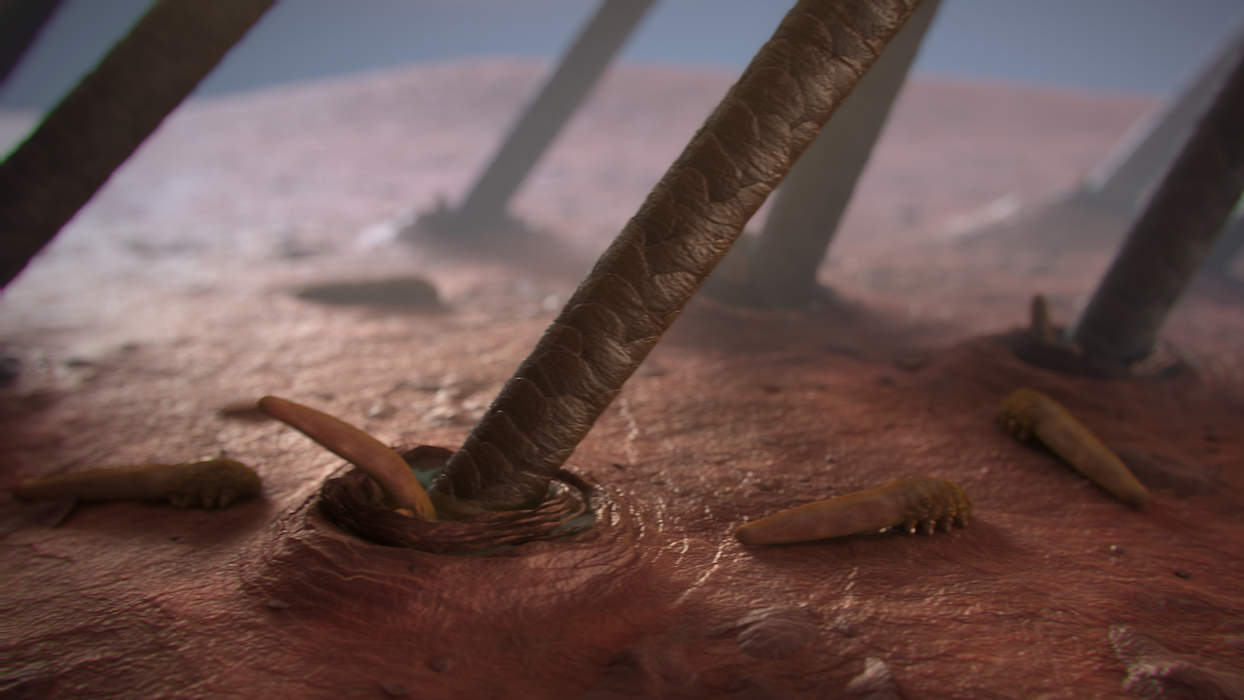
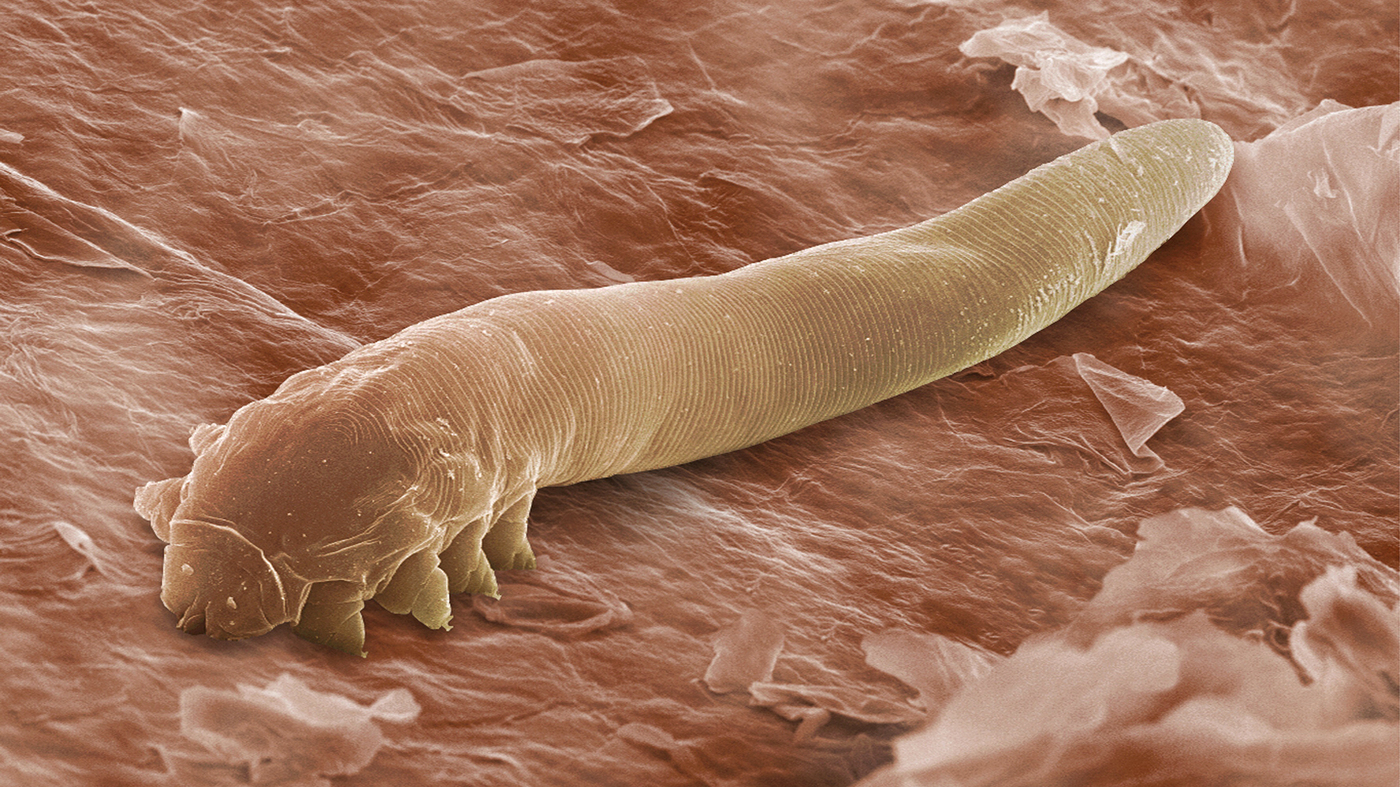
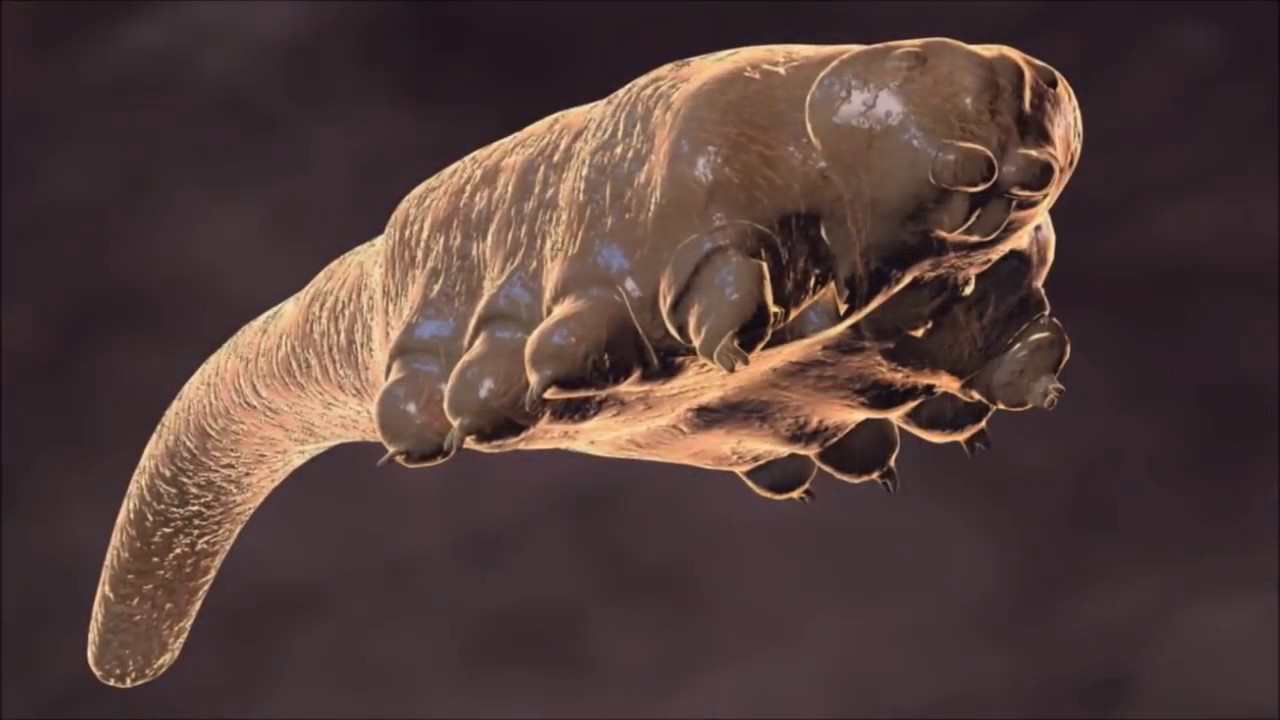
The demodex mite is a permanent, invisible to the eye, inhabitant of the surface layer of the skin of humans and mammals. Under favorable conditions, it is activated, multiplies intensively and causes demodicosis. With delayed treatment, the disease leaves irreversible cosmetic defects.
Material Content:
What is human demodicosis
Biologists have discovered 65 subspecies of Demodex mites, but only two of them live on human skin:
- demodex folliculorum lives in the mouths of hair follicles;
- demodex brevis is concentrated in the sebaceous excretory ducts, pores, and meibomian glands along the edge of the eyelids.
Another name for demodex is acne. The size of ticks does not exceed 0.5 mm, the life cycle lasts 14 days. They feed on sebum, lymph, follicle cells, keratinized scales. At night they come to the surface for mating, the female lays up to 25 eggs per day. Outside the human body, they live in a humid environment for 3 weeks, in a dry environment - up to 2 days.
Biologists classify demodex as a group of opportunistic organisms. If for 1 square. less than 5 individuals inhabit the skin, ticks do not harm, even bring some benefit. They reduce the number of bacteria in the pores, follicles, sebaceous glands, stabilize the acid-base balance on the surface of the skin.
With an increase in population, the peaceful coexistence of demodex and humans turns into a parasitic disease, demodicosis. Ticks injure the skin, capillaries, hair, and bulbs. The products of metabolism and decay poison the body. Pathogenic bacteria penetrate through skin lesions; streptococcal infection sometimes develops against the background of demodicosis.
Demodex spreads on the surface of the body unevenly.It reproduces more intensively in areas of increased fat secretion: nasolabial folds, chin, eyelid borders, nose wings, scalp, forehead. The back and chest suffer less often.
Causes of inflammation
Demodecosis occurs when the immunity ceases to restrain the spread of the tick, the barrier functions of the skin are disrupted.
This is due to internal causes:
- infectious and chronic diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- psycho-emotional and physical overload;
- impaired fat metabolism;
- hormonal failure during pregnancy, diabetes;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- skin lesions (acne, acne);
- surgical operations;
- severe injuries, burns.
In addition to internal problems, the mite population is affected by external causes:
- abuse of cosmetic creams with phytohormones;
- unbalanced nutrition with excess fatty, spicy, floury dishes;
- uncontrolled visits to the solarium, sauna, bath;
- excess tan;
- inadequate hygiene;
- improper skin care.
Exacerbations of demodicosis are noticed in warm and humid seasons: in spring, summer, and early autumn.
How is the disease transmitted?
Ticks pass from one person to another with close physical contact, contact of hair. Passed through common clothing, bedding, blankets and pillows, personal hygiene items. However, the development of demodicosis requires internal or external prerequisites. In medical practice, cases of infection of healthy people with normal immunity from a patient with demodicosis, including within the family, have not been recorded.
On dogs and cats, other subspecies of the tick parasitize. They are not adapted for life on the human body, so you can not get infected from pets.
Symptoms and signs of demodicosis
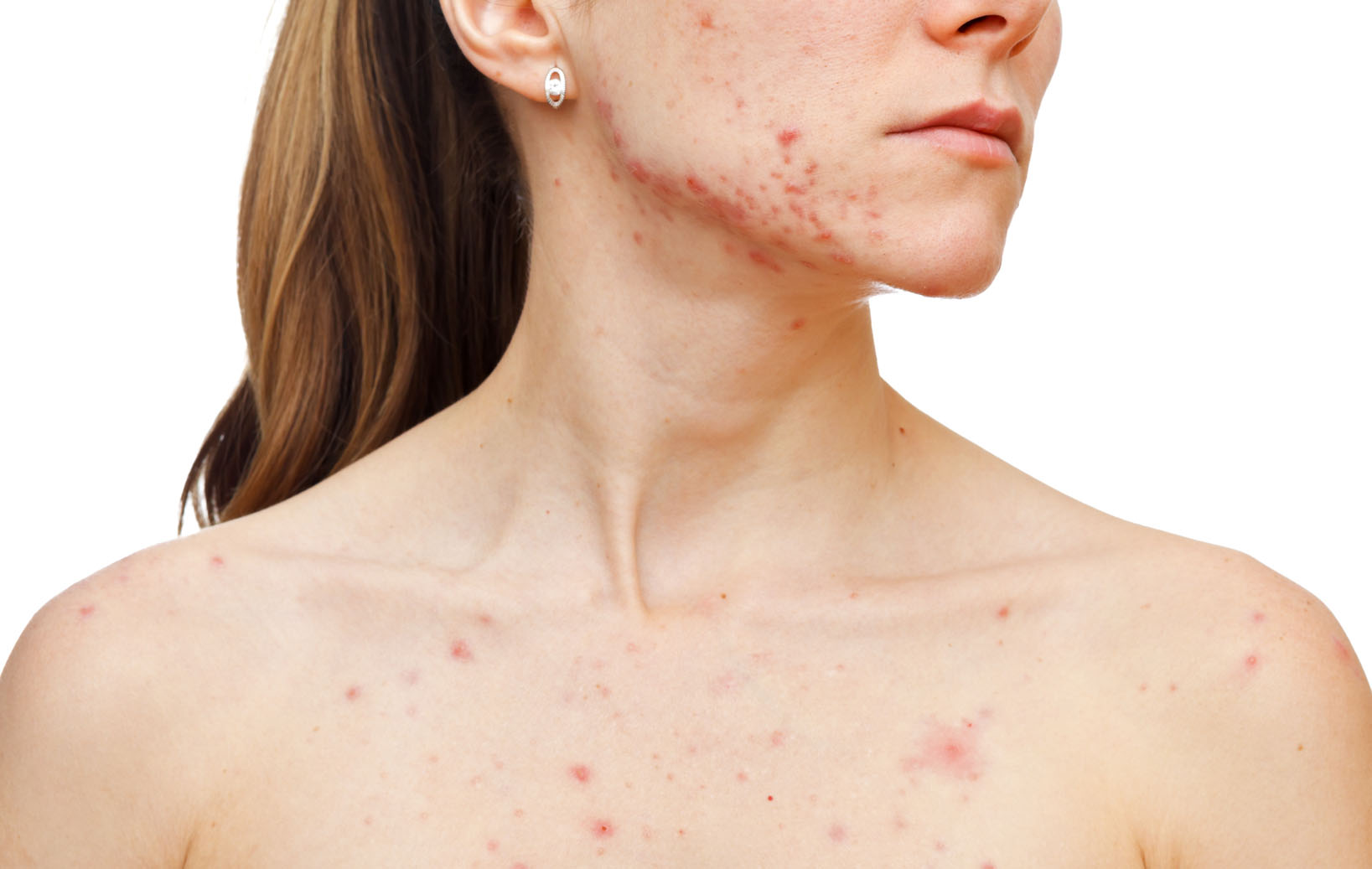
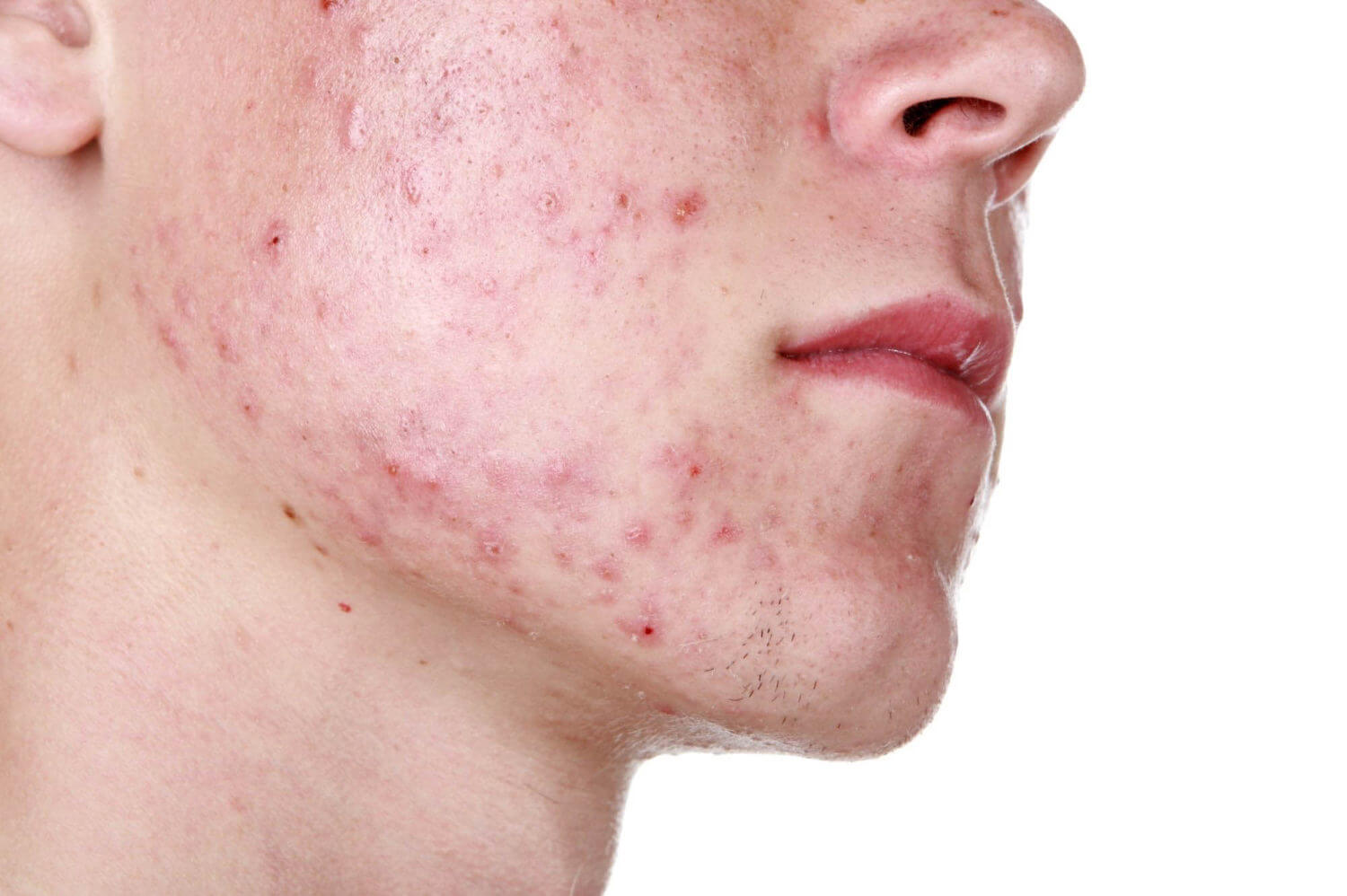
External manifestations of the disease depend on the number and localization of parasites, skin type, health status. Symptoms of demodicosis in humans increase as the tick multiplies:
- The skin is shiny due to increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, after washing and processing with cosmetics, the oily sheen does not disappear completely.
- Some areas turn red as a result of a rush of blood and the expansion of capillaries.
- On the head under the hair, redness is not visible, the development of the disease is signaled by seals, peeling, scales that resemble dandruff.
- With a strong accumulation of parasites, the sebaceous ducts become clogged, against the background of redness, nodules, acne with purulent contents appear.
- In severe cases, the damaged cells are replaced by connective tissue, the skin thickens in places.
The disease is accompanied by itching. It intensifies in the evening and at night, when the demodex creeps to the surface, does not allow normal sleep. When affected by a ciliary mite, the following symptoms appear:
- eyes get tired from the slightest load;
- the eyelids turn red;
- the edges are covered with sticky secretions;
- eyelashes stick together, fall out, their growth slows down.
Sometimes inflammation passes to the eyes: tearing increases, the sclera turns red.
Diagnostic measures
Demodicosis is treated by a dermatologist, the eye form is treated by an ophthalmologist. The disease can not be determined on the basis of examination, external signs resemble acne, rosacea, certain types of dermatitis. The only way to make a final diagnosis is a microscopic analysis of the following materials:
- Scraping for demodex. The doctor punctures the abscess, scraped off the contents of the rashes, placed on a glass slide and examined under a microscope.
- Ciliary test. For research, take 1-3 eyelashes or discharge from the border of the eyelid.
- Adhesive tape from the lesion. In the evening, a piece of adhesive tape measuring 5 by 2 cm is attached to the inflamed area, peeled off in the morning, placed on glass and carried to the laboratory.
The diagnosis is confirmed when more than 5 individuals are found. The results of the study will be unreliable if you do not prepare for it.A week before the visit to the dermatologist do not use decorative cosmetics, 2 days - soap, gels, it is better not to wash your face at all for a day.
Methods for treating ailment
Before a tick-borne therapy, a dermatologist during a survey tries to find out the root cause of demodicosis. If internal disturbances are detected, directs to a narrow-profile doctor: gastroenterologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, immunologist.
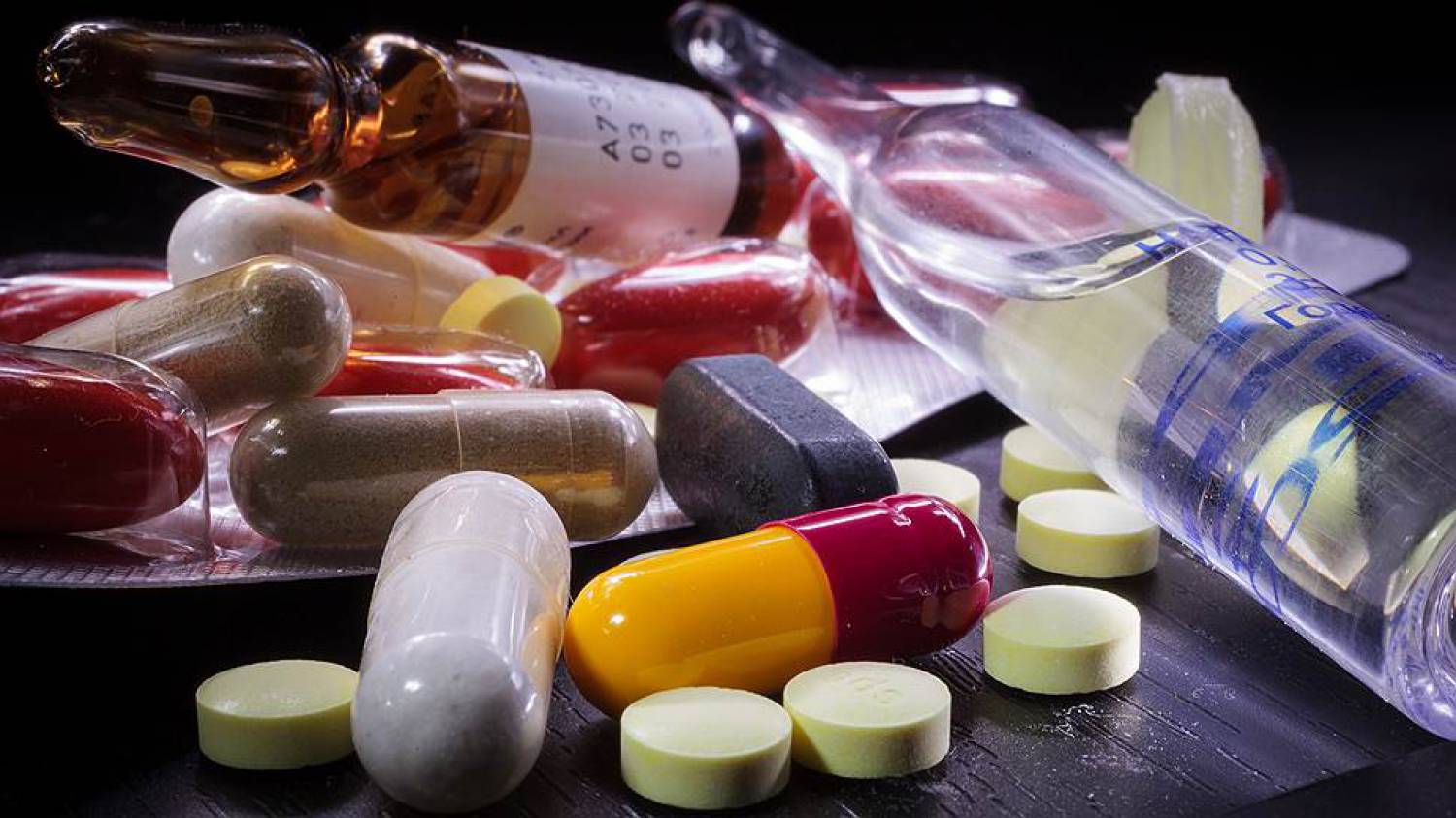
The main method of combating ticks is drug therapy, it includes the following drugs:
- external acaricidal drugs for the treatment of demodicosis - destroy, stop the growth of the tick population;
- local anti-inflammatory drugs - reduce irritation, soothe and restore the skin;
- antihistamines - eliminate the manifestations of allergies from vital products of demodex;
- antibiotics are prescribed when ulcers appear.
With demodicosis, drugs with metronidazole are used, however, demodex has become resistant to this substance. Dermatologists sometimes prescribe anti-itch mite agents instead, they also destroy demodex:
- aerosol Spregal;
- emulsion with benzyl benzoate;
- cream and crotamiton lotion;
- permethrin ointment;
- concentrate 5% Medifoks based on permethrin.
Sometimes veterinary drugs act more effectively on demodex: Amitrazine solution, aversectin ointment, Amidel gel. With the ocular form of the disease, drops of Carbachol, Armin, Physostigmine are prescribed. To reduce inflammation, the eyelids are treated with Demazol cream or Blefarogel 2.
During treatment, dermatologists recommend adjusting the lifestyle:
- Revise the diet: increase the proportion of fiber, eliminate fatty, fried, spicy dishes.
- Refuse foundation, powder, scrubs.
- Switch to medical and cosmetic care products, for example, STOP Demodex, Demodex Complex.
- Wash bedding, underwear at temperatures above 60 degrees.
- Change pillowcases daily or iron with a hot iron.
- Wash with tar soap, wipe your face with disposable paper towels instead of cloth.
- Disinfect glasses and a razor every day with alcohol.
- Until recovery, do not go to the bath, tanning bed, do not sunbathe.
After completing the treatment of demodecosis on the face, it is useful to strengthen the protective barrier of the skin with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures: cryomassage, laser coagulation, ozone and phototherapy.
The prognosis and consequences of the disease
The treatment of demodicosis will take from 4 weeks to a year. After recovery, pink, reddish spots remain on the skin, which disappear with time. If provoking factors are not eliminated, getting rid of the tick is more difficult. The disease becomes chronic: periods of improvement are followed by exacerbations of symptoms.
If treatment is delayed, cosmetic flaws remain on the skin. At the place of rashes, acne, if combed, bumps, scars, bumps appear, pores expand. The skin thickens, parts of the face increase, facial expressions are broken. In doubtful people, dissatisfaction with appearance leads to the development of psychological complexes, neuroses.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely remove ticks, the main task is not to create conditions for the activation of parasites:
- In time to treat systemic, infectious diseases, foci of inflammation.
- Regularly undergo preventive medical examinations.
- With the appearance of suspicious rashes, see a dermatologist.
- Carefully care for the skin: cleanse, moisturize, remove excess sebum.
- Maintain clean razor and cosmetic accessories: puffs, sponges, tweezers, brushes.
- Do not abuse tonal powder, it becomes a breeding ground for the tick.
You can’t try to cope with demodicosis yourself. Only scrupulous implementation of doctor's prescriptions will stop the spread of parasites, and compliance with preventive measures will help to avoid relapse.