Vaginal cyst - a tumor-like formation located on the back or side wall of the vagina, in its upper section. Most often, this anomaly is congenital in nature. A tumor of this type never becomes malignant, does not affect the development of the fetus during pregnancy, but nevertheless brings inconvenience, carries certain risks for the body.
Material Content:
Causes of the development of vaginal cysts
Such cysts are of two types: true and acquired, or congenital and traumatic. The former are very easy to detect - they are on the wall of the vagina.
A vaginal cyst may be the result of a traumatic abortion. The reason for her appearance is the girl’s ignorance of the rules of personal hygiene, what is considered the main reason for the appearance of this benign formation.
Types of entities
As already mentioned, vaginal cysts are divided into true and acquired. According to the cellular structure, such tumors are divided into the following types:
- epithelial;
- germinogenic;
- granulosa cell;
- tumor-like, etc.
They are divided into different types and depending on the location. For example, there is a cyst of the Bartholin gland, which is located on the eve of the vagina. These are paired glands, which are very important for the secretion of mucus-like fluids. If their work is impaired, discomfort appears during sexual activity. And also the dryness of the vestibule can cause inflammation.
Another common form of formations is the Gartner stroke cyst.It appears as a result of traumatic birth.
Typically, the size of the vaginal cysts varies from 1 to 10 cm.
Symptoms and signs
This disease does not have a pronounced symptomatology. Most often, the patient does not even suspect the presence of a cyst exactly until the moment when the formation grows to a certain size. Only after this, the woman notices discomfort and pain, can blood appear during intercourse, unusual for part of the excretion cycle. A cyst on the eve of the vagina can be visible to the naked eye with an independent examination of the organ.
Expressed in words that are understandable to every person, a cyst is a bag of liquid. Therefore, its growth may be accompanied by symptoms of colpitis, namely:
- sensation of itching and burning in the vulva;
- copious discharge in any part of the cycle;
- swelling of the external genital organs (this symptom usually becomes familiar to a woman that something is happening to the body);
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- pain and frequent urination;
- an increase in the abdomen, independent of the menstrual cycle and diet;
- aching or throbbing, pulling pain below.
Sometimes nausea, vomiting, profuse sweating, fever may appear. Thus, it becomes clear that the disease does not have pronounced symptoms that would specifically indicate the presence of a vaginal cyst. But in any case, every discomfort in this area should be discussed with your doctor. If a woman has discovered a strange growth in the place of the external genitalia, which grows and causes discomfort, you should immediately contact a gynecologist to determine the cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis depends on the location and specific type of neoplasm. For example, a cyst of the vestibule of the vagina is easy to notice on its own. In the event that an unusual formation is noticed in such a place, contact a specialist to establish, confirm or refute the diagnosis. In no case should you do this yourself and begin to be treated with alternative methods, which are not only useless, but even dangerous for the female body.
The following diagnostic methods help doctors evaluate neoplasms:
- gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound
- MRI
- radiography;
- biopsy;
- endoscopy;
- laboratory analysis of blood, as well as smears;
- CDK.
Periodic examinations by a gynecologist will help monitor the development and growth of the cyst. If it increases markedly, the doctor will be asked to perform an operation to remove the vaginal cyst. Before surgery, an assessment of the state of all gynecological organs is mandatory. This is done in order to verify their health, to exclude the development of the oncological process.
Be careful: a competent doctor can confirm the diagnosis only after examination with a gynecological mirror, as well as an ultrasound and a smear.
Course during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a previously acquired cyst may make itself felt or a new one may form. In any case, it will not affect the development of the fetus and the birth process. The main role in the decision to take the necessary measures is played by the size of the cyst. There are situations when they grow to such large volumes that it interferes with the natural process of the birth of a child. In such cases, liquid is usually pumped out of the cyst sac, and formation is removed after delivery.
If it is too large for such events, a cesarean section is possible.
Removal and treatment of benign education
Each woman, after detecting a vaginal cyst, wonders what to do next. Treatment can be either temporary for the purpose of alleviating pain syndromes, or complete.
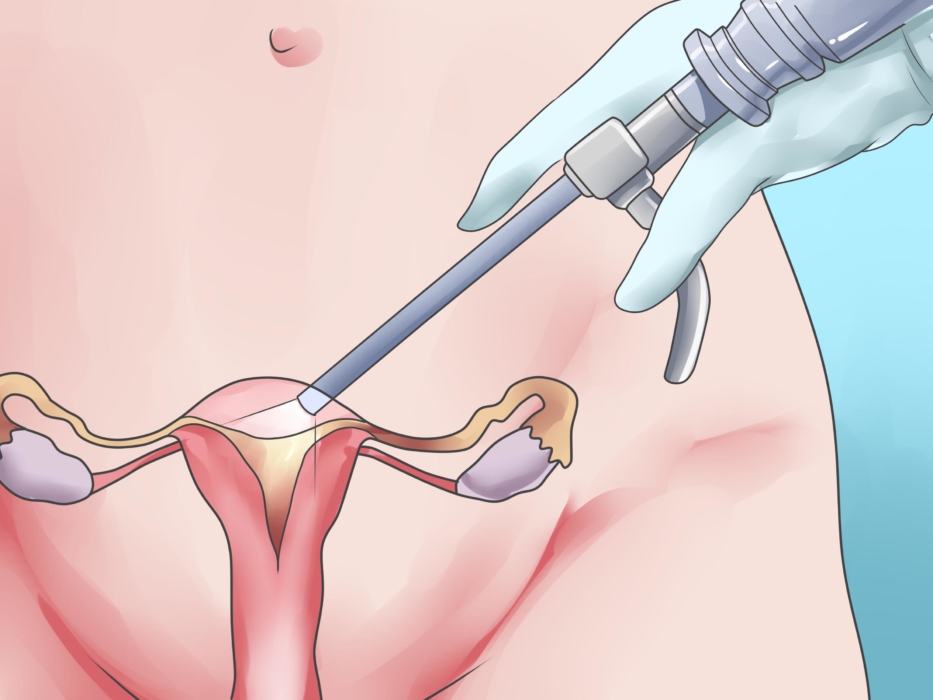
The first option includes puncture aspiration, pumping fluid from a cyst.This method is used in the case when the abnormal size formation appears in a pregnant woman, preventing the natural exit of the fetus. Over time, the fluid accumulates again and after childbirth, the cyst is removed operatively.
Surgery is usually indicated, the extent of which depends on the specific clinical picture. In the most difficult cases, it can reach the complete removal of the uterus with appendages. But currently, gentle treatment methods such as marsupialization are preferred. The bubble of the cyst is dissected, the fluid leaves the membrane, and the rest is sutured to the vaginal tissue. In addition to the treatment itself, this method of surgical intervention is aimed at combating relapse, the reappearance of fluid in the sac.
The operation to remove the true vaginal cyst is much more complicated. Such a pathology can very closely border on important organs. It happens that removal directly through the vagina is impossible. In this case, a laparotomy is used. In the absence of signs of bleeding, the patient is discharged a few days after treatment. There are cases that the operation is performed on an outpatient basis.
If a cyst is detected in the early stages of development, medications can help. But in such situations, therapy should be carried out by qualified doctors who will prescribe treatment depending on the type of cyst and its size. Healing by folk methods is unacceptable.
If the disease does not bring the patient any discomfort, she can do without medical assistance. The only thing recommended in this case is constant monitoring by a gynecologist to monitor the possible growth of education.
Possible complications
A cyst in itself can be the result of an unsuccessful surgical intervention. Although such a benign formation causes some discomfort and pain, it never becomes a cancerous tumor.
The cyst also does not affect the menstrual cycle, the function of conception and childbirth. But complications can be in the form of infection of the contents of the sac or postoperative wound, as well as relapse after incomplete removal of the neoplasm. Damage to the wall of the urethra is possible.
Prevention
Even after the cyst has been removed, there is a chance of its reappearance. The best way to prevent this is to see a gynecologist, regularly consult a doctor twice a year or more.
In order to protect the daughter, who has not yet been born, from a congenital cyst, the expectant mother must avoid any external factors that during pregnancy can adversely affect the formation of fetal tissues and its organs.
In other words, she needs to abandon the following actions:
- taking drugs;
- drinking alcohol;
- smoking;
- some drugs.
In addition, it is recommended to comply with the required conditions:
- monitor personal hygiene, which is important not only to prevent relapse, but also to eliminate the risk of other pathologies;
- avoid hypothermia;
- cure all infectious diseases to the end;
- take timely measures to diagnose the symptoms of various ailments.
And you should also carefully perform any intravaginal manipulations that, due to carelessness, can cause damage to the vaginal mucosa.