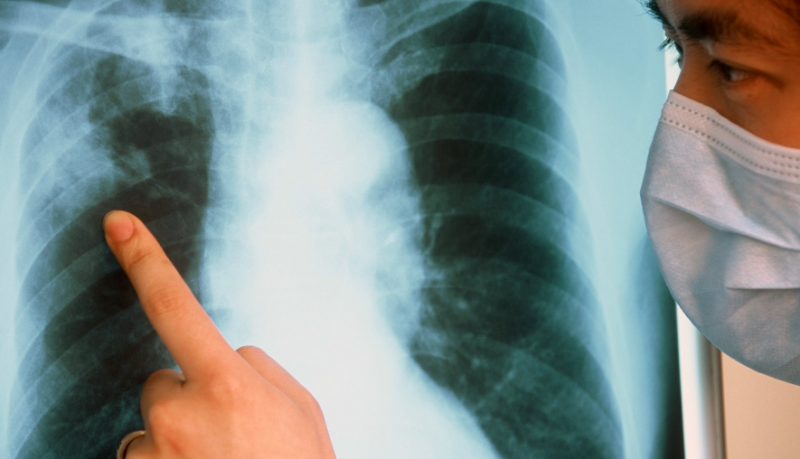
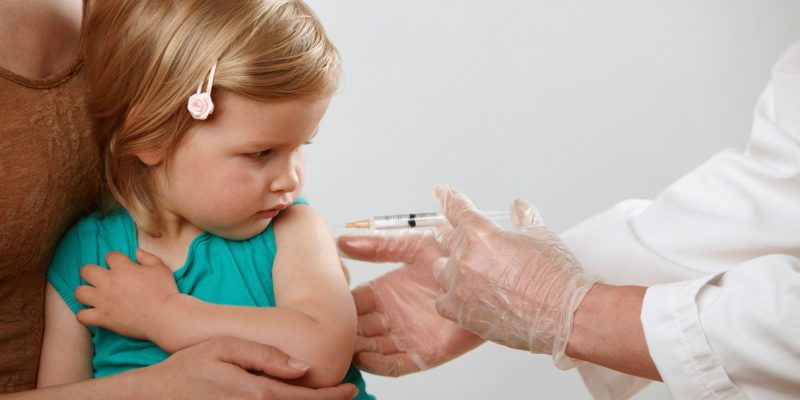
Caseous pneumonia is one of these pathologies, a characteristic feature of which is the rapid progression with an increase in intoxication of the body and destruction of lung tissue. A whole branch of medicine called phthisiology is devoted to the study of tuberculosis, since this infection can cause serious complications, often ending in death.
Material Content:
What is caseous pneumonia?
Tuberculosis, or pulmonary consumption, is not only a medical, but also a social problem, since the incidence of this infection is constantly supported at a certain level by a specific contingent from the adult population. The causative agent of the disease is Koch's wand, which, once in the patient’s body, remains there forever, causing severe lung damage.
The disease can develop independently or be a complication of the tuberculosis process against the background of a decrease in the body's defenses. The disease proceeds in the form of acute inflammation, accompanied by caseous (or cheesy) decomposition of the lung tissue with the formation of large or several small cavernous cavities.
The disease proceeds with the active release of tubercle bacillus in combination with severe symptoms.
In the clinical picture of the course of caseous pneumonia, the following types are distinguished:
- acinous form - acini (structurally functional units of the lungs) are involved in a large amount of the pathological process, provoking a complication of the current acute process of miliary tuberculosis;
- lobular form - there is a lesion of the lobes of the lung, resulting in multiple plots of caseous necrosis;
- lobar form - the pathological process affects the entire share of the respiratory organ, melting and forming specific destructive cavities, often manifests itself as an independent disease.
The course of the process and its prognosis will depend on the area of damage to the lung tissue. The danger of the disease lies in its rapid spread and extremely low resistance to infection. Early diagnosis and timely prescribed therapy contribute to a more favorable prognosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
The occurrence of caseous pneumonia occurs due to a sharp increase in the volume of the pathogen. The decrease in the number of cellular structures responsible for immunity occurs due to the toxic effect of Koch bacilli on them.
In the lesion focus caseous pneumonia with tuberculosis, blood flow is disturbed, which leads to the formation of blood clots in the vessels. Lack of proper nutrition of the lung tissue leads to its destruction, that is, caseous necrosis occurs. The main reason for this rapid development of the pathological process is a sharp decrease in immunity and massive contamination of the lungs with Koch mycobacterium.
Such a process is most often observed in people at risk, which includes the following population:
- Persons engaged in vagrancy without a fixed place of residence;
- refugees
- patients with chronic alcoholism;
- drug addicted patients;
- AIDS patients
- contingent of labor institutions;
- patients receiving for a long time according to indications preparations with a cytostatic effect, hormonal agents;
- medical personnel working in tuberculosis hospitals and leading the reception of tuberculosis patients;
- patients with endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus).
Of great importance in the occurrence of this pathology is an unbalanced diet, contributing to a decrease in the body's defenses, as well as heredity.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
The disease has an acute onset. In this case, it does not matter how it develops, that is, it doesn’t matter, it will be an independent pathology or a complication of the current process.
Symptoms of caseous pneumonia are manifested by the following clinic:
- a sharp rise in body temperature to 40 degrees, the values of which can then fluctuate;
- headache, chills, weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- sleep disturbance;
- severe sweating at night;
- against the background of pallor of the face, a blush appears on the side of the affected lung;
- dry cough with a small amount of sputum of a mucous nature at the very beginning of the development of pneumonia, accompanied by shortness of breath;
- after 1 - 2 weeks, the nature of the released sputum changes, it becomes purulent, yellow-greenish in color;
- the progression of respiratory failure with increased shortness of breath, the development of heart palpitations, the appearance of cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle;
- the appearance of hemoptysis with the possible development of bleeding.
The fever then subsides. The temperature drops to normal or subfebrile indicators. But manifestations of intoxication increase, and the patient's condition worsens. If pleura is involved in the pathological process, pain syndrome, which progresses in its intensity, is attached to shortness of breath.
An increase in pulmonary heart failure is noted. Clinical manifestations of caseous pneumonia can develop to a greater or lesser extent, depending on the volume of the affected lung tissue.
In some cases, the onset of specific pneumonia is masked as a catarrhal infection, when there is aches in the body, malaise, runny nose, sore throat, a slight increase in temperature.
But the rapid progression of the pathology, the appearance from the first days of the disease of important clinical symptoms in the form of cough and shortness of breath, as well as the patient’s history, indicate the development of a specific pathological process.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of caseous pneumonia in the initial stage of its development causes certain difficulties, since the manifestations of the pathology are identical with croupous pneumonia, acute respiratory viral infections, and flu. The Mantoux test for this pathology will be negative. A large role in establishing the diagnosis is played by the patient's history.
Diagnosed tuberculosis of any localization or contact with a patient with this pathology allows one to suspect the development of a specific process.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following research methods are used:
- examination of the patient and assessment of objective data - when listening to the lungs (auscultation), bronchial breathing with a large number of moist rales is observed on the affected side;
- with percussion (tapping of the chest), dullness of sound above the focus of altered lung tissue is determined;
- blood, urine for a general analysis;
- X-ray of the lungs in 2 projections - changes in the lung tissue in the images will be typical of tuberculosis;
- according to indications - MRI;
- sputum microscopy to detect Koch's bacillus is performed a week after the onset of the disease;
- bronchoscopy with taking material for histology.
The results of a comprehensive examination of the patient in combination with his complaints, anamnesis and objective data help to establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Important! Early diagnosis of caseous pneumonia and timely prescribed complex treatment give a chance to stop the progression of the pathological process and avoid lung resection.
Caseous pneumonia treatment
Therapeutic measures for patients with a specific process are carried out in a hospital. Treatment is selected taking into account the development of caseous pneumonia, its form, the condition of the patient and his individual characteristics.
Drugs and antibiotics
The doctor’s tactics in the treatment of pathology is aimed at stabilizing the process and preventing its progression.
For this, complex therapy is prescribed, which includes the following types of drugs:
- Specific etiotropic chemotherapy aimed at suppressing the growth of Koch's bacillus is prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen to drugs.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed to suppress the pathogen of a non-specific nature and prevent the development of purulent inflammation.
- Intravenous administration of saline solutions, glucose, polyglucin, hemodesis - to relieve intoxication.
- Hormone therapy using corticosteroid drugs.
- Immunity enhancers.
- Vitamin Therapy.
- General strengthening drugs.
If the treatment of caseous pneumonia gives a positive effect and the progression of the disease is stopped, the specific etiotropic treatment continues for a long time. But most often, in connection with the caseous process, leaving behind multiple or single cavities of large sizes, surgical treatment is indicated.
It is carried out in the period of remission or for health reasons, when a part of the organ is removed (lung resection), after which the patient continues to take specific treatment. The dynamics of the stabilization of the process is monitored by laboratory indicators, as well as by x-ray control.
The bulk of patients undergoing caseous pneumonia passes through surgery due to the extensive damage to the lung tissue.
Folk remedies
With a specific infectious process, the use of traditional medicine recipes is possible only as an adjuvant. At the same time, drug therapy as the main treatment remains unchanged. It is possible to use folk remedies only on the recommendation of the attending physician.
Medicinal herbs in the form of infusions or decoctions for caseous pneumonia can be used as expectorant and restorative agents.
The most popular are the following:
- Decoction of raisins. 100 g of dried berries are crushed and filled with 200 ml of boiling water, followed by boiling over low heat for a quarter hour. After this, the broth is filtered and squeezed. Used in 100 ml three times a day.
- Decoction of figs. 2 - 3 dried berries are poured with 200 ml of milk, followed by heating to a boil over low heat for a quarter hour. After cooling, the broth is ready for use. Drink 100 - 150 ml twice a day.
- Infusion of pine buds. 15 g of dry raw material is poured into a glass of boiling water and infused for 2 hours, after which a quarter of a glass is taken 2 to 3 times a day. You can add a spoonful of honey to the infusion.
- Infusion from the collection of herbs of coltsfoot, chamomile flowers, birch leaves and rosemary in a ratio of 1: 1: 3: 5. A tablespoon of raw materials is brewed with a glass of boiling water in a thermos and infused for 2 hours. A quarter cup is taken 3-4 times a day.
The duration of the intake of herbal folk remedies and their type will be determined only by a specialist.
Is pneumonia contagious to those around you?
The transmission of the pathogen from the patient to a healthy person occurs by airborne droplets. Because caseous pneumonia is contagious to others, as the pathological process progresses, and the patient secretes Koch's wand into the environment.
If a healthy person has weakened immunity, the risk of contracting tuberculosis increases several times.
Forecast and possible complications
Given the severity of the tuberculosis process, the prognosis for caseous pneumonia is always very serious, since the pathology is fraught with complications during the disease.
These include:
- hemoptysis or pulmonary hemorrhage;
- infectious toxic shock;
- spontaneous pneumothorax;
- pulmonary heart disease;
- cavity formation.
The course of caseous pneumonia often ends in death from such complications or disability of a patient with fibro-cavernous tuberculosis that persists until the end of his life.
Preventive measures
Specific preventive measures begin to be carried out from childhood by BCG vaccination at specific times in the life of the child. To maintain high immunity, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle, as well as a full balanced diet and exercise.
In addition, it is mandatory to undergo an annual medical examination with fluorography. Patients with HIV infection are given prophylactic treatment with tuberculosis drugs.
Regular monitoring and conducting a full course of treatment for tuberculosis will significantly reduce the risk of developing caseous pneumonia and its consequences.