Cardiomegaly is a pathological increase in the size and weight of the heart, in advanced cases life-threatening. This is not a disease in the literal sense of the word, but a syndrome in which there is a change in the basic parameters of this vital organ.
Material Content:
What is cardiomegaly in humans?
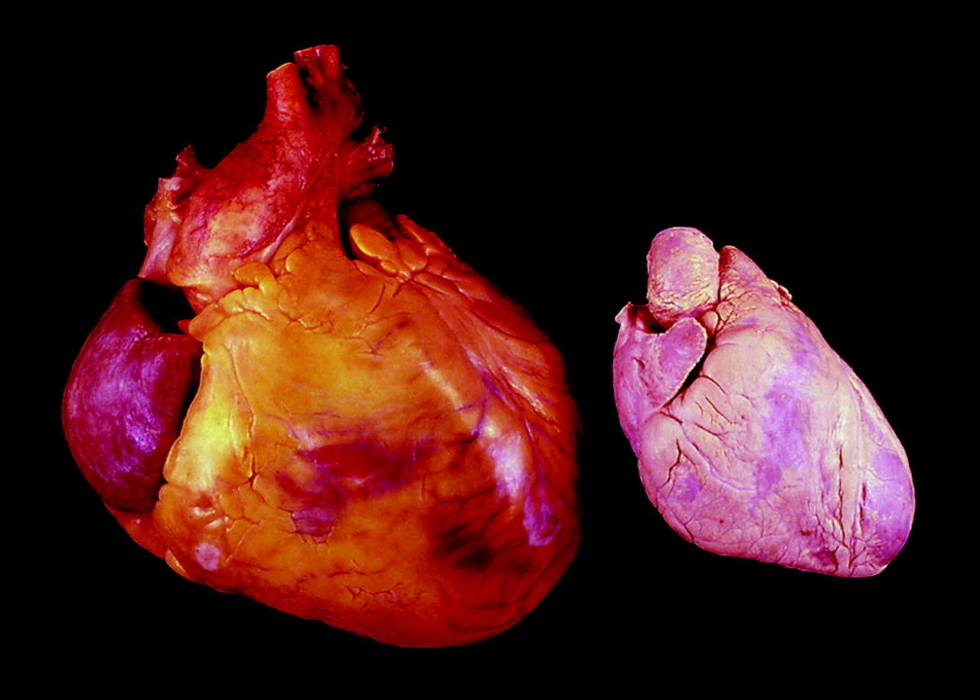
This pathology can be either congenital or acquired due to complications of various diseases of the cardiovascular system. The disease “bull’s heart” (as it was called in everyday life) is not so common. An increase in the heart muscle occurs due to the gradual compaction and thickening of the walls of the myocardium. In the vast majority of cases, it is the left atrium that increases, which performs the main work of transporting arterial blood to the structures of the brain.
Sometimes, a slight change in the size and weight of the heart towards an increase is a natural process. It is usually observed in professional athletes or people who engage in heavy physical labor. Due to heavy loads, the heart is constantly forced to pump large volumes of blood, as a result of which myocardial fibers increase to withstand such a rhythm of work. This is normal. Moreover, such physiological hypertrophy never leads to a significant increase in size, is not accompanied by malfunctions of the cardiovascular system and a deterioration in well-being.
If cardiomegaly syndrome is formed, the organ greatly increases in size, but at the same time it is depleted, since the fibers do not develop.
Due to myocardial thinning, normal blood circulation in the chambers of the heart becomes impossible. Muscle wear is a direct path to the development of heart failure and death.
Causes and symptoms of occurrence
An enlarged heart is often formed in the period of intrauterine development due to some kind of malfunction. Often a significant role is played by heredity.
Causes of heart enlargement (if acquired):
- arterial hypertension;
- ischemia;
- a history of heart attacks;
- myocarditis;
- tumors of different origin;
- diabetes;
- endocrine disruptions;
- obesity;
- heart defects;
- strong sports loads;
- bad habits;
- lack of oxygen (work in hazardous industries, living in environmentally disadvantaged areas);
- pathologically increased pressure;
- taking certain potent anticancer drugs.
There are no specific specific symptoms. Very often, the disease is almost asymptomatic or “disguised” as other diseases. The severity of symptoms always depends on the underlying disease, the underlying cause. Sometimes the patient complains:
- uncomfortable sensations in the heart;
- heart palpitations;
- reduced ability to work;
- dizziness;
- swelling of veins on the neck;
- fatigue;
- swelling;
- shortness of breath.
Because of this, the detection of pathology occurs most often by accident during a routine examination or when contacting a cardiologist for other heart diseases.
Child's syndrome
Unlike an adult, a child's organ can increase several times. The enlargement process is also accompanied by clogging of the heart chambers with blood clots and the expansion of the holes in the valves.
A child with such a pathology is often born blue, which directly speaks of a malformation. During crying, such a baby develops severe shortness of breath. Breathing becomes superficial, palpitations - rapid. Around the lips and nose appears cyanosis, the skin turns pale.
Older children complain of a loss of appetite, a constant feeling of fatigue and pain in the chest area. The child becomes irritable, nervous, emotionally unstable, can not cope even with minor stresses.
Heart enlargement
There are 3 stages of violation:
- first - indicators exceed the norm by no more than 1.5 mm;
- the second - the thickening increases to 2 mm;
- the third - the walls are thickened by more than 2 mm.
If at the first stage the disease proceeds almost imperceptibly, then over time, violations become apparent.
Diagnostic measures
The sooner a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, the higher the chances of a more or less favorable outcome, so if you have any suspicions, you should immediately contact a specialist. In any case, there is always the opportunity to slow down the pathological process and improve the quality of life of the patient.
At the reception, the doctor collects a family history, and also clarifies information regarding the patient’s lifestyle, palpates. Then the patient is prescribed a number of methods of differential diagnosis, including x-ray, ECG, echocardiography, ultrasound. Cardiomegaly on an x-ray to an experienced eye is immediately visible, therefore it often serves as the first way to detect pathology. In rare cases, a biopsy is necessary when a microscopic piece of tissue is taken from the inner surface of the ventricle for a detailed examination.
Bull Heart Treatment
If the pathology is acquired, therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. For example, when the underlying cause of the disease is arterial hypertension, the doctor will prescribe medications that normalize the level of pressure.
Treatment of cardiomegaly can be conservative or surgical.Conventional methods are used only if there is hope that the factors that triggered the increase can be removed with the help of drugs, abandonment of bad habits and normalization of lifestyle.
If the cause of the disease is a violation of the structure of the heart or birth defects, an operation cannot be dispensed with. In such cases, the specialist must definitely consult the patient in detail about the surgical procedure.
Therapeutic drugs
As a rule, a cardiologist prescribes diuretics, inhibitors, glycosides, nitro drugs. One of the popular remedies is Digoxin, which helps restore cardiac functions. These drugs increase the strength and effectiveness of heart muscle contraction, reduce the likelihood of a heart attack or other complications, and lower blood pressure.
Folk remedies
Folk recipes can only be used as an adjuvant. Decoctions of medicinal plants are not able to return the heart to its original state, however, they can help to some extent restore the function of the heart muscle.
Herbalists recommend paying attention to the extracts of St. John's wort, calendula, viburnum, motherwort, mint.
Diet for cardiomegaly
Patients need to limit physical and emotional stress, and also follow a diet. It is necessary to reduce the amount of fluid consumed, to reduce the amount of salt. It is advisable to supplement the diet with vegetables and fruits with a lot of vitamins, seafood, as well as food that does not contain animal fats. Eating behavior should be adjusted to limit foods saturated with cholesterol and triglycerides.
Eat five times a day in small portions. The volume of liquid should not exceed one and a half liters.
Diet No. 10 is often taken as the basis. Its main characteristics are a slight decrease in energy value, restriction of salt and other substances that excite the heart and nervous system.
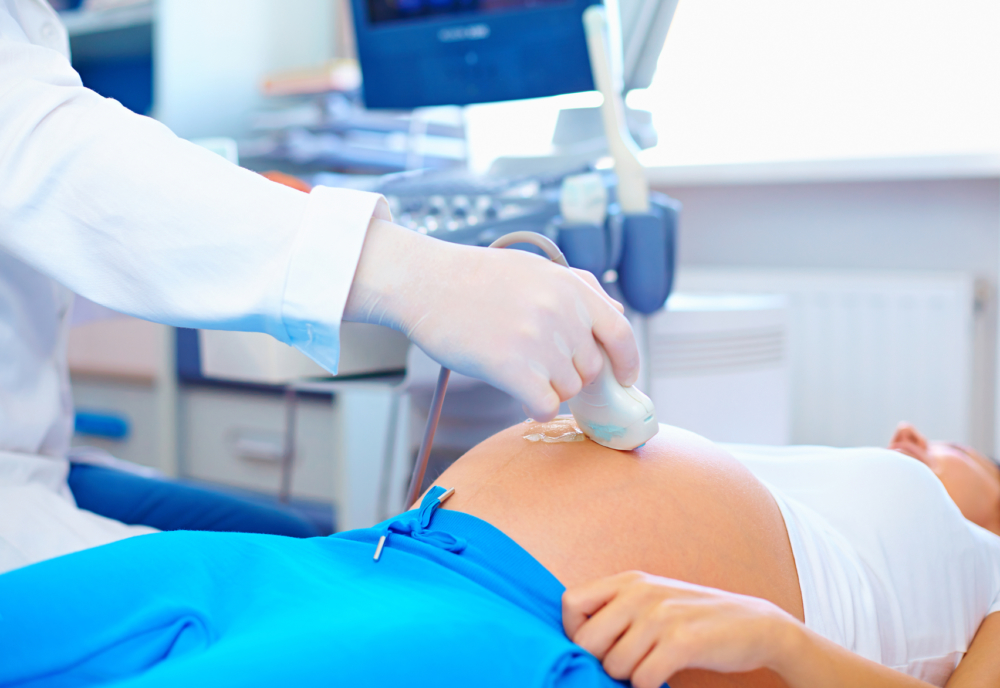
Diagnosis of the fetus
A congenital form of the disease is very rare. The prognosis in half of the cases is unfavorable: no more than 45% of newborns fully recover. About a quarter of young patients develop heart failure, and about 30% of sick babies die in the first 8-12 weeks of life.
Pathology can be detected during ultrasound. Infants with this syndrome are often born with severe hypoxia or CNS injuries. Sometimes a problem first manifests itself after birth, and this happens suddenly. Parents suddenly begin to notice that the child suffers from shortness of breath, refuses food, and his heart beats suspiciously often.
To prevent the occurrence of cardiomegaly in the fetus, pregnant women must:
- carefully follow the doctor's recommendations;
- completely abandon bad habits, avoid all kinds of radiation exposures;
- eat right and eat only healthy foods;
- strengthen immunity and avoid crowded places (especially during seasonal colds).
Of course, no one canceled the hereditary factors, but no one can somehow influence them.
Consequences and Complications
The result of treatment largely depends on the root causes and stage of detection of the disease. Some patients lead a habitual lifestyle after therapy, others are forced to take medication constantly.
Pathology is considered irreversible, therefore conservative treatment only provides the prevention of heart failure.
Only in very rare cases, when an enlarged heart is detected in the early stages, is it possible to return to its normal size.
An increase in this important organ can provoke many other, no less serious health problems.People with this pathology are at risk of blood clots, stroke, pulmonary embolism, they often have a normal heart rhythm. A direct consequence of the disease may be cardiac arrest.
Preventative measures
Prevention is very simple and consists in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The risk of getting cardiomegaly in people who do not have bad habits, exercise regularly, eat right and monitor their weight and pressure, is low.
Therefore, to prevent the occurrence of heart diseases, which are often the cause of cardiomegaly, you need to avoid stress, prevent the appearance of extra pounds, practice moderate physical activity.