Inflammation of the lungs is a disease that requires an immediate reaction and appropriate therapy. After all, it can seriously harm health with improper treatment. Therefore, it is important to know how to treat pneumonia, and whether it is worth it to decide on the use of certain methods of therapy. Parents of young patients should be especially careful about the disease, because the consequences of improper treatment can be severe.
Material Content:
Causes and symptoms of pneumonia
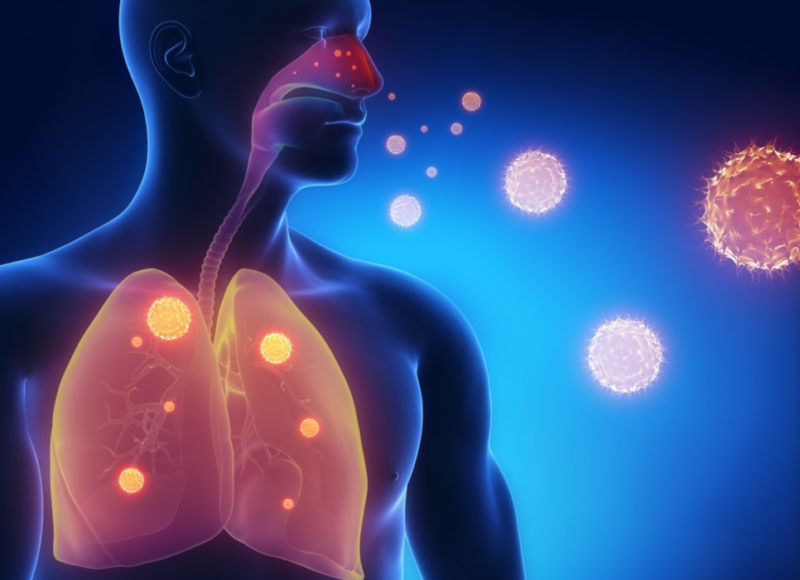
This disease most often has an infectious etiology. Bacteria or viruses infect the tissues of the lungs and other organs of the respiratory system, provoke the appearance of rapidly spreading inflammation.
Most often, pathogens are:
- pneumococcus (in young children);
- chlamydia, mycoplasma;
- staphylococcus;
- enterobacteria;
- hemophilic bacillus;
- pneumocysts;
- legionella;
- Klebsiella;
- E. coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The infection enters the body by airborne droplets, there are cases of penetration and spread through the bloodstream.
Optionally, the presence of infection in the body causes pneumonia. The disease appears in people with weakened immune systems who are predisposed to such a development of events.
Pulmonology names the factors contributing to the appearance of inflammation:
- complications after improper treatment of respiratory diseases, flu;
- hypothermia;
- chronic bronchitis, asthma, laryngitis;
- cardiac pathologies (heart disease, insufficiency);
- vitamin deficiency, rickets;
- decreased immunity;
- long bed rest;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- surgical interventions;
- elderly age.
The course of the disease can be different, it all depends on the severity of the pathology and the condition of the patient. Therefore, the symptoms also vary, especially at different ages.
Adult patients receive pneumonia most often due to hypothermia. Among the first signs of the disease at this age are:
- a sharp increase in temperature to febrile indicators (from 38.5);
- headache, weakness throughout the body;
- dry cough (for 2-3 days), turning into wet, with sputum;
- pain in the chest, aggravated by coughing;
- dyspnea.
In children, symptoms of pneumonia are:
- cyanosis (cyanosis) of the area around the lips, fingertips and nails;
- low-grade fever (37-38);
- drowsiness, lethargy;
- paroxysmal cough;
- irritability, frequent crying;
- trouble sleeping;
- loss of appetite;
- rapid breathing, shortness of breath.
These signs require an immediate reaction and an urgent consultation with a doctor for diagnosis and proper treatment.
Types of pneumonia
There are several classifications that distinguish between forms of pneumonia.
According to the appearance conditions, they share:
- community-acquired form;
- nosocomial (when the disease occurred in a patient in a hospital during the treatment of another pathology).
Depending on the pathogens, there are such forms:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- fungal;
- mycoplasmal;
- mixed.
According to the development mechanism, there are:
- primary form;
- secondary (as a complication of another pathology);
- post-traumatic;
- postoperative.
By localization:
- unilateral pneumonia (right or left lung);
- bilateral;
- segmental (part of the lung).
There are 3 degrees of severity:
- heavy
- average;
- easy.
According to the features of the course, they distinguish:
- acute pneumonia;
- chronic.
After diagnosis, when it is known what type of pathology the patient has, the doctor determines with the methods of therapy.
Is it possible to be treated at home
If the disease proceeds in a mild form, and it is detected on time, then there is no need for hospitalization. In a hospital, it is necessary to treat pneumonia in children, patients with an acute form, with a late-diagnosed disease and people with cardiac pathologies.
In other cases, after examination by a doctor and prescribing a course of therapy, you can be treated at home.
Breathing exercises
Inflammation causes breathing problems, which is why the body does not get enough oxygen needed for all organs to work. With the help of breathing exercises, you can quickly normalize the condition of the patient with pneumonia.
You can start gymnastics only after examining a specialist and in the absence of contraindications.
You can not carry out breathing exercises:
- in the presence of high temperature;
- with intoxication of the body;
- heart failure patients;
- with oncology;
- people with weakened immunity;
- during a fever.
It is necessary to begin exercises after an acute period of pneumonia in order to accelerate recovery.
The essence of classes is to hold your breath for several seconds after inhaling. The algorithm is simple:
- deep breath;
- delay;
- exhalation;
- deep breath again;
- breath holding, already more than 10 seconds;
- exhale.
Repeat inhalation-exhalation should be 10 times, such courses should be about ten per day every hour.
You can inflate balloons - this is a very pleasant way of breathing exercises. Such gymnastics helps to increase lung capacity, improving the general condition of the patient.
It is important to control the pulse during exercise. If it increases by more than 10 strokes - gymnastics must be stopped.
Antibiotic therapy
Without antibiotic therapy, none of the types of pneumonia can be cured.
Different groups of drugs can be used:
- cephalosporins;
- levofloxacin;
- amoxicillin;
- sulfamethoxazole;
- clavulanate.
The decision on which of the groups to use is made by the pulmonologist, depending on which pathogen caused the inflammation. It is not always possible to establish the exact etiology at the initial stage, therefore, often the prescription of drugs is empirical, based on observations, the course of the disease and the experience of the doctor.
Antibiotic treatment
For therapy, antibiotics in tablets are used:
- Amoxiclav;
- "Sumamed";
- "Azithromycin";
- Cefaxon
- Amoxil.
And also the doctor can prescribe injections of drugs:
- Ceftriaxone;
- Ofloxacin;
- Ampioks;
- Ampicillin
- "Timentin";
- "Cefazolin";
- "Meropenem."
The main rule of antibacterial therapy: as soon as the body temperature normalizes, it is necessary to take the medicine for another 3 days, and not to stop taking it immediately after the condition improves.
The doctor will definitely warn about this, based on the patient's condition. Otherwise, the treatment will not give proper results and complications of pneumonia are possible.
Folk remedies
Together with the main therapy, with the consent of the doctor, alternative methods of treatment can be used. They in no case replace the mandatory antibiotic therapy, but only help to improve the patient's condition.
Healers suggest to use for the treatment of pneumonia:
- herbal teas that improve expectoration;
- cough tinctures;
- compresses for warming;
- plant inhalation;
- ointments with natural ingredients.
When using herbal remedies, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of an allergy to components. Parents of young patients should be especially careful.
If the condition of the patient being treated at home worsens, it is necessary to transfer him to a hospital for daily monitoring and correction of therapy.
Which doctor should I contact
If the patient suspects that he has symptoms of inflammation, it is necessary to consult a specialist in pulmonary diseases. Which doctor treats pneumonia? This is a pulmonologist, it is he who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies associated with lung damage.
The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe additional examinations to make a diagnosis.
Among them:
- biochemical and general blood test;
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the pleural region;
- sputum analysis;
- tomography of the sternum (in severe forms);
- bronchoscopy;
- blood culture (for information on etiology).
How much pneumonia is treated in a hospital
It is necessary to treat pneumonia in a hospital for children, the elderly, as well as patients with a severe form of the disease. Treatment at home will not be effective enough in this case, because you need constant monitoring by the doctor over the patient's condition.
The duration of therapy depends on individual indicators and the clinical picture. A pulmonologist prescribes a treatment that lasts at least 10-14 days. Pneumonia in children is treated for about 4 weeks. But if the form is severe, it is possible to continue therapy up to one and a half to two months, until the pathological symptoms disappear.
What drugs are prescribed in a medical institution
In the hospital, the patient is immediately prescribed medication to eliminate the infection. First of all, the doctor prescribes antibiotics for pneumonia.
In addition to antibiotics, it is necessary to take symptomatic drugs depending on the severity of the condition and the overall clinical picture.
The doctor will prescribe:
- expectorant medicines if sputum is difficult to get out;
- antiviral drugs for certain forms of pneumonia;
- antipyretic, painkillers for fever;
- detoxification agents for serious toxic lesions of the body;
- oxygen therapy procedures - if there is a decrease in lung functionality;
- hormonal drugs in case of toxic toxic shock;
- immunomodulating medications - to strengthen immunity during the period of subsiding of the disease.
Doctors recommend a full course of comprehensive treatment in order to defeat the disease and prevent complications.
The consequences of not treating pneumonia
Doctors insist that a complete treatment of pneumonia in adults and children is necessary, with the passage of a full course of antibacterial therapy. Otherwise, there may be harmful effects to health.
If the disease is not treated or not treated (having stopped the course of therapy earlier than the period recommended by the doctor), then there is a high risk of complications in the operation of all body systems.
Among them:
- local pneumosclerosis (an increase in connective lung tissue);
- pleurisy;
- lung pathology - abscess, edema, gangrene;
- bronchial obstruction;
- acute respiratory failure;
- myocardial tissue inflammation - myocarditis, endocarditis;
- meningitis, encephalitis;
- anemia;
- sepsis, which causes infection of an infection of the whole organism, which leads to an infectious toxic shock.
If you do not take measures to eliminate the infection, death is possible.
Prevention
To make less likely the occurrence of pneumonia, it is necessary, first of all, to lead a healthy lifestyle, which includes:
- good nutrition;
- regular exercise;
- healthy sleep;
- uniform alternation of work and rest;
- giving up bad habits - smoking is especially dangerous, it significantly reduces the resistance of the respiratory system to viral diseases.
As well as doctors recommend vaccinating people at risk - the elderly, with reduced immunity, having diseases of the cardiovascular system and chronic lung diseases. A vaccine is used against streptococcus, which most often causes pneumonia. There is a special vaccine for asthmatic children.
Do not neglect the annual vaccination against influenza on the eve of the epidemiological period. After all, respiratory diseases most often become the precursors of pneumonia. The best period for vaccination is October or November.
For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to regularly wash hands with soap in order to destroy bacteria that can cause pneumonia and also avoid hypothermia. In case of symptoms of SARS or influenza, you should immediately consult a doctor and start treatment to prevent complications of the disease.