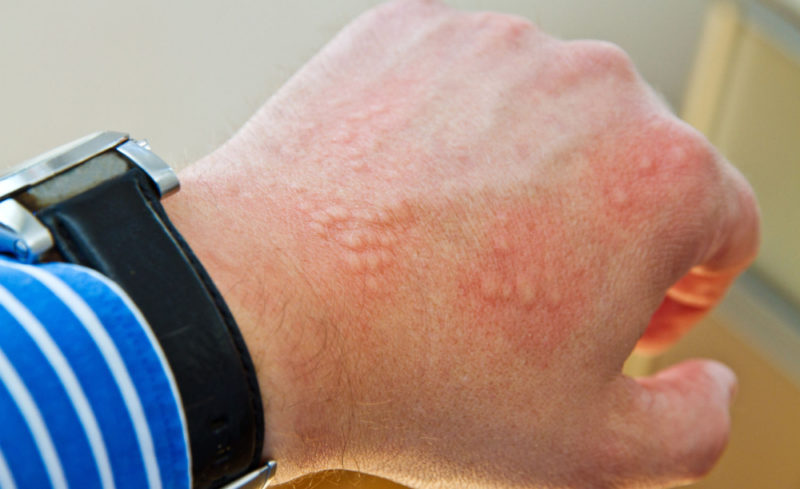
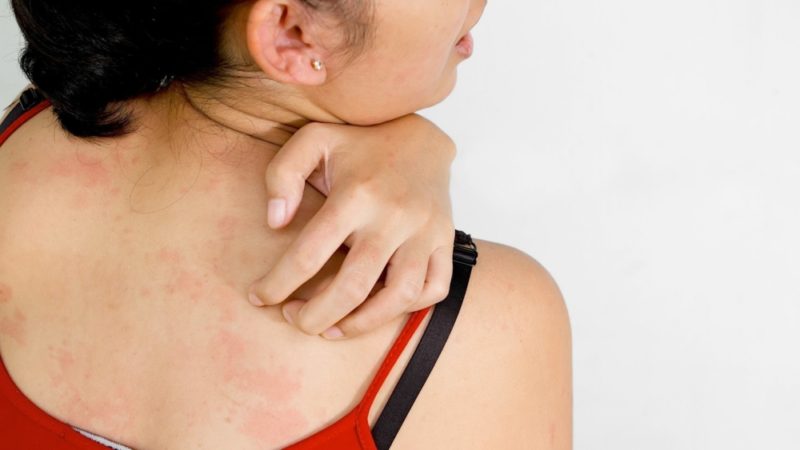
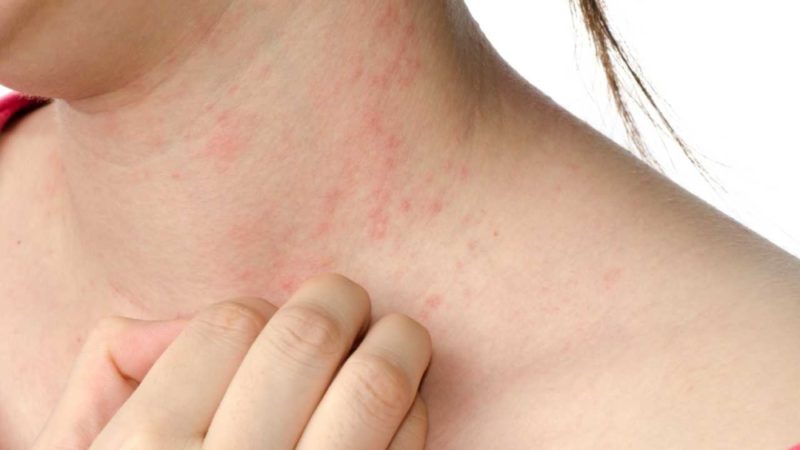
Idiopathic urticaria is an allergic dermatosis, which is manifested by characteristic skin rashes. There is another name - urticaria.
Material Content:
What is idiopathic urticaria
The disease received its first name due to the similarity of rashes with irritation on the skin after contact with nettles. Hippocrates noticed this feature several centuries before our era. However, this name was not widespread. Only a little over 200 years ago, the term became firmly established, although its etiology and pathogenesis have not yet been sufficiently studied.
This diagnosis is made if systemic diseases that can cause urticaria are not detected. The disease occurs in 3% of the world's population, with approximately the same frequency in men and women, adults and children, regardless of racial differences.
But still, women between the ages of 30 and 50 are more likely to get sick.
According to the duration of the course, two forms are distinguished:
- acute (within a few weeks);
- chronic idiopathic urticaria (lasts for months and years).
There is also another classification.
According to her, urticaria is:
- true (as a result of a reaction to a specific allergen);
- pseudo-allergic (chemical or physical effects on the skin);
- contact (arising from skin contact with allergic substances).
Causes of the development of pathology and symptoms
Very often, doctors say that the cause of the disease is unknown, because it’s difficult to understand the mechanisms that trigger the disease.
However, provoking factors may be:
- chronic stress and nervous breakdowns;
- weakened immunity;
- taking certain medications;
- the influence of various allergens (household chemicals, insect bites, plant pollen, products);
- negative environmental impact (for example, minus temperature);
- viral diseases, infections, tumors.
Often, the disease also occurs during pregnancy.
This skin disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- the formation of pink-crimson blisters with clear borders, ranging in size from one and a half to 3-4 cm;
- angioteki of surrounding tissues;
- severe itching;
- burning;
- anxiety and irritability.
An allergic rash is accompanied by swelling and a lot of uncomfortable sensations, so the patient may develop various disorders due to nervous system and even depression. There are also subjective sensations of different intensities in the form of a headache, fever, weakness. The quality of life is noticeably deteriorating, which also leads to social discomfort and unwillingness to contact people due to cosmetic defects.
Dermatosis lasts more than 6 weeks, this is at least. Often, rashes remain on the skin for several months, as there is constantly a new pouring of blisters that will spread to nearby healthy areas.
Diagnosis
Do not delay a visit to the doctor. An allergic reaction is so strong that it poses a danger to life. If the patient suddenly feels severe weakness, experiences increasing difficulties with breathing and swallowing, he needs to urgently call an ambulance.
An experienced doctor can make an accurate diagnosis at a glance. However, he is faced with the task not only to diagnose the disease, but also to establish its root cause. This is necessary to select the optimal treatment method. Therefore, at the first appointment, a dermatologist must conduct an examination and collect an anamnesis.
Almost always, general clinical tests of urine and feces blood are prescribed, as well as parasitological studies. If an allergen or provoking factor is still not found, the doctor will prescribe a referral to narrower specialists - an otolaryngologist, urologist, gastroenterologist. Additional examinations will help diagnose a systemic disease that may be a likely cause of urticaria.
Treatment methods
Treatment of idiopathic urticaria is aimed at reducing the inadequate immune response to the allergen, as well as removing harmful products from the body.
Of the most commonly prescribed medications, mention should be made of:
- antihistamines (well-known "Loratadine");
- sorbents (Enterosgel);
- glucocorticosteroids;
- enzymes (Mezim).
If there is a need for this, the patient is additionally prescribed antifungal, sedative and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Physiotherapeutic methods (electrophoresis, ultraviolet radiation), as well as folk remedies are often used. Also, the patient is recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and try to eliminate things and means from everyday life that can somehow provoke allergic reactions.
Forecast and Prevention
The main thing is not to delay the treatment and prevent the transition of the acute form to the chronic one. In such cases, the prognosis is quite favorable. In rare cases, even a spontaneous disappearance of the disease is possible.
In the case of a chronic course, constantly recurring relapses of the disease can be replaced by rather long remissions, however, the condition can worsen every time.
If each new attack is heavier than the previous, this indicates the approach of idiopathic anaphylaxis.
Preventive measures are very simple.
A person needs:
- eat right, refuse to use allergen products;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- minimize the number of stressful situations;
- give preference to organic analogues of household chemicals with proven hypoallergenic properties;
- choose clothes made from natural materials.
People with this diagnosis should carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations and undergo routine examinations in time.