Many are faced with chronic tonsillitis - usually it begins to manifest itself in preschool and primary school age, and lasts for many years. The development of this disease in the absence of adequate therapy is fraught with serious complications. Everything that you should know about the treatment of chronic tonsillitis in adults, we will consider in this article.
Material Content:
Causes of the disease and risk groups
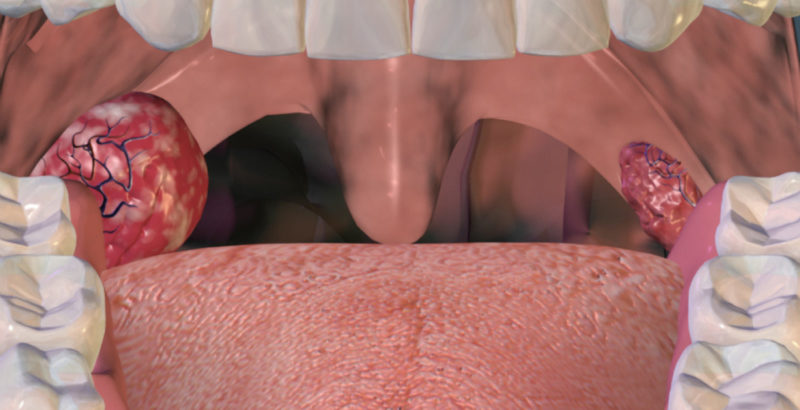
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, mainly palatine, provoked by bacterial or viral infections. Palatine tonsils or tonsils are a kind of “barrier” that protects the respiratory tract from the penetration of various pathogens, and they also perform the function of hematopoiesis. Acute tonsillitis is known as angina, it occurs due to inflammation of the tonsils after infection with bacteria (staphylococci and streptococci), viruses or fungi. With regular and frequent relapses of the acute process, as well as with improperly conducted treatment, tonsillitis can go into the chronic stage.
In the latter case, the tonsils are most of the time in an inflamed state, eventually lose their protective function and themselves become a focal point of infection, so it is extremely important to start treatment of the pathology in time.
The main causes of the development of chronic tonsillitis are as follows:
- Incorrect treatment scheme for tonsillitis.One of the most common causes is incomplete treatment, when the patient ceases to follow the doctor's recommendations after the symptoms of acute inflammation disappear.
- A prolonged decrease in the body's immunity.
- Other chronic infections of the respiratory tract and oral cavity.
There are statistics that up to 35% of the population of Russia suffer from chronic tonsillitis, and in the North-West region due to the climate this figure reaches higher values.
An interesting fact is that there is a connection between tonsillitis and chronic fatigue syndrome, which is still not well understood, but is already considered one of the most serious problems of mankind.
The risk group for the development of chronic inflammation of the tonsils among the adult population includes those who regularly communicate with a large number of people by type of activity: doctors, teachers, sellers, and others. The risk of getting a sore throat or respiratory virus in winter or in springtime is especially high, when the body is struggling with the threat of infection due to weakened protective mechanisms.
Symptoms and clinical presentation
Persistent symptoms of chronic inflammation of the tonsils occurs usually after a few acute tonsillitis.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis include:
- hypertrophied tonsils (oversized, friable, with uneven edges);
- redness and sore throat, observed not only during the acute phase of SARS or sore throat;
- swollen cervical and submandibular lymph nodes - felt on palpation, usually painful;
- long-lasting elevated temperature, reaching subfebrile values (up to 37.5 degrees);
- too long a period of rehabilitation after colds and seasonal flu;
- the appearance of purulent contents in the gaps of the tonsils;
- general weakness, fatigue.
In most cases, chronic tonsillitis is characterized by frequent tonsillitis (on average twice a year), but there is also a non-angina option for the development of the disease, which is much less common.
In the absence of timely and proper treatment, tonsil inflammation can go into a decompensated stage. This is a more serious condition, fraught with serious complications such as damage to the kidneys, joints and the development of acquired heart defects.
Methods and treatment regimens for chronic tonsillitis
To diagnose the disease, you should consult a therapist and get a referral to an ENT doctor. An anamnesis is collected, sowing tonsils on the microflora and a general clinical blood test. Based on the information obtained after the examination, the doctor makes a decision on the desired method of treatment.
Tonsil inflammation
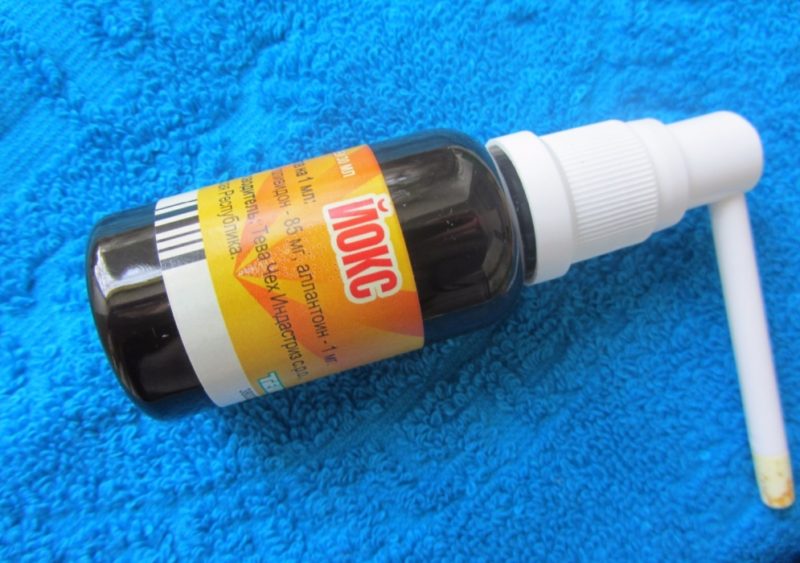
The most effective drugs for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis are considered antiseptics in the form of sprays, aerosols or rinses. The most commonly used solution is furatsilina or iodinol rinses, sprays Hexoral, Yoks, Proposol or their analogues.
In the period of exacerbation, antibiotics are used to treat chronic tonsillitis: penicillin group drugs are usually prescribed. A specific medicine should select the ENT based on the information obtained from the analyzes. With antibiotic therapy, it is important to complete the course of treatment, even if the symptoms of the disease are stopped. Otherwise, the resistance (resistance) of pathogenic microflora is produced and the disease is more difficult to treat.
Do not self-medicate - this can be fraught with complications.
Folk remedies
Therapy for inflammation of the tonsils should always be comprehensive. Despite the fact that there are a large number of folk remedies that have proven themselves in the treatment of tonsillitis, you can not be limited only to them. Similar techniques are good for adjunctive therapy and symptom relief.
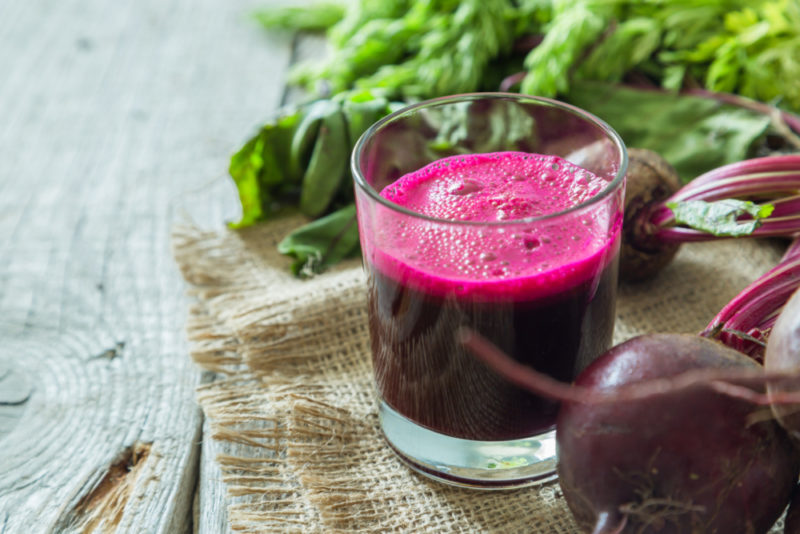
Beetroot broth.Porridge from finely grated root vegetables is poured with boiling water in a thermos and left for 5-6 hours. After being filtered and used for regular rinses.
It helps to alleviate the condition of the sea buckthorn berry. Fruits are recommended to be consumed fresh, slowly chewing one at a time, approximately 10 pieces at a time.
A great tool that many doctors advise using for treatment at home is honey. It has a softening and enveloping effect, calming the inflamed mucosa. It is recommended to add the bee product to warming tea or use it to gargle (at the rate of 3 tablespoons per glass of warm water). With caution, honey should be used by patients with a tendency to allergic reactions.
Very useful for rinsing with tonsillitis medicinal herbs:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort
- currant leaves;
- eucalyptus.
The compositions are mixed in various combinations, brewed with boiling water, well insisted and used for washing and rinsing.
Removal of tonsils
About half a century ago, tonsillectomy was considered a common practice for any form of development of chronic tonsillitis, however, such a treatment regimen is not approved by doctors today: tonsils are an organ that performs a protective function in the body, and their complete removal can seriously harm.
However, in those cases when the organs themselves, due to the long-running chronic process, become gates for the infection to enter the body, a decision is made on surgical intervention. Manipulations are performed if conservative methods for the treatment of tonsil inflammation do not bring any result.
There are a number of main indications, on the basis of which the ENT doctor decides that surgical intervention is required:
- The risk of complications such as rheumatism, heart defects against the background of frequently occurring tonsillitis, glomerulonephritis, etc.
- Toxic and allergic forms of the disease, the most severe.
- The appearance in the tissues of the tonsils of the tonsils with abscesses.
- Frequent (up to 4–5 times) exacerbations in the form of a sore throat with adequate therapy.
Surgical removal of tonsils is performed in medical facilities, usually under local anesthesia. The operation itself takes time up to half an hour.
The duration of the rehabilitation period is about a week. After removal of the glands, patients are recommended a sparing diet that excludes hot, solid, salty or spicy foods. Alcohol, tobacco, and vocal cord stress are prohibited.
Physiotherapeutic treatments
Physiotherapy is widely used in a comprehensive treatment regimen for chronic tonsillitis.
Most patients are prescribed washing tonsil lacunae in order to eliminate the occurring purulent deposits. It is performed using antiseptic solutions at a reception by a therapist or in a day hospital. The average duration of treatment is up to 10 procedures.
A positive effect is exerted by ultraviolet light on the tonsils in order to disinfect the tissues of the throat.
Another good physiotherapeutic method is a gentle warming of the throat. It can be performed at home. To do this, take ordinary buckwheat, warmed up in the oven and put into a clean bag of cloth. Cooling to a warm, tolerable temperature, apply for 10-15 minutes to the throat.
One of the modern methods of physiotherapy is the impact on the affected tonsils with a laser. This method of treatment reduces edema and allows blood to circulate better.
Preventative measures
In order to prevent the occurrence of chronic inflammation of the tonsils, it is recommended first of all to strengthen the immune system. You can not neglect hardening and physical activity, if necessary, you can ask your doctor to prescribe drugs that stimulate the immune system.
Avoid overcooling - in winter, make sure that the shoes are always warm and dry, and the clothes are appropriate for the season. Multivitamin courses will support the body and help to adequately resist infections in the cold season.
With the development of acute conditions, such as angina, flu or acute respiratory viral infections, it is necessary to strictly observe the doctor’s instructions, drink the courses of drugs to the end, if necessary, do not throw treatment in the middle. It is very harmful to endure an ailment on the legs, going to work or study. It is better to take sick leave to avoid the severe course of the disease.
Chronic tonsillitis in adults is one of those conditions that is easier to prevent than completely cure. A healthy lifestyle is the best way to avoid many diseases.