Material Content:
- 1 How does an allergy to cold manifest?
- 2 Causes of Cold Allergies
- 3 Symptoms of a cold allergy. Where is it manifested?
- 4 Family cold syndrome
- 5 Atypical hereditary cold allergy
- 6 Diagnostics
- 7 Cold allergy medication
- 8 Treatment of cold allergies with folk remedies
- 9 The benefits of hardening, like accustoming the skin and blood vessels to the cold.
How does an allergy to cold manifest?
Cold allergy is a pathological condition of the body that occurs in people with abnormal intolerance to low temperatures.
It occurs in the following cases:
- If a person is in the cold in the environment (in a harsh wind, humid cool air, frost). Cold allergies in children, especially infants, can lead to an attack, even with normal ventilation of the room or the transition from a place in the sun to a shadow.
- In contact with cold objects, including snow, ice, water, rain, and even a cold bed.
- While taking chilled drinks and meals.
Moreover, the time of development of painful signs varies depending on the form of the disease from 1 - 10 minutes to several hours, in rare cases - days.
Features of Cold Allergy

Many experts attribute this disease to pseudo-allergy, since the mechanism of its development differs significantly from other allergic reactions.The fact is that the allergen that excites the body’s response does not exist, there is an effect of the physical factor - cold.
Since an allergy to cold is manifested in local changes on the skin, similar signs of urticaria, itchy blisters, edema, erythema (redness), the disease is also considered as one of the subspecies of physical urticaria.
But cold allergies also cause more severe general organ disorders, which require special therapy. Therefore, pathology is not at all as harmless as it might seem. Yes, in most cases, it is manifested by sneezing, skin rashes, spasms, shortness of breath from the respiratory system, progressing to "peak" conditions. She is able to kill a person, like the most abnormal frost.
Treatment of a chronic cold allergy lasts from several months to a number of years, but in half of patients the disease can stop spontaneously over time. Almost 85 - 90% of patients at 5 - 7 years of age, the severity of the disease is significantly reduced, especially with active therapy.
Risk group
It was found that in almost 70% of the disease affects girls and women. Most often, the primary signs are diagnosed at 22 - 26 years of age. The disease is rarely observed in children younger than 2 to 3 years old.
It is noted that in every third patient a cold reaction develops with the already existing sensitization (especially high sensitivity) of both skin receptors and nerve centers to the effects of allergic and physical irritants. Therefore, it is often the case that a patient is simultaneously diagnosed with cold allergy in combination with various dermatitis, with thermal, cholinergic urticaria, and utricarian dermographism.
Causes of Cold Allergies
Classification
Two types of cold allergy stand out:
- Acquired or secondary, that is, not associated with genetic abnormalities, and occurring most often in adulthood.
- Hereditary (i.e., genetic conditional) or familial cold auto-inflammatory syndrome. Signs are recorded already in infants. This type of pathology is transmitted to a child with a mutant gene from one of the parents through an autosomal dominant type of inheritance.
The types of the acquired form of cold allergy are isolated:
- local, local, in the form of cold urticaria, the symptoms of which appear only on a certain and limited part of the body.
- forms of immediate type and with a delayed reaction, characterized by the time of onset of the first symptoms;
- systemic (generalized) form - the most severe reaction of the body.
Causes

Pathogenesis, that is, the main causes and features of the process of manifestations of a pathologically acute reaction to low temperature, is not exactly established and continues to be investigated.
It is determined that the development of this type of allergy is associated with:
- With the development of special protein compounds - cryoglobulins, activating the "release" of histamine, the main hormone that regulates the body's response to aggressive factors.
- With increased secretion of acetylcholine and abnormal susceptibility of cells to it.
- With a mutation of a special gene (in the hereditary form), which, through the transformation of the cryopirin protein, leads to the active release of interleukin proteins that stimulate inflammatory reactions.
However, these pathological mechanisms are "triggered" only when exposed to external factors that create the conditions for their development:
- skin contact with chilled objects, snow, water during work, cleaning;
- hypothermia of the whole body in an environment of low temperatures of air or water (bathing, being outdoors in cold weather, in the rain);
- ingestion of frozen foods (fruit ice, ice cream), drinks (sparkling water, smoothie, beer, cocktails).
Internal predisposing factors include:
- low level of immune defense - local and general;
- severe diseases of an infectious, inflammatory nature;
- vitamin deficiencies, stresses that cause weakening of the immune system;
- viral mononucleosis, mumps, measles;
- lymphoid leukemia, hepatitis C, mycoplasma pneumonia;
- cancerous processes;
- pathologies of autoimmune origin, vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- thyroid function disorders, neurological disorders;
- dermatological diseases;
- parasitic infections, including aggression of ticks, helminths;
- taking Griseofulvin, oral contraceptives, tetanus vaccination;
- serum sickness, hemophilia, syphilis, stinging venom.
Symptoms of a cold allergy. Where is it manifested?
How to recognize a disease whose symptoms are diverse and depend on the type of cold allergy, severity, concomitant diseases, age of the patient?
Symptoms in a typical course of local cold allergy
All skin areas that respond to low temperatures are characterized by:
- fast, within 1 - 5 minutes, the onset of skin changes;
- urtical manifestations, similar to signs of a nettle burn (urtica - nettle, lat.) in the form of:
- itching, burning, tingling;
- the formation of edema in the place of touching a cold object;
- severe redness (erythema);
- the appearance of flat whitish or bright pink blisters, or a small red rash;
- peeling, which occurs later;
- the appearance of bruises in the areas of rashes after 24 - 48 hours is often.
Usually, symptoms reach a maximum when warming the affected areas, when moving from a cold place to a warm place, and not only in cold weather, but also in cool, damp weather.
Abnormal changes in the skin subside within 0.5 - 2 hours.
Sometimes the phenomena of urticaria occur later (after 10 - 20 minutes) and last up to 7 - 12 days.
The next exposure to cold (local or general), allergic manifestations usually increase.
Features of cutaneous local manifestations of the disease in a typical form are shown in the table.
| Localization | Manifestations |
|---|---|
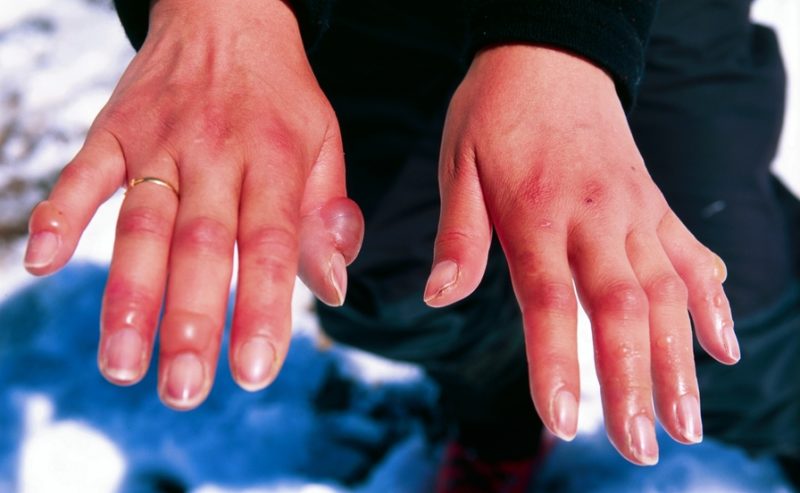
| On hands | It begins with mild itching, dryness, cracks in the skin. As the disease progresses, there are: • severe itching, tingling and burning; • the appearance of itchy pink flat blisters of various sizes, filled with liquid; • noticeable swelling of the hands and fingers, peeling of the skin. Often, the signs are mistaken for the symptoms of dermatitis, but in contrast, cold changes on the skin intensify when heated (moving to a warm place, wrapping with a towel, warming up in electrical appliances, stoves, in warm water), and after 30 to 90 minutes (in typical cases) , the skin becomes clean. |
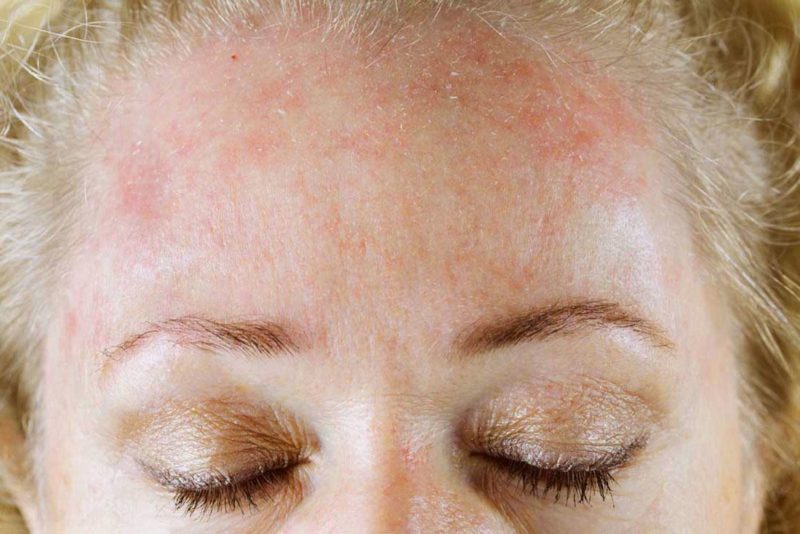
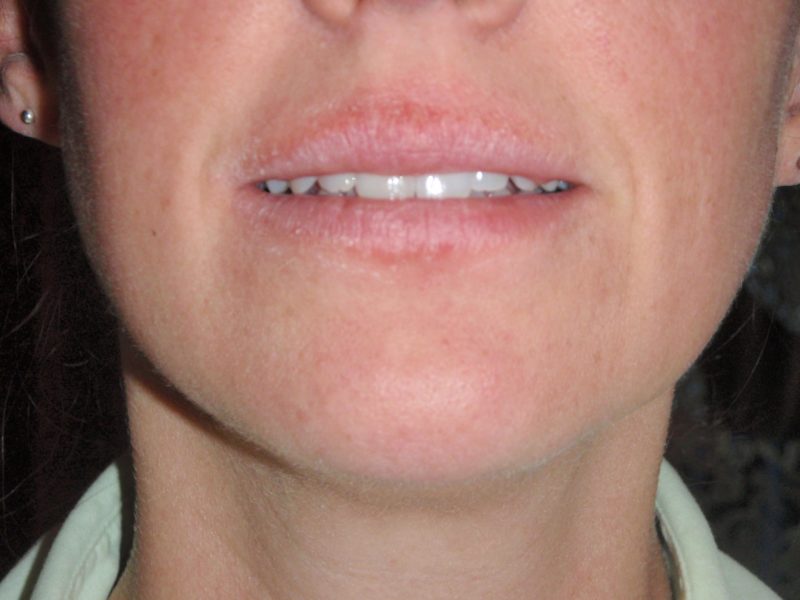
| On the face | • erythema (redness) of the cheeks, chin, skin in the nasolabial fold, skin soreness; • severe burning, tightness, a feeling of dryness; • edema, swelling of the skin to varying degrees; • itchy rashes - red dots or similar to herpes - in the form of dense vesicles of pink and whitish color with swelling around them. Edema and rashes appear around the lips, on the red border, especially after eating cold dishes and drinks. Manifestations of a cold allergy in the face and especially lips are dangerous due to sharp swelling of the tongue, oropharynx and larynx, which can lead to blockage of the airways and asphyxiation. |
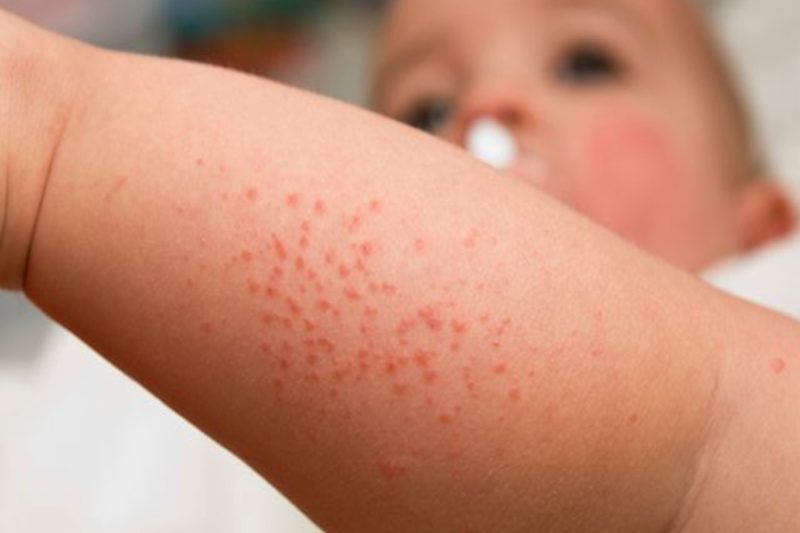
| On foot | In the area of the legs, especially on the hips and calves, there are: • small and large itchy and painful rashes of red-pink color; • swelling and hyperemia in the lesion, an unpleasant sensation in the knee joints; • fine plate peeling. Children have red spots, vesicles usually capture the area under the knees, the inside of the calves and hips. |
Atypical course of local cold allergy
Reflex urticaria
A feature of this condition is the appearance of a small-pointed red-pink urticaria rash and blisters not in the most chilled area, but around it. At the same time, skin subjected to aggression of cold is not affected.
Delayed Allergy

It is characterized by impaired timing of the appearance and subsidence of skin changes. An abnormally slowed skin reaction to cold aggression is characteristic of such a condition - ranging from 3 to 4 hours to 2 days, as well as prolonged retention of all symptoms for up to 7 to 14 days.
Such an atypical reaction warns of the possibility of other serious disorders that require immediate diagnostic measures.
Systemic Allergy to Cold
The severity of the general manifestations is determined by:
- age and sensitivity of a person to cold, histamine, acetylcholine;
- area of hypothermia;
- intensity and time of low temperature exposure.
- existing diseases of blood vessels, respiratory organs, heart.
In addition to skin changes, when exposed to cold, in many patients, low temperature provokes systemic (corporate) signs of cold damage:
- sneezing, mucous discharge from the nose;
- swelling and complete nasal congestion;
- sore throat, paroxysmal dry cough;
- lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids, itching and irritation of the conjunctiva, intolerance to light;
- itching throughout the body, small blistering rashes;
- feeling of fatigue, depression, neurosis.
The patient has several symptoms or all of the symptoms simultaneously or sequentially.
In acute individual intolerance to low temperature, if cooling of the whole body occurs, a generalized form of cold allergy develops.
This is a very dangerous condition that borders on an anaphylactic reaction and is characterized by:
- bursting pain in the back of the head, forehead area;
- shortness of breath with shortness of breath;
- dizziness, tinnitus;
- nausea, weakness, joint pain;
- the reduction of the muscles of the face, neck, fingers.
Subcooling anaphylaxis
Prolonged cooling of a large area of the body leads to serious disorders due to the release of large portions of histamine, acetylcholine into the blood. With such an abnormal state and the spread of the process, dangerous changes occur in the body, up to the anaphylactic reaction that threatens a person’s life.
For this condition, acute local and general manifestations are characteristic:
- fusion of blisters into extensive dense swelling throughout the body, accompanied by acute itching;
- Quincke's edema - swelling of the lips, eyelids, internal organs;
- swelling of the tissues of the larynx and tongue, leading to asphyxia (very often in childhood due to narrow airways and friability of the tissue of the larynx and mucous membrane);
- shortness of breath, cough due to spasm of the bronchi and swelling of the respiratory tract, larynx and pharynx;
- severe fatigue with nausea, bouts of vomiting;
- pain and feeling of fullness in the head;
- rise in temperature to 38 - 39C with chills;
- blanching of the skin with cyanosis in certain areas, more often in the area of the nasolabial triangle, earlobes, fingers;
- heart palpitations, rhythm disorder (arrhythmia);
- cramping in the stomach, abdomen, diarrhea;
- acute drop in blood pressure, loss of consciousness, coma.
In practice, deaths of patients exposed to aggression of cold were recorded: after freezing, drinking cold water, frostbite, and being in cold water.
Family cold syndrome
This pathology is associated with gene mutation and is already diagnosed in infants up to 6 - 9 months old.
An allergic attack usually develops even with mild hypothermia of the body (when ventilating the room), almost all (93 - 94%) when bathing, taking chilled foods and drinks, after long games in a strong wind, at low temperature (including the positive temperature range).
Symptoms
A specificity of family cold allergies is the delayed (delayed) appearance of skin and systemic changes - from half an hour to 2 to 3 hours after a cold attack and their long-term preservation, up to 24 - 48 hours.
Characteristic features:
- acute itching, red dense spots, watery blisters, burning;
- recurring episodes of high fever, chills;
- systemic manifestations in the form of lacrimation, conjunctivitis;
- joint pain, in severe cases — arthritis of large joints;
- elevated white blood cell count;
- children often experience nausea, acute thirst, sweating, irritability, damage to the central and peripheral nervous system;
- there is an increased ESR in the blood and a high concentration of C-reactive protein.
Manifestations with a hereditary form of allergy to cold increase within 7 to 9 hours, gradually subsiding by the end of 1 to 2 days.
A diagnostic feature of hereditary pathology is the negative result that is obtained during a standard cold test by applying ice to the skin to provoke local allergies.
In addition, with this form of pathology, edema, an urticaria rash often appear even later - within 8 to 40 hours after a cold exposure, which makes it difficult to diagnose.
Atypical hereditary cold allergy
The initial signs of the disease are observed already in infancy. The specificity of the clinical picture of atypical allergy is expressed in the absence of such general signs as nausea, fever, arthralgia (joint pain).
In this form, the main symptoms are manifested by convulsions, loss of consciousness, severe, dense swelling of the tissues. Babies are often diagnosed with laryngeal edema.
Diagnostics
Often, pathology is confused with dermatitis, the common cold, and respiratory viral infections, because when a person is weakened by vitamin deficiency, dysbiosis, and other diseases, including dermatitis, allergic, vascular, and infectious pathologies, a cold allergy is always more severe and with frequent exacerbations.
In the case of a typical form of cold allergy, the disease is diagnosed by conducting a provocative test (Duncan test).
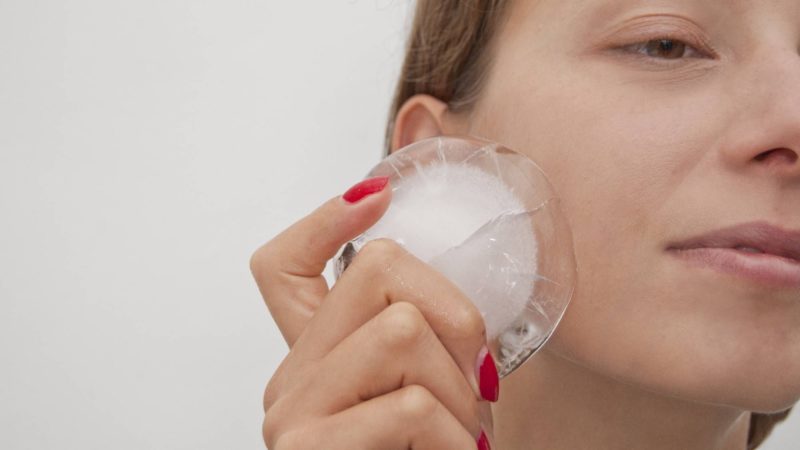

For this, an ice cube is applied to the skin of the forearm from the inside for 3 to 4 minutes, observing the reaction. The ice must be placed in a thin plastic bag so that there is no direct contact with the skin in order to avoid an incorrect diagnosis in case of a positive test. This can happen if the patient does not have a cold allergy, but an aquagenic urticaria (water allergy).
After 10 minutes, the result of the Duncan test is assessed as positive if a dense bladder, erythema, itching, burning, and sometimes a point rash appear at the site of ice application.
In people with abnormal cold intolerance, skin manifestations can develop within 30 seconds, in others, the reaction is noted after 20 - 30 minutes. In patients whose body reacts only to lowering the temperature of the whole body, or with a hereditary form and atypical development of pathology, local signs may not occur at all.
If a provocative test is unreliable, a blood test should be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
If the Duncan test does not show anything, but the patient later shows characteristic symptoms, the diagnosis is confirmed when cold antibodies (agglutinins), cryoglobulins, cryofibrinogen, and sometimes paroxysmal hemoglobinuria are detected in the plasma.
Family cold syndrome (in contrast to the typical form) is characterized by an increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and an increased concentration of C-reactive protein.
Today, competent doctors do not use other types of tests for diagnosis in the form of finding the patient for 10 to 15 minutes without clothes in the room at + 4C or lowering their hands to the elbows in cold water, since there is a high risk of a systemic reaction with the development of severe general organ symptoms.
Cold allergy medication
How to treat cold allergies correctly?
To mitigate the manifestations of a cold attack, the patient is treated comprehensively, providing for the use of both external drugs and oral medications aimed at eliminating various symptoms.
Local preparations
An itchy rash, blisters, severe redness, soreness and swelling are removed with ointments, gels, sprays, creams.
Among them: Nezulin, Fenistil-gel, Soventol, Protopic, Gistan, La Cree, Elidel, Radevit, Psilo-balm, Skin Cap.

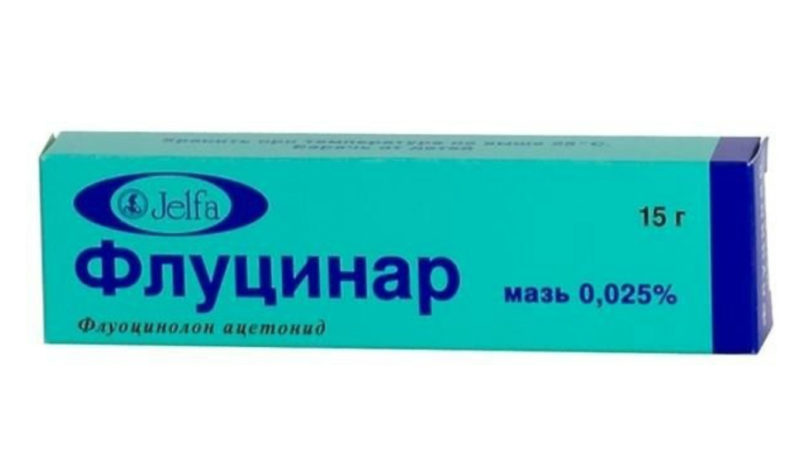
Of hormonal ointments with severe edema, pain, painful itching, it is allowed to take short courses (under the supervision of a dermatologist): Flucinar, Hydrocortisone, Sinaflan, Laticort, then the stronger Gistan N, Momat, Sinaf ointment, Acriderm GK, Celestoderm, Lorinden S, Advantan , Eloc. And the most powerful glucocorticosteroids Cloveit, Dermoveit.

Medicines in tablets and injections
Inside appoint:
II-III generation antihistamines that reduce the response to histamine release, reduce inflammation, itching, swelling: Fexofenadine (Allegra), Claritin, Erius, Zirtek, Gismanal, Tofrin, Cetirizine, Cyproheptadine, Tsetrin, Levocetirizine.
If they give a weak effect, use the means of the 1st generation: Akrivastin, Diphenhydramine, Diazolin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Pipolfen, Cyproheptadine. Although the drugs have a certain number of side effects, they can quickly relieve painful symptoms.
In case of acute allergic attacks, antiallergic drugs are injected.
With a long-running allergy with frequent exacerbations, Ketotifen, Ebastin can help.
A more pronounced therapeutic effect is observed with a combination of antiallergic medicines of the 1st generation with new drugs of the 3rd-4th generation.
If the patient does not have a positive response to antihistamines, a diagnosis of cold cholinergic urticaria is possible.
In this case, apply:
- H2 receptor blockers: cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine;
- preparations with m-cholinergic antagonists: Belloid, Cyproheptadine, Bellaspon, Bellataminal.
Hormonal medicines.
Glucocorticosteroids are usually prescribed for a short time (up to 7 days) to patients who do not respond to antiallergic therapy, and for a long time - in severe forms of the disease and at high risk of acute anaphylaxis. Drugs of choice Prednisolone and Dexamethasone.
Additional medicines
If frequent exacerbations deplete the nervous system, the patient suffers from neurosis, insomnia, severe itching, appoint:
Antidepressants (Paxil, Doxepin, Sibazon, Fluoxetine), which are combined with the first 4-6 weeks of use with tranquilizers-benzodiazepines, which relieve side effects of antidepressants.
Treatment of familial form of cold urticaria
With severe manifestations of the diagnosed hereditary cold syndrome of autoimmune origin, currently use:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoid therapy in high doses;
- drugs with inhibitory effects on the immune system: Cyclosporin, Omalizumab (Xolar)
- antiviral interferon beta, which in 85 out of 100 patients leads to almost complete elimination of cryoglobulins in plasma and the elimination of severe symptoms;
- Interleukin-1 blocker - Anakinra, showing a pronounced therapeutic result;
- androgens.

other methods
Other methods used in patients with severe exacerbations include:
- Extracorporeal cleansing of blood from cryoglobulin proteins.
- Autolymphocytotherapy is a method that eliminates the cold allergy of people of any age, with contraindications to other treatment options. The patient is injected subcutaneously 8 times with lymphocytes extracted from his blood. The cure rate for the disease is almost 90%.
Acute anaphylactic reaction to cold
Situations in which cooling causes a state similar to anaphylactic shock threaten the patient’s life and require immediate subcutaneous injection of Adrenaline at the exact age dosage, the introduction of a large dose of prednisolone, as well as other drugs that are mandatory for use in anaphylactic shock.
Treatment of cold allergies with folk remedies
Any home-made recipes using natural remedies have only an auxiliary value, especially for moderate to severe illness.
Important! When treating cold allergies with folk remedies, always remember that herbs, beekeeping products and other active natural substances can worsen the course of the disease, cause additional allergy manifestations. Some natural remedies are not approved for oral use in diseases of the kidneys, heart, liver, gallstone disease, have an abortive effect and are absolutely contraindicated for pregnant women.
Common recipes:
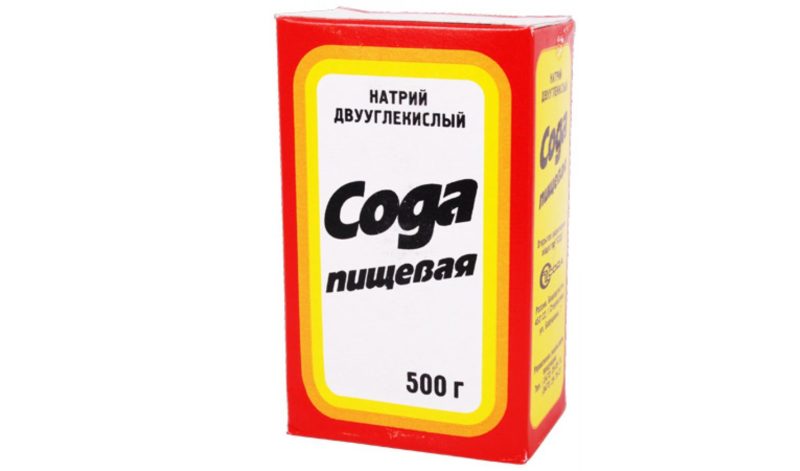
- With severe itching, you can use a solution of 1 teaspoon of soda in 200 ml of water, gently treating the itchy areas.
- Infusion of lingonberry leaves. Pour boiling water (glass) 1 tablespoon of lingonberry, insist 60 minutes and take a quarter cup 2 times a day.
- Infusion of nettle flowers. A tablespoon of inflorescences is poured with a glass of boiling water, insist for 30-60 minutes and drink after meals 150 ml up to 3-4 times a day warm.

Besides:
- Wash your face with warm infusion and wipe the affected area with it.
- Lubricate exposed areas of the body with fatty creams containing vitamins A and E. You can use high-percentage butter or vegetable oil.
- Before going outside in the cold season, never use moisturizers: the freezing water contained in them will only accelerate the manifestation of allergies.
- In cold weather, put badger fat, baby fat cream on your face and hands.
The benefits of hardening, like accustoming the skin and blood vessels to the cold.
Important! Hardening in severe manifestations of the disease, especially with its hereditary nature, or in children of an early age group, is a deadly event.
A low-temperature allergy against the background of general cooling passes with a massive release of histamine, and the patient, even after a cool shower, douche, bathing, can die due to the defeat of the whole body and cold shock.

All warnings on hardening are particularly relevant for children in whom an acute attack occurs suddenly and unpredictably.
Babies with cold urticaria up to 3 - 4 years old are prohibited from any preventive measures associated with exposure to cold.
Patients older than 4 to 5 years can gradually and with the greatest care accustom the skin vessels to the effects of low temperature. To do this, hardening begins with wiping the hands, feet and face with cool water. This is done with careful monitoring of any skin and general changes. Approaching the “threshold” temperature, when primary abnormal signs appear on the skin, hardening is limited by the limits of this temperature, observing. If the "cold threshold" increases over time (the reaction at this temperature no longer bothers the patient), begin the next stage, slowly lowering the degree.
Next, they carefully proceed to hardening with dousing of the hands, feet and face, moving very slowly to individual areas of the whole body.
Important! With any hardening procedures, you should be prepared to immediately stop the process, and if an attack begins, have all the necessary medicines to stop it.
It is strongly not recommended to start with pouring the whole body, especially with the use of a shower, since pressure on the skin with a jet of water can cause, in addition to cold allergies, physical urticaria.












