An ailment that affects an important organ of the human body - the brain - is called purulent meningitis. Caused by the vital activity of certain bacteria, this pathology can provoke multiple complications. Can purulent meningitis be traced, is it subject to therapy?
Material Content:
Causes of purulent meningitis
Purulent meningitis is provoked by meningococci (20% of all cases), hemophilic bacillus (50%) and pneumococcus (13%). In other words, the nature of this ailment is bacterial, the manifestation of the main symptoms is provoked by microorganisms.
Additional factors contributing to the development of meningitis include:
- sinus injuries;
- past stress;
- a sharp change in climate;
- ARVI;
- debilitating physical activity;
- hypovitaminosis.
Did you know? 5-10% of adults are considered carriers of meningococci. At the same time, they themselves do not get sick, but pose a potential threat to others. In crowded places, the risk of infection increases to 60%. It is for this reason that infection is more often monitored in schools, barracks, kindergartens and more.
Doctors share secondary and primary purulent meningitis. Infection occurs by airborne droplets and directly by contact due to contact with patients.
On a note! Parents often scare meningitis with naughty children who do not want to wear a hat in the cold season. These fears are fully justified, and the hat is, indeed, an essential item in winter.But the chain of cold-cold-meningitis is not justified: the cause of the development of purulent pathology is microorganisms, and not weather conditions.
Symptoms in children and adults
Another common myth is the claim that meningitis is an exclusively childhood illness. This is a mistake, since people of different ages can be affected by this pathology.
The acute onset of the pathology is accompanied by a meningial syndrome, which includes:
- rapid increase in temperature (40 ° C);
- nausea
- hemorrhagic rash;
- repeated vomiting;
- severe headache;
- delirium, impaired consciousness;
- chills;
- optic nerve disorders
When the inflammation of the membranes of the brain gradually passes to the brain substance, the patient is monitored for meningoencephalitis. The process is accompanied by increased muscle tone, impaired speech and memory, paralysis, hallucinations and more.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
In order to diagnose purulent meningitis, the following diagnostic measures are performed:
- Inspection by a neurologist. Typical signs of meningeal syndrome, focal symptoms may indicate meningitis.
- Lumbar puncture.
- Blood test, cerebrospinal fluid.
- Smear microscopy.
- Analysis of elements of skin rash.
For a more accurate diagnosis, an X-ray of the lungs and paranasal sinuses is performed.
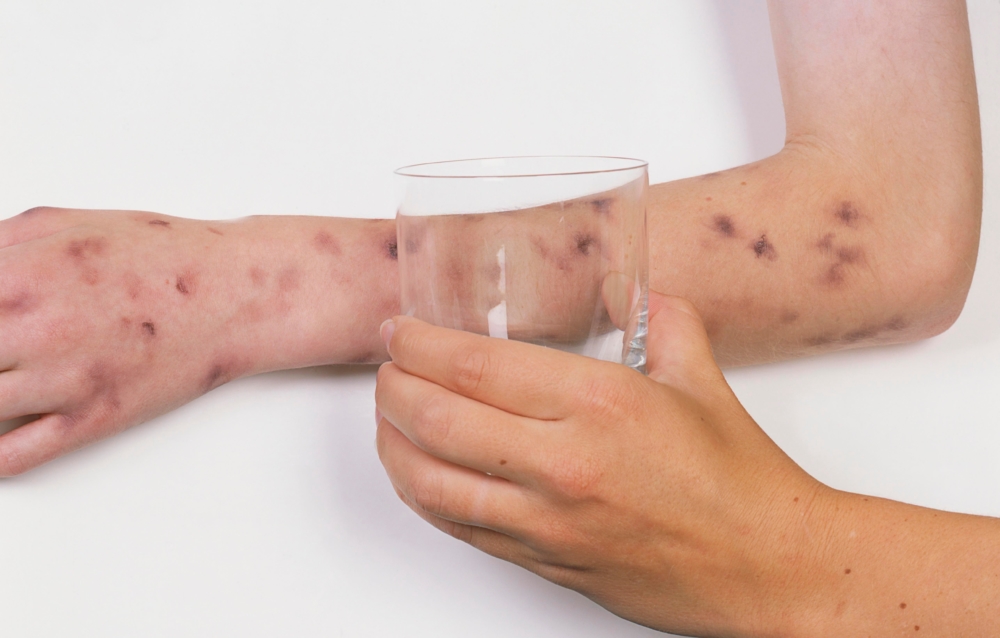
Advice! The simplest diagnosis of meningitis can be done at home. The disease caused by meningococcus provokes a characteristic rash on the patient's body. Having applied a glass to the patient’s skin, you need to observe skin spots. If the cause of their occurrence is not meningitis, the spots will turn pale from pressure. If the rash appears through the glass as brightly, you should immediately consult a doctor: with a high degree of probability, these manifestations are characteristic of meningitis.
Defeat purulent meningitis involves a hospital stay. A similar diagnosis requires the appointment of antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime, etc.).
If the etiology of meningitis is not defined, aminoglycosides (Kanamycin, Gentamicin) are administered intravenously. A severe form of the disease requires the introduction of antibiotic intrarectal administration.
To reduce cerebral edema, dehydration drugs (Furosemide, Mannitol) or glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) can be prescribed. Sometimes the symptoms of meningitis are eliminated exclusively by surgery: debridement, frontotomy, etc.
Prognosis for recovery
Purulent meningitis is fatal in about 15% of cases. But subject to the early treatment of the disease, a favorable prognosis and elimination of symptoms that are dangerous to health and life are guaranteed.
Early symptoms and therapy will also help to avoid all sorts of complications, manifested against the background of past inflammation of the brain. Measures to eliminate the alarming signs should be taken on the first day after the onset of the disease.
Possible complications
Possible complications associated with meningitis include:
- pyelonephritis;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- sensorineural hearing loss;
- asthenia;
- cystitis.
The most dangerous consequence of meningitis is recognized as cerebral edema. This condition can provoke an increase in pressure in the brain stem and an increase in the centers located here. Edema is observed 2-3 days after the onset of the disease, but a fulminant variety of the disease affects a person in a matter of hours.
Prevention
The basic method for the prevention of purulent meningitis is vaccination. In the Russian Federation, these vaccinations are carried out at the request of the patient or the available indications, since they are mandatory.
Note! Unvaccinated people should be aware that meningitis is not a disease to which immunity forms. A person who has had an illness once, risks being infected again.
Vaccinations against hemophilic infections are given to children 3 months to 5 years old.Vaccinations are also subject to people suffering from immunodeficiency conditions that developed against the background of HIV, who underwent spleen removal, cancer, and so on. For children under 1.5 years of age, vaccination can be recommended for a number of indications, especially if the disease was monitored by his relatives.
Modern medicine can eliminate the symptoms of purulent meningitis and protect the patient from the development of complications associated with this disease. However, this does not at all reduce the danger of meningitis to human health and life. The main method of preventing this disease is considered timely vaccination.