When choosing medications, experts recommend paying attention to such parameters as safety, tolerability and effectiveness. Ciprofloxacin eye drops meet all reliability parameters, and also have a fairly wide range of pharmacological characteristics.
Material Content:
The composition of the drug
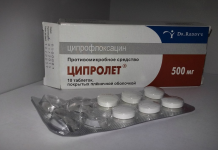
Antibacterial eye drops contain 0.003 mg of the main compound - the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Also, the composition of this medication contains other anti-inflammatory compounds: mannitol, disodium edetate dihydrate, benzalkonium chloride, acetic acid, purified water. The drug is produced by pharmaceutical companies in the form of a 5 ml dropper bottle.
Pharmacological properties
The main active compound refers to antibiotic agents from the group of fluoroquinols, which combine a whole range of pharmacological effects. Ciprofloxacin exhibits therapeutic activity against bacterial microorganisms that retain their resistance to penicillins, tetracyclines, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides and some other antibacterial drugs.
The pharmacological effect is due to the ability of the drug to penetrate into pathogenic microorganisms, and then affect the possibility of their further vital activity and development at the DNA level.Due to the therapeutic effect of ciprofloxacin, the formation of new pathogenic bacteria stops, which as a result leads to the elimination of the cause of the disease.
This medication is also able to exert a bactericidal effect on most gram-negative bacteria that are in a period of rest and division. Impact on gram-positive microorganisms is carried out during the period of their direct division. A distinctive advantage of Ciprofloxacin is that an addictive effect develops rather slowly to this remedy. Also, the medicine has a cumulative property, as a result of which there is a constant therapeutic effect.
What Ciprofloxacin Drops Help
Ciprofloxacin refers to drugs with antibacterial activity and antimicrobial effects. In medical practice, this drug is most in demand for the treatment of various forms of conjunctivitis and similar diseases that are accompanied by an inflammatory process.
And also there are a number of other inflammatory diseases in which the use of this drug is advisable:
- Blepharitis and blepharoconjunctivitis (an inflammatory disease of a chronic nature in which there is a lesion of the outer edge of the eyelid).
- Conjunctivitis of the eye.
- Barley (acute purulent inflammation of the sac of the eyelash, mucous membrane of the eyelid or sebaceous gland).
- Keratitis or keratoconjunctivitis (an inflammatory disease with clouding that affects the cornea of the eye).
- Bacterial corneal ulcer.
- Injury to the mucous membrane of the eye, which led to tissue damage by infection.
- Chronic dacryocystitis (inflammatory lesion of the lacrimal sac of the eye).
And also this antibacterial drug is prescribed by ophthalmologists after surgery to prevent the development of an infectious disease, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process.
Instructions for use of the antibiotic
Before applying these eye drops, it is recommended that you carefully study the instructions for use.
The dosage and duration of therapy is determined by the established diagnosis:
- With blepharitis and conjunctivitis - one or two drops up to 8 times a day. The duration of the course is a maximum of two weeks.
- Patients with keratitis will need one drop 6 times a day. The duration of treatment is from two weeks to a month.
- With a bacterial corneal ulcer, in the first 6 hours, drip one drop every 20 minutes. Then - every 30 minutes. The next day - every hour. From the third day until the second week of treatment, the patient uses the medicine every four hours.
- In the case of dacryocystitis, drops are used every two hours for two weeks. Dosage - one drop.
- Patients with trauma should use the drug every 5 hours for two weeks.
During therapeutic treatment, time intervals should be strictly observed to avoid overdose.
Elderly patients and children dosage adjustment is not required.
During pregnancy and lactation
Ciprofloxacin eye drops are not used during gestation and lactation. For therapy, it will be necessary to search for a substitute, since the main active compound is able to penetrate the placental barrier and provoke the development of negative consequences (delayed fetal development, arthropathy). The substance is also excreted in breast milk, so lactation should be abandoned during therapy.
Drug interaction
According to the results of studies, ciprofloxacin combines well with other drugs. With parallel use with medicines from the quinoline group, an increase in theophylline level in blood plasma is noted. Also during therapy, the absorption of caffeine is reduced, the effect of anticoagulants is enhanced.With the combination of ciprofloxacin with cyclosporine, the concentration of creatinine in the blood increases. It should not be combined with any alkaline solutions.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
In the annotation to the described drug, a list of contraindications is indicated, in which it is strictly not recommended to use Ciprofloxacin eye drops.
These conditions include the following list:
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- children up to one year old;
- in case of inadequate reaction to a specific component from the composition;
- individual intolerance to the antibiotic compound.
In the event that a patient with any of the above contraindications uses these drops for the eyes, the occurrence of undesirable reactions is not ruled out. However, in some cases, side effects are the result of an allergic reaction and intolerance to the component composition.
The patient may experience the following side effects:
- Allergic manifestations: intense burning sensation, discomfort, mild pain, itching and lacrimation.
- Increased swelling.
- Temporary loss of vision.
- Increased sensitization to daylight or artificial light.
- Keratopathy or keratitis.
- Corneal Infiltration.
- The appearance of spots.
If undesirable reactions occur on the part of the visual organ, the patient should refuse to use a drop. With an overdose, there is an increase in negative manifestations, as well as possible damage to the cornea. The victim should seek help from a specialist.
Analogs
Analogues of eye drops Ciprofloxacin have a similar pharmacological effect, and are also prescribed for the same diseases. The composition of synonymous drugs may vary. Such substitutes include the following medicines: Ciloxane, Sulfacil, hydrocortisone ointment, Vitabact, Albucid, Toradex. The selection of a similar drug should be carried out during consultation with an ophthalmologist.