Thyroid insufficiency is a pathology of the endocrine system, which is accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood or their inferiority. The disease is manifested by a delay in development, apathy, prolonged closure of fontanelles. For early diagnosis of hypothyroidism in children in maternity hospitals, all newborns are screened. If abnormalities are detected, the kids are sent for additional examinations - ultrasound, scintigraphy, blood tests.
Material Content:
Causes of congenital and acquired hypothyroidism in children
Congenital hypothyroidism in children occurs due to malfunctions in the functioning of one of the three organs of the regulatory system - the hypothalamus, pituitary, and thyroid gland.
Such factors can provoke the appearance of a primary disease:
- fetal malformations of the thyroid gland;
- adverse effects of environmental factors on the pregnant woman (radiation, chemical agents);
- intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- the use of certain drugs during the gestation of the baby (thyreostatics, bromides, heavy tranquilizers);
- lack of iodine in the nutrition of the expectant mother;
- autoimmune thyroiditis in the history of mother;
- accommodation in endemic areas.
Secondary hypothyroidism (which does not depend on the state of the thyroid gland) occurs due to abnormalities of the pituitary and hypothalamus, genetic defects of hormones, and tumor formations in the brain.
Acquired hypothyroidism develops in an initially healthy child due to a negative effect on a small organism:
- foci of inflammation in the thyroid gland;
- neoplasms in the endocrine organs;
- injuries or surgical interventions on the thyroid gland;
- dysfunction of iodine metabolism;
- lack of iodine rich foods.
To prevent hypothyroidism, it is recommended to use iodized salt and foods (seaweed, seafood, fruits).
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Symptoms of hypothyroidism in children may vary and depend on the form of pathology.
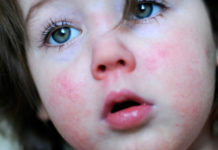
With a congenital disease, children have a large mass and a characteristic painful appearance:
- cyanosis of the area between the nose and lips;
- swelling of the eyelids, lips, other soft tissues;
- a disproportionately large tongue that falls out of the mouth;
- rude crying;
- jaundice that does not pass more than 10 days.
At an older age, there is a lag in development, up to the onset of cretinism, prolonged closure of the fontanel, and slow tooth growth. Sick children of low stature, have a weak level of mental development, are prone to various chronic diseases. The early start of substitution therapy will help to avoid unpleasant consequences, and the child will be able to lead a full life.
At three to four months of age, dry skin, gastrointestinal problems in the form of constant constipation, and a decrease in body temperature are noted. The patient's face is puffy, over time there is a deformation of the bones on the skull, arms and legs.
In older children, the development of hypothyroidism can be recognized by a change in behavior:
- lethargy;
- delayed response to irritants;
- secrecy of emotions;
- memory impairment, learning problems;
- difficulty communicating with peers;
- loss of appetite;
- excess body weight, puffy appearance;
- reduction and dullness of hair.
At the initial stages, the symptoms are erased, it can be confused with other diseases and even just with a bad mood.
If a previously cheerful child began to constantly be in a depressed mood - this is a reason to beware and consult an endocrinologist.
The disease may have an asymptomatic course - subclinical hypothyroidism. It does not interfere with the functioning of internal organs, but is manifested only by clinical changes in the blood test.
Diagnostic measures
For the early detection of pathology, all newborns are obligatory screened on the 4th - 5th day of life: a few drops of blood are taken from the heel and the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone is determined in it. If the result is positive, a second test is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
To differentiate the disease and determine the cause, the kids are sent for additional examinations:
- determination of the level of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- analysis for the concentration of ATPO;
- thyreoliberin test;
- ultrasound and x-ray of the thyroid gland.
If you experience symptoms of hypothyroidism at an older age, you should contact your family doctor who will conduct an examination and schedule a study.
Treatment of hypothyroidism in children of different ages
The treatment for hypothyroidism is replacement therapy, which will need to be taken for life.
It is important to start drinking drugs as early as possible to prevent the development of cretinism. Children, whose treatment began in the first two weeks of life, lead an active lifestyle and are no different from their peers.
Medications
The basis of treatment is a synthetic thyroxine analogue that must be taken throughout life. An individual dose of the drug is selected for each child, since the sensitivity to hormone therapy is different for everyone. To support the body, resort to the use of vitamins and nootropic drugs.
Subclinical hypothyroidism does not need treatment, but patients should constantly monitor the level of hormones in the blood.At the late start of treatment, when cretinism has already developed, it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, but regular use of the drug improves the quality of life of such patients.
Folk remedies
With the help of traditional medicine, you can not get rid of hypothyroidism, but some methods and recipes help the body cope with the lack of hormones:
- a decoction of dill seeds will reduce puffiness;
- herbs with a laxative effect will help get rid of constipation - sorrel, cystic, rhubarb;
- improve digestion, normalize intestinal motility, based on chamomile, mint, dill, caraway seeds;
- burdock oil to improve hair quality;
- St. John's wort struggles with depression;
- hawthorn and ginseng will increase stamina, relieve constant drowsiness, normalize sexual function.
An important role is played by nutrition. To improve well-being, you need to eat foods rich in iodine - sea fish, kelp, cod liver, champignons, seafood.
Possible complications
Thyroid hormones affect almost all organs, so their lack leads to serious complications:
- cretinism;
- stunting;
- frequent infections due to low immunity;
- disruption of the central nervous system;
- accumulation of fluid, swelling;
- digestion problems;
- autoimmune diseases;
- increased risk of oncology.
In adulthood, the early appearance of atherosclerotic plaques, the development of a stroke or heart attack are possible. Sick women and men most often cannot have their own children due to sexual dysfunction.
Prediction and prevention of pathology
The prognosis of the disease depends on the cause of hypothyroidism, the age of the patient, the time of initiation of therapy, and its correctness. With the timely appointment of substitution medicines, the child quickly catches up with peers in development. Lack of therapy or going to the doctor too late leads to irreversible consequences.
Prevention of hypothyroidism is the use of a normal amount of iodine with food or, if necessary, with medicines. In endemic regions, pregnant women are prescribed iodine preparations for the entire period of bearing the baby.