In many, the diagnosis of herpes is associated with inflammation in the form of vesicles near the mouth. But there are many varieties of this virus. Herpes type 6 in children is a frequent, but poorly studied pathology, the symptoms, causes and methods of treatment of which will be discussed in detail below.
Material Content:
What is herpes type 6
HHV-6 is similar to other types of virus, but it also has many differences. The herpes simplex virus type 6 in children often affects lymphocytes, is resistant to antiviral agents.
Infection is divided into two types:
- A is a neurotropic virus, it plays a role in the development of multiple sclerosis.
- B is a more common species that causes the development of childhood roseola, lymphoproliferative and immunosuppressive diseases.
HHV-6 babies are more prone to three years of age.
How is the virus transmitted?
Once entering the body, herpes remains in it for life.
Unfortunately, it is not in our power to protect children from this virus, because it is transmitted not only through direct physical contact with the carrier, but also by airborne droplets. For example, a child can catch an infection in a kindergarten, talking with peers, using toys and utensils with them, because it’s hard for kids to explain that you can’t drink from another mug with another boy or girl.
In addition, the virus can be transmitted "by inheritance" to the baby by the mother during the period of fetal development or when passing through the birth canal at the time of birth.
After the first infection, antibodies begin to form in the blood, so the rash goes with or without treatment. Further, without reason and prerequisites, relapse begins.That is, even if the child was ill once, and then did not contact the carriers, herpes will again appear, but in a different form.
Signs and symptoms of HHV-6 in a child
From the moment of infection in children, the symptoms of type 6 herpes do not appear immediately. The incubation interval lasts from one to two weeks.
Further, the development of the disease can occur according to two scenarios:
- The baby begins a fever, accompanied by a high temperature (from 39 to 40.5 degrees). The heat can last from three to five days, while many children have an increase in lymph nodes, runny nose.
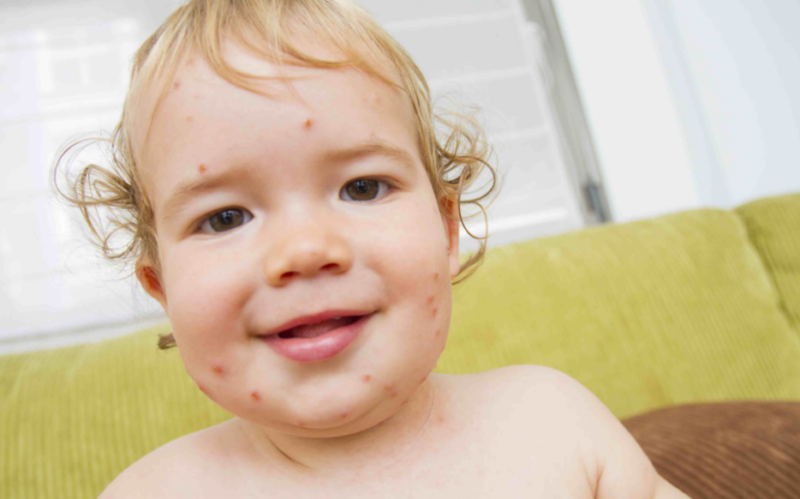
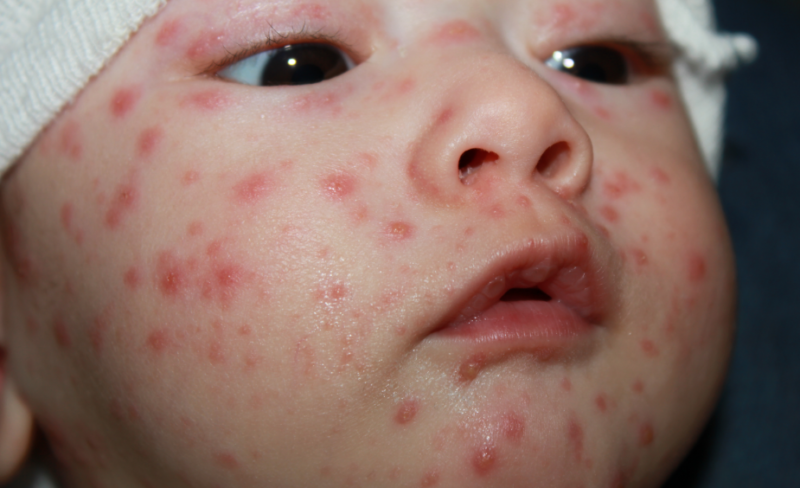
- After the temperature drops, within a day, a sudden exanthema — roseola — appears on the child’s body, characterized by a rash on the skin in the form of pink flaky spots. The first rash appears on the back, then begins to spread to the stomach, to the area behind the ears, neck and limbs.Symptoms are confused with rubella, but you can quickly refute it by pressing on the spot. If it turns pale, then the baby has roseola, if not, rubella.
- Literally, within two days the rashes disappear, small rough areas remain, but even they leave without a trace in the next couple of days.
The second development option is without the appearance of spots. A baby is tormented by a fever from 3 to 5 days, high temperature is very difficult to get off. Further, the child fully recovers without showing any more symptoms.
During the illness, when the fever has already subsided, but spots have appeared, children are active. Rashes do not bother them, the appetite does not disappear. Only a pediatrician can make an accurate diagnosis after examination.
Diagnostic measures
Not all patients are assigned an analysis to detect the virus. The doctor will send for diagnosis only in case of a severe course of the disease, when it is necessary to accurately and quickly identify the virus that caused the enlargement of the lymph nodes. Once the results are obtained, the doctor will be able to prescribe a suitable antiviral medication.
Two types of analysis are usually assigned:
- CPR - detection of virus DNA in biological fluids (blood, saliva, urine).
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (detects the presence of specific antibodies).
Diagnostic measures are prescribed only during a period of very high temperature.
When a rash appears on the child’s body, it is pointless to conduct tests to identify the type of virus, because by the time the results are obtained, the baby is completely recovering.
Treatment of viral disease in children
At the first manifestations of infection, it is even difficult for a specialist to recognize the type of virus, but as soon as the baby has a high fever, you need to show it to the doctor. You can’t just start a course of antiviral drugs, because herpes is resistant to many.
The treatment of herpes type 6 involves an integrated approach. Be sure the doctor will prescribe an antiviral drug that suppresses herpes. Dosage is calculated based on the age of the patient.
The following anti-HHV-6 drugs have proven themselves well:
- Foscarnet;
- Lobucavir
- "Zidofovir";
- "Ganciclovir";
- Adefovir.
To reduce the temperature, it is necessary to give an antipyretic medicine:
- Ibuprofen
- Nurofen
- "Panadol";
- Tsefekon.
For infants, medicines are used in the form of rectal suppositories, as they begin to act quickly, without irritating the gastrointestinal mucosa. You can use syrup to relieve heat in children from a year.
A child with fever is prone to dehydration. To avoid this, you must follow the drinking regimen. Give the baby decoctions of herbs (cloudberries, chamomile, currant leaves), berry and fruit compote, fruit drink.
As already mentioned earlier, the rash does not bother the child, so there is no point in conducting special treatments. In order for the patient to recover quickly, he is prescribed a course of vitamins.
After the baby has had type 6 herpes, he develops stable immunity.Further, “colds” may appear on the lips or on the mucous membrane in the nose, but this disease will not be accompanied by roseola and fever.
Consequences and Complications
What is the virus dangerous?
There are many consequences that herpes of type 6 leads to:
- Infectious mononucleosis. Manifested by fever, enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, liver.
- Often after HHV-6, a child develops a sore throat.
- Dangerous and very high temperature. Heat leads to febrile seizures - rolling eyes, fainting, involuntary muscle contraction. These convulsions can further provoke the development of epileptic seizures.
In very rare cases, the consequences are more serious. A child may develop pneumonia, myocarditis, meningitis, or encephalitis. That is why it is important at the first symptoms of herpes to go to the hospital and strictly adhere to the doctor's recommendations.
Prevention
The complications of herpes are quite serious, and the disease itself is very difficult for the baby. Therefore, it is necessary to take all possible measures to prevent infection with this virus.
Pediatricians recommend the following activities:
- Proper nutrition is the key to strong immunity. The baby should receive from food all the necessary trace elements, vitamins, fats and proteins.
- Exchange rate seasonal consumption of antiviral drugs.
- Lack of close contact with people who carry herpes.
Do not allow unauthorized persons to use the dishes of the child, even toddlers. If the guests were children and played with the toys of your child, you need to disinfect them in the future. This is a simple but necessary precaution, which will reduce the likelihood of a baby getting herpes.
Children to whom the virus could be transmitted from the mother should receive many vitamins, and during the period of colds and flu, they must undergo an antiviral treatment course.
For some, herpes is a common virus present in the blood of almost every person. For others - a huge problem that I want to get rid of completely and forever. But it is important to understand that herpes is a life partner if it has once entered the bloodstream. Do not worry too much about the presence of this disease, because thanks to it, many other viruses will pass by as the immune system of the herpes carrier is always on guard. But it is simply impossible to neglect a dangerous condition, especially in children, because the lack of therapy can lead to serious consequences.