One of the most serious liver diseases is viral hepatitis, which is transmitted through the bloodstream and “ripens” for a long time, asymptomatic. If you do not detect the disease on time and do not start treatment, then it can develop into cirrhosis of the liver and lead to death. Hepatitis C, the symptoms of which are almost not manifested during the period of infection and incubation, is one of the most severe varieties of this disease.
Material Content:
Forms and stages of the virus
Viral hepatitis C is an infectious disease of the liver, which is characterized by inflammation and the gradual death of liver cells, which leads to irreversible damage to the organ. This serious illness was discovered only in the 80s and still does not have effective preventive measures, such as hepatitis B, from which vaccinations exist.
The causative agent of the disease is a virus of the family Flaviviridae 30-60 nm in size, which contains RNA. Only 11 genotypes of the virus were detected, and some of them have their own subtypes. For countries of Eastern Europe, only 4 genotypes of the hepatitis C virus are characteristic - subtype 1b, 3, 1a and 2.
They differ from each other in aggressiveness and pathogenicity. The most dangerous is the 1 genotype of the virus, which penetrates the body through the blood, and the most common is the subtype 3a, most often found among drug addicts.
In total, there are two main ways of infection:
- Through the blood when using unsterilized needles (injections, manicures, tattooing) or during childbirth;
- Through seminal fluid during intercourse (only 5% of cases).
Once in the bloodstream, the virus reaches the liver and begins its defeat, simultaneously weakening the immune system. Unfortunately, the infection and the incubation period are asymptomatic, so the person simply does not know that he is already sick.
There are 3 stages of the course of the disease:
- Acute form - lasts the first 2-20 weeks after infection, when the body can overcome the virus (only in case of very strong immunity) or the disease will gradually go into the second stage. Full recovery occurs only in 15% of cases, the remaining 85% in these 20-25 weeks may begin to manifest acute hepatitis C.
- Latent form - can last up to 20 years, not accompanied by symptoms at the same time. The disease simply “ripens” in the body, but markers already appear in the blood and the liver can be enlarged.
- A form of reactivation - hepatitis C virus begins to proliferate, leading to degeneration of liver tissue and their death.
Any person can become infected with viral hepatitis C simply by going to an unscrupulous manicurist who does not sterilize instruments or who receives unverified blood during transfusion. It is difficult to protect yourself from this disease, but you can detect it in time and start therapy.
The first signs in men and women
Worldwide, there are more than 600,000 million patients with hepatitis C and their number is growing annually. Scientists call this massive defeat a silent epidemic, since most infected people are unaware that they are sick.
The incubation period lasts from 2 weeks to 6 months, and during it a person does not experience any discomfort that would force him to see a doctor, which is typical for 80% of patients.
In the remaining 20%, the first clinical manifestations of the disease occur 2-3 months after infection and are extremely similar to the common cold, among them:
- constant fatigue;
- heat:
- frequent headache;
- body aches;
- decreased intellectual performance.
 The acute stage of the disease is accompanied by such symptoms, but after a while it becomes chronic, which is characterized by nothing but constant fatigue and frequent ailments. How many people in the modern world pay attention to these symptoms?
The acute stage of the disease is accompanied by such symptoms, but after a while it becomes chronic, which is characterized by nothing but constant fatigue and frequent ailments. How many people in the modern world pay attention to these symptoms?
Signs of hepatitis C in women are almost no different from men, with the exception of changes in the latter in the menstrual cycles - menstruation can be much more painful than usual, characterized by a high profusion of discharge. Sometimes bleeding can begin in sick women, but most often this is attributed to changes in the hormonal background.
Characteristic symptoms
After the incubation period, the chronic stage of the course of the disease occurs, which is also able to proceed asymptomatically. Nevertheless, in a blood test, the patient may reveal characteristic markers or notice an increase in the liver by ultrasound.
In 60% of patients can also be observed:
- heat;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
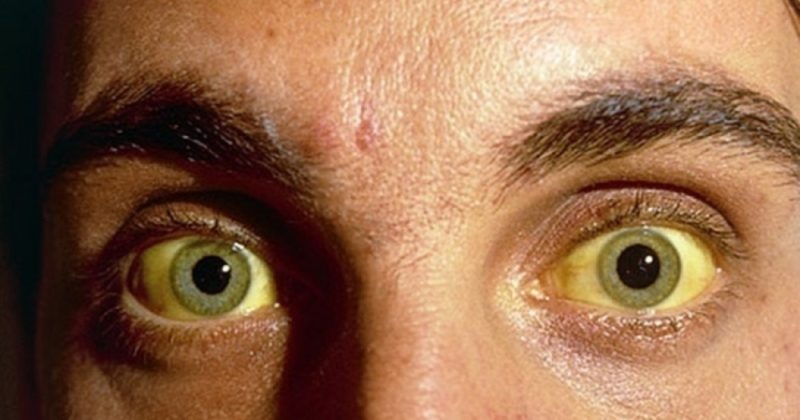
- yellowing of the skin and eyeballs;
- nausea and diarrhea;
- joint and muscle pain;
- discoloration of feces;
- dark urine.
These symptoms may be mistaken for manifestations of a cold or jaundice, but they require attention and a mandatory preventive examination by a doctor.
Diagnostic measures
After detecting alarming symptoms, a person should contact a therapist to refer him to an infectious disease specialist or gastroenterologist. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the treatment will be handled by a hepatologist specializing in viral hepatitis. To begin with, the patient is sent for a blood test to determine the presence of antibodies to the hepatitis virus (anti-HCV).
 To confirm the diagnosis, a potential patient must undergo a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations:
To confirm the diagnosis, a potential patient must undergo a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations:
- Biochemical blood test - the level of bilirubin is studied and the enzymes AlAT and AsAT are monitored.
- The RNA of the virus and its genotype are detected.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity to determine the condition of the liver and its size.
- A liver biopsy, CT scan or MRI scan is done to determine the degree of fibrosis.
After making an accurate diagnosis, an analysis of the viral load is also carried out - this is the determination of the amount of virus in the blood. This indicator is necessary for the choice of therapy, tracking positive dynamics and also affects the success of treatment.
General treatment for hepatitis C
Hepatitis C therapy aims not only to reduce liver inflammation, but also to reduce the amount of virus in the body. Despite the large number of genotypes of the pathogen virus, treatment for hepatitis C is standard - it is based on the use of interferon-alpha, which prevents infection of liver cells and stops its inflammation.
Standard HCV therapy involves taking medications containing interferons and ribavirin, or taking a combination drug that contains these substances. This treatment regimen is approved by WHO and has a 95% recovery rate despite severe side effects.
During therapy, patients take powerful hepatoprotectors to protect unaffected liver tissue and slow down fibrosis. This treatment method gives good results and in most cases leads to a complete recovery. Although sometimes the genotype reacts poorly to antiviral drugs and then the treatment period increases from the standard 6 months to 12.
New to virus treatment
In the last decade, new drugs have been developed that contain several active compounds and are direct-acting drugs.
Among them are drugs:
- Sofosbuvir;
- Velpatasvir;
- Daclatasvir;
- Ledipasvir.
The mechanism of manifestation of these substances is similar to antibiotics of antibacterial action - the molecules of the substance are embedded in the RNA of the virus and destroy it, thereby stopping the reproduction and spread of inflammation.
The advantages of the new therapy are its duration - the course of treatment is 3 months, and the disadvantage is the cost of about 400-500 dollars.
Diet for HCV
The main rule of therapy for HCV is the rejection of alcohol and drugs. Small doses of ethyl alcohol not only negatively affect the liver, but also activate the virus, accelerating its reproduction. This makes antiviral therapy pointless and speeds up the fibrosis process.
 As for food, there are no strict restrictions; doctors only recommend to refuse or significantly reduce the consumption of food fatty, fried and spicy. It will be reasonable to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet during the course of treatment - eat balanced dishes, give up bad habits, cook in a double boiler, etc.
As for food, there are no strict restrictions; doctors only recommend to refuse or significantly reduce the consumption of food fatty, fried and spicy. It will be reasonable to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet during the course of treatment - eat balanced dishes, give up bad habits, cook in a double boiler, etc.
Life expectancy with disease
This question can be answered only by studying a specific patient and various features of his disease, from the virus genotype to the history of the disease. Chronic hepatitis C can “sleep” from 2 to 20 years, which depends on the strength of the patient’s immunity, his lifestyle, the presence of bad habits, the speed of diagnosis and the start of therapy.
In 20% to 80% of patients with HCV without treatment, cancer or cirrhosis of the liver eventually develops, so it all depends on how quickly the patient starts treatment. Some develop cirrhosis in 2 years, while others live to old age, starting treatment on time. The question is not how long one can live with hepatitis C, but how quickly it can be detected in order to start therapy, because this disease is completely treatable.
Preventive measures
Unfortunately, there is no single effective vaccine against HCV, so you cannot protect yourself from the disease.
How is the prevention of the disease recommended:
- Visit only professional dentistry and nail salons, monitoring the quality of sterilization of instruments or insisting on the use of disposable ones.
- Do not use drugs.
- Protected during sexual intercourse with a condom.
- Do not use other people's hygiene items that may contain blood (razors, toothbrushes, earrings).
- Take regular tests and undergo examination by a doctor.
It is impossible to completely protect against hepatitis C, but regular examination and testing will help to identify the disease in the early stages and begin therapy.












