A vascular tumor is a colored spot with a flat or elevated surface. By itself, it is not dangerous, but it can grow into neighboring organs and interfere with their work. In addition, there were cases of malignancy of education - degeneration into oncology. The causes of hemangiomas in newborns are not fully known, there are several theories of their appearance, but none have been proven. Treatment of the pathology depends on the type and location of the tumor - possibly surgical or laser removal, cryodestruction, hormone therapy.
Material Content:
What is infant hemangioma?
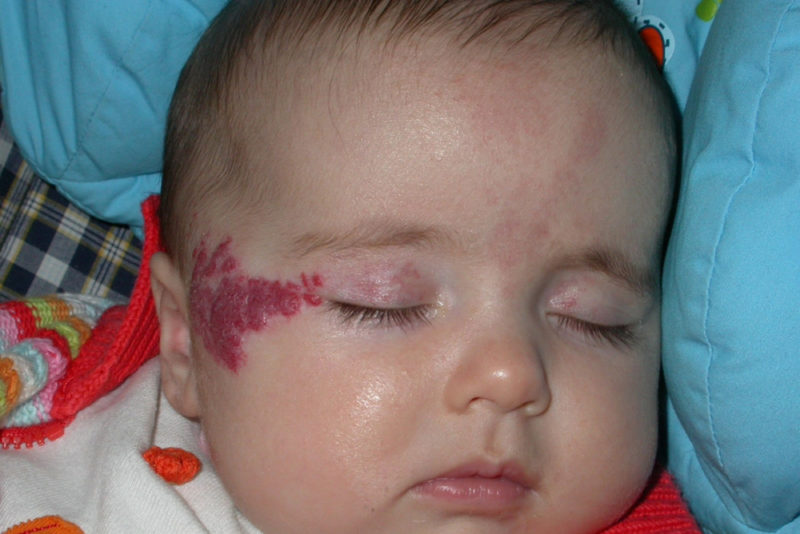
Skin hemangioma is a benign tumor formed by vascular endothelial cells. It occurs in 10% of children in the first year of life. A neoplasm can occur on the skin, mucous membranes, and even on internal organs. In boys, it is diagnosed twice less than in girls.
Despite the fact that the formation is benign, it is prone to rapid growth, proliferation in different directions and the destruction of surrounding tissues.
Hemangioma on the face can provoke a violation of the functions of vision, hearing. In addition, complications such as infection, ulceration, or bleeding are common.
Types of pathology
The classification of formations according to morphological characteristics distinguishes three types of pathology:
- simple (the second name is capillary);
- cavernous (cavernous);
- combined.
Capillary hemangioma does not penetrate further than the epidermal layer of the skin, has clear boundaries and a tuberous structure. In its structure there are only endothelial cells.Characteristic is a blue-purple color. The spot turns pale when pressed, and then quickly returns to its original color.
Cavernous hemangioma is located in the deeper layers of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. It consists of a large number of clots filled with blood. Outwardly, it looks like a swollen bruise, elevated above the surface of the skin. When pressed, the blood flows from the lumps, so the tubercle turns pale, and when the pressure rises, for example, due to a cough, it turns a deeper color and increases.
With a combined hemangioma, the neoplasm combines the signs of both forms of pathology. In addition, it can consist not only of blood vessels, but also of other tissues: nervous, connective, lymphoid.
Causes of occurrence
So far, it has not been possible to prove the connection of the occurrence of hemangiomas with any concomitant pathologies or external influences.
It is assumed that trigger factors may include:
- viral diseases of the mother during pregnancy in the early stages (3-6 weeks) - at this time the laying of the cardiovascular system;
- negative Rh factor of the mother and positive in the fetus;
- the use of medicines that adversely affect the unborn child;
- the use of alcoholic beverages, tobacco products;
- hormonal disruptions in the body of a pregnant or baby;
- poor ecology in the woman’s place of residence;
- hereditary addiction.
These factors are only hypothetical, the presence of none of them does not guarantee the appearance of hemangioma.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of pathology is the study of topography and the depth of germination of education. Examinations are carried out by several doctors at once - the therapist, surgeon and dermatologist. It is important to distinguish a vascular benign tumor from squamous cell carcinoma, or glomus, nevus or cyst, pyogenic granuloma.
Hemangioma in newborns on the head must be examined by a neonatologist, ophthalmologist and ENT specialist. In some cases, you may need to consult a gynecologist or urologist, orthodontist and other specialists.
During the initial appointment with the therapist, the doctor will conduct an examination, palpate the neoplasm and determine its surface area.
Then he will give directions for additional examinations:
- blood test to control its coagulability;
- ultrasound examination of the tumor;
- assessment of blood flow velocity and blood supply inside the hemangioma;
- contrast radiography of local vessels;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography.
In children with hemangioma, blood coagulation is often impaired, so it is important to regularly monitor coagulation and platelet concentration in the blood.
Tumor treatment
The choice of treatment depends on the results of the examinations. In the neonatal period, wait-and-see tactics are needed - monitoring the tumor. If the formation does not change the size and color, does not interfere with the functioning of neighboring organs, then it is left until the patient is a little older. If hemangioma is characterized by aggressive growth, is a life threat, then conservative or surgical removal is performed.
Treatment of hemangiomas in children is carried out in several ways:
- surgical - surgical intervention;
- conservative - cryotherapy, sclerotherapy, electrocoagulation, radiation therapy.
During the operation, the surgeons completely or partially excise the tumor tissue, and the patient’s skin flap is transplanted to an open area from another part of the body. This method is indicated for significant sizes of education, with its rapid growth, malignant localization. In childhood, surgical interventions are performed only in extreme cases using general anesthesia.
- Cryotherapy consists in freezing hemangiomas with carbon dioxide. The method is effective only against small formations (up to 2 - 3 cm in diameter).Cold is applied to the affected area, creating local artificial frostbite. After some time, a fossa appears at the site of the tumor, which turns into a bubble, it bursts, the wound surface is covered with a crust and is tightened by healthy skin.
- When the tumor is located in hard to reach places (vulva, eyelid, mouth), they resort to sclerotherapy of its vessels. This will require several injections with 70% alcohol and quinine-urethane, which are carried out with an interval of several days.
- With the help of electric current, coagulation and necrosis of hemangioma tissue is achieved, which is covered with a crust and heals like a normal wound.
- Radiation therapy negatively affects the entire body, therefore, it is resorted to only in life-threatening situations - localization of cavernous hemangioma on internal organs. The use of this method is possible only from the age of six months.
Hemangioma and vaccinations
Despite the fact that there is an opinion on the Internet about the connection of vaccinations with the growth of hemangiomas, this fact has not been scientifically confirmed. In the first months of life, the child is given many routine vaccinations, and this period coincides with an active increase in tumor size. But the vaccines themselves do not affect the neoplasm in any way.
Danger and consequences
The presence of hemangiomas requires constant monitoring by a doctor.
Despite the fact that it seems harmless, in some cases, pathology is capable of dragging grave consequences:
- germination in surrounding tissues and organs, violation of their functions;
- compression of the spinal cord and, as a result, paralysis;
- the development of anemia;
- decreased platelet count in the blood;
- infection of formations;
- bleeding
- the appearance of ulcerative surfaces;
- malignancy;
- defect in appearance.
The most terrible is the malignancy of hemangiomas. In order not to miss a dangerous condition, you need to pay attention to the slightest changes in the tumor: the appearance of nodular areas, loosening of tissues, peeling, inflammation, an increase in local temperature, a different color of the spot.