A furuncle is called an acute inflammatory-purulent formation on the skin, starting with inflammation of the hair follicle with subsequent involvement of subcutaneous tissues in the process, which causes golden or white staphylococcus. How to quickly cure a boil at home and prevent complications?
In everyday life, pathology is called an abscess or boil. The boil can form on any part of the body, except the palms and soles, where there are no hair follicles, but more often develops on the face, back of the head, back, buttocks, hips, and in the ear canal.
With the spread of the process (the formation of multiple abscesses), or their frequent appearance, the disease is diagnosed as furunculosis.
Material Content:
- 1 Causes of the boil
- 2 Symptoms of a boil
- 3 Treatment of a boil at home
- 4 Ointments and agents that accelerate the breakthrough of an abscess
- 5 Boil removal
- 6 Care for the foci of the abscess after opening
- 7 When to start drinking antibiotics?
- 8 Alternative methods for treating boils
- 9 Treatment of furunculosis in children
- 10 Nutrition for furunculosis
Causes of the boil
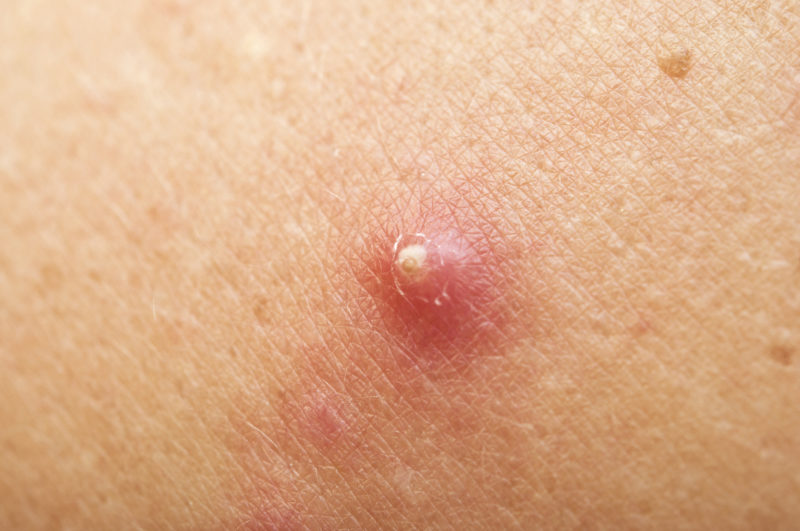
The main causes of this pathology include:
- excessive sweating, excessive secretion of sebum, acne;
- rare flushing and frequent skin contamination;
- hormonal imbalance;
- the consumption of foods that are poor in vitamins, an excess of trans fats, fast carbohydrates in the diet;
- low immune defense (local and general);
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine, neurological disorders, blood diseases, blood vessels;
- intestinal dysbiosis, hepatitis;
- foci of recurrent chronic diseases in the body;
- chronic poisoning, including intoxication with alcohol and industrial substances;
- prolonged stressful conditions.
The degree of danger of an abscess is associated with its location.
The greatest risk of complications is from abscesses that occur on the head (especially in the area of the lips and nose), on the back of the head and neck, in the groin, in the folds of the buttocks, in the armpit, in the depth of the ear canal.
These areas are saturated with a large number of blood and lymph vessels located close to the surface, so pyogenic organisms easily enter the bloodstream, causing:
- abscess of the meninges, meningitis, septic phlebitis of cerebral vessels;
- inflammation and thrombosis of the lymphatic and venous ways, phlebitis of the facial veins;
- lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- multiple lesions with purulent metastases of the liver, kidneys, heart, joints;
- blood poisoning.
Symptoms of a boil

Painful symptoms are associated with the stage of development of the abscess.
- Stage of infiltration.
Tingling, itching occurs on the skin, and after 1 to 2 days a painful hardening and redness appears.
2. The stage of ripening.
On the 3rd - 4th day in the center of the infiltrate, an inflamed conical node rising from the skin level from 2 to 50 mm in size is formed. The skin acquires a crimson color, becomes hot, swelling of the tissues progresses. The patient suffers from severe “jerking” pain.
On the 5-7th day, the abscess swells even more, blushes, and on its top in the form of a yellow-white head, a pustule is formed - a bubble with pus. Inside, in the center of the node, a core is formed and compacted, consisting of dead (necrotic) tissues and pus.
On the 7th - 9th day, the abscess is opened with the expiration of a large amount of purulent discharge. The inner core is rejected for another 1 to 2 days. After opening the pain, they immediately subside, and the inflammatory phenomena decrease.
3. The stage of healing.
The ulcer at the site of the opened abscess is cleared of residual contents and is gradually tightened by scarring, acquiring a reddish-cyanotic color.
General signs of the disease manifest themselves in different ways, which depends on the location of the boil, its size, and the patient's age.
If the inflamed node is large, located in the head region, or there are multiple formations on the skin, there are: fever, chills, headache, nausea, in the blood - increased ESR, increased white blood cell count.
The duration of the pathological process, provided the time taken for treatment from 10 to 12 days.
A boil should be distinguished from ostiofolliculitis - superficial inflammation at the outlet of the hair bulb, acne - acne, in which acne appears due to impaired outflow of sebum, and inflammation of the ducts of the sweat glands in infants.
Important! Do not miss the development of more severe pathologies, the signs of which are similar to the symptoms of a boil. They require intensive antibiotic therapy, surgical treatment only in a hospital. These include: carbuncle, abscess, hydradenitis ("bitch udder"), phlegmon.
Treatment of a boil at home
How to get rid of a boil at home, given what phase of maturation it is in.
Treatment at home is possible only if the boil is small (up to 5 mm), there is no fever and signs of poisoning with bacterial toxins (nausea, weakness, headache).

Immediate medical attention is required in the following abnormal conditions:
- the temperature rises (from 37.5 C);
- symptoms of inflammation and infection of adjacent tissues appeared - the redness area around the abscess increases;
- for a long time the “head” does not mature (more than 7 days);
- a large inflamed node formed in a child younger than 10 years old;
- an abscess appeared on the face, neck or in the ear canal;
- pathology occurred in a patient with heart disease, immunodeficiency, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, cancer, while taking antitumor, hormonal drugs, drugs that suppress the immune system.
What can not be done:
- Squeeze, puncture and cut the boil.Such manipulations very often lead to a wide spread of infection, the development of an abscess, facial vein thrombophlebitis, infection of brain tissue and general blood poisoning with a high risk of death of the patient.
- Use warming procedures in the first phase - when only redness of the skin, tightening and soreness is observed, but a clearly shaped conical bulge has not yet formed. It also contributes to the deepening and expansion of the infectious process.
- With a different diagnosis, some medical and folk remedies can be harmful. So, Vishnevsky ointment is not used for lymphadenitis, suppurative lipoma, and is not used on the face.
Ointments and agents that accelerate the breakthrough of an abscess
Local treatment of the abscess is aimed at accelerating the process of maturation and opening of the abscess, reducing swelling, pain, preventing the spread of inflammatory phenomena to neighboring tissues.
Before applying ointments, it is necessary to treat the skin around the abscess with 3% hydrogen peroxide, salicylic, boric, camphor alcohol from the edges of the inflammation zone to the center to prevent dissemination of the purulent process.
Iodine and zelenka are not recommended due to a possible burn and masking of skin manifestations in the area of inflammation.
You should not spend money on expensive drugs, because old, but effective means are much more effective.
External products that help to mature the “head”, soften the epithelium and reduce pain:
- Salicylic acid in the form of an ointment 10% or powder;
- Levosin, Vishnevsky ointment, Ichthyol, Bactroban, Yodditserin.
Dressings with Vishnevsky, Ihtiolova, Levosin ointment, which activate blood circulation in the suppuration zone, lead to accelerated maturation of the boil. Twice a day, use the so-called "ichthyol cake", applying pure ichthyol to the abscess and covering it with a small loose layer of natural cotton wool. When drying, “cake” is easily washed off with boiled water. Procedures are done 2 times a day, until pus expires.
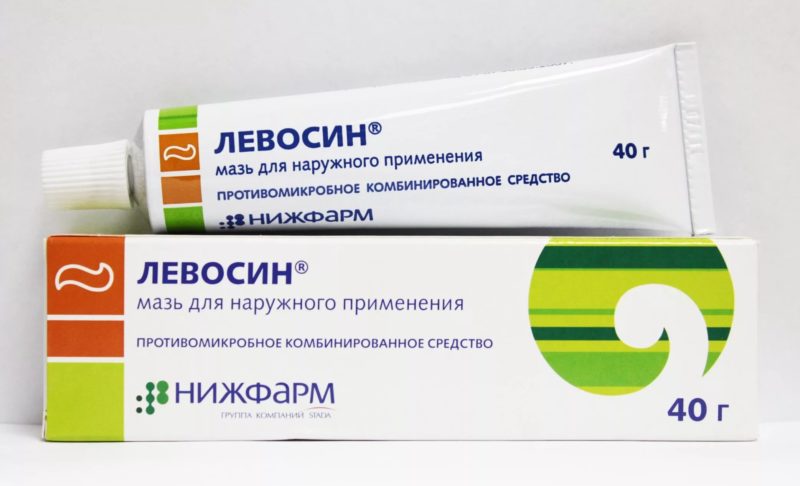
The liniment of Syntomycin draws out pus even with protracted pathological processes.
- If the outlet of the central purulent-necrotic core is delayed, special enzymes are used, both in the form of a solution, and in the form of powder: immobilized trypsin 0.5-1%, chymotrypsin, chymopsin. They contribute to the rejection of dead tissue, facilitate the release of pus, liquefying it, accelerate healing.
Important! Many surgeons actively object to the use of moist warming compresses, poultices, explaining this by maceration (wet swelling) of the skin around the abscess, which facilitates the spread of infection.
Therefore, to accelerate the maturation of the abscess head, it is better to use dry compresses, which are carried out up to 10 times a day for 15 minutes.
Apply either a natural heated tissue or a bag of fine salt, which actively disinfects the inflamed area, accelerates maturation and limits the inflammatory process, preventing it from expanding.
Important! Remember that no thermal procedures are permissible at elevated temperatures.
It is good to irradiate the inflamed area with ultraviolet light (if there is a UV lamp at home) or allow the sun's rays to warm it and disinfect it. According to the doctor's prescription, UHF currents are used at the ripening stage.
With severe “jerking” pain, it is advisable to take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Ketanol, Analgin in combination with Paracetamol (half a tablet);
- externally, to reduce pain, apply a bandage with silver nitrate (1% solution).
Boil removal
Doctors insist that independence in removing a festering formation is dangerous, but if the boil has already "matured" and is not in the head area, you can be especially careful to help it open.
How to understand that an abscess can be opened?
You should wait for the stage at which the boil is already "ready" to burst on its own.This stage is characterized by the following features:
- Suppuration lasts at least 7 days.
- A protruding white-yellow lesion has formed at the top of the inflamed node.
- The area of redness around the cone of the abscess decreased and became more clearly defined, delimiting it from healthy skin.
Remember! Opening up an absent abscess, you only "help" the infection spread deeper into neighboring tissues.
The operation to open the abscess and remove the rod
- It is advisable to wear glasses to prevent purulent secretions from entering the mucous membrane of the eye.
- Treat the entire area of inflammation with alcohol. Carefully pierce the purulent tip with a sterile needle from the syringe (preferably slightly from the side). This does not hurt, since there are no nerve receptors in this area.
- Collect leaking pus with sterile wipes, constantly changing them. Do not use cotton wool - its fibers clog the channel of the outflow of pus.
- If a dense shaft appears along with pus, gently pull it out with forceps. The stem from dead cells and pus is removed only when it is fully formed and separated from adjacent tissue.
- You can very easily press on the boil from below to remove all its contents until the sucrose (fluid with blood) appears from the wound.
If you made a mistake with the ripening stage and see that the pus is not removed completely, do not continue to press on the seal.
- Treat the wound with hydrogen peroxide (3%) and apply a gauze dressing with Levosin ointment or Levomekol ointment.
If the pus will accumulate again, or the rod has not yet been torn away, 2 to 3 days will have to repeat the procedure for removing the contents.
Attention! Contact your surgeon immediately:
- if the temperature rises, the general condition worsens;
- if the abscess is opened, but the rod has not come out, or the purulent contents come out for more than 3 days;
- if the area of redness has increased, swelling, hardened, or became brighter;
- if jerking or dull soreness intensified, or spread to a neighboring area.
Care for the foci of the abscess after opening
How to treat a boil after it "broke"?
The center after opening every day before the application of the therapeutic ointment is treated with hydrogen peroxide and gauze dressings impregnated on it with NaCl solution for a period while the wound is cleansed of discharge.
Since the wound bed after opening is a purulent wound, the use of antibiotic local drugs is required, destroying the entire pathological flora.
Use: Stellanin-PEG, Levomekol and Levosin, Lincomycin 2% ointment, Bactroban, Mupirocin, Tomicide, Dimexide, Gentamicin, Bactrian, Ioddicerin, Polcortolone, Iruksol, Oflokain, Fusidin-sodium gel.

Keep in mind that Vishnevsky ointment and Ichthyolova after opening are not applied to the wound itself, but applied to the area around it. Means dissolve stagnant processes, thus accelerating the outflow of contents, prevents infection of healthy surfaces.
If everything is done correctly, and the pathological process subsides, then on 2-3 days the elevation on the skin and redness around it decreases and takes on a clear boundary, the edema subsides.
When the wound begins to overgrow, covered with a crust, do not remove it, as it protects the inlet and covers the delicate, newly emerging tissue. If you do not touch the crust, the likelihood of gross scarring is minimal. At this stage, it is possible to gradually cancel all antibacterial ointments, lubricating the healing area with “green”.
In principle, surgical procedures in a hospital are not much different from a home procedure. But the surgeon has more treatment options.
So, if the formation cannot be completely freed from the pathological contents, the doctor puts a drainage - a special tube or turundum, through which the discharge goes out.
In addition, the doctor often pricks the diseased area with antibiotics with an anesthetic solution (blockade), which very quickly leads to the resolution of the process and prevents its spread.
When to start drinking antibiotics?
Antibiotic therapy for boils is necessary only in certain conditions.
Antibiotic drugs taken in tablets or administered intramuscularly are prescribed for 5 to 10 days in the following cases:
- if the foci of suppuration is more than 5 mm;
- if there are many ulcers;
- if the temperature rises and signs of intoxication appear;
- if the abscess is in the groin, armpit, on the back of the head, near the nose or lips, inside the nostrils, in the ear;
- there is a complication in the form of lymphangitis and lymphadenitis;
- the process deepens to the development of carbuncle, abscess, hydradenitis, phlegmon;
- in patients with diabetes mellitus, severe pathologies of the kidneys, heart.
Most often prescribed:
- Macrolides - Erythromycin, Spiramycin or cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cephalexin);
- Cloxacillin (for adults 4 times a day, 500 mg each), Rifampin 600 mg once a day, Clindamycin in a daily dose of 150 mg;
- Lincomycin (Mitsivin, Lyocin), Fusidine;
- Trimethoprim, Rimactan, Sulfamethoxazole, Rifampicin, Doxycycline, Vibramycin, Minocycline;
- sometimes - dicloxacillin.
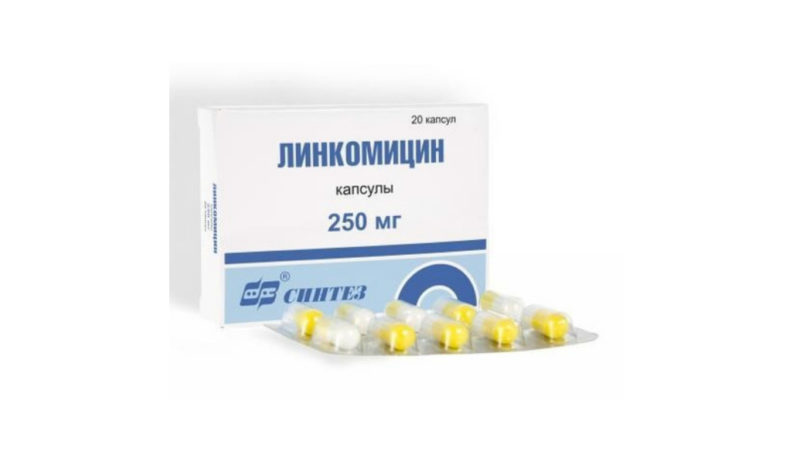
Staphylococcus is able to quickly gain resistance to antimicrobials, so you should not prescribe them yourself. In many cases, it is necessary to conduct bacterial "culture" - a study on the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics.
In cases of skin lesions with a methicellin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus, the doctor may prescribe Vancomycin.
In addition, antibiotic therapy is often combined with the appointment of sulfonamide and antihistamines, such as Pipolfen, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, calcium chloride, which reduce the sensitivity of cells to bacterial poisons and toxins of decaying tissues.
Alternative methods for treating boils
Folk remedies are effective as an auxiliary therapeutic agent.
Doctors did not agree on the correct use of warming moist compresses.
Many experts fear that this will only aggravate the process. Therefore, all folk remedies using lotions, compresses, wet procedures should either be agreed with the doctor, or carefully monitor the "behavior" of the abscess during the use of such funds. At the slightest deterioration, increased compaction or redness, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Among home recipes that help speed up the process of stretching pus and forming the head of a boil, the following are considered the most effective:
- Scones made from a mixture of rye flour, warm water and honey. A thick mass is applied to the site of inflammation, changing after 3 to 4 hours. This procedure gives the result at an early stage, when the boil has not yet formed. Often suspends its development.
- After opening the abscess, salt lotions with ordinary and iodized salt can be used every 4 hours. To get a saline solution of the desired concentration for adults, mix 3 tablespoons of salt (not more) with 1 liter of water. To treat a child, take 2 teaspoons in a glass of boiled water.
- Stretching pus with a bow. The onion is cut, baked for 30 minutes in the oven at 180 ° C, then the flesh is densely distributed in the suppuration area, fixing with a soft bandage. Change after 5 - 6 hours.
- Raw potato treatment. Rub the vegetable, squeeze it, sometimes add a teaspoon of honey, and make dressings with therapeutic mass up to 3-4 times a day.
- Stretching pus with aloe or “agave.” Cut a young tender leaf, remove the thorns and knead. A bandage is applied to the boil, which is changed 5-6 times a day. With a ripening boil, all processes are accelerated, and the abscess opens faster. Apply at any stage.With an absent boil in the early stage, the complete abatement of inflammatory phenomena is possible.
- At the stage of expiration of the contents from the opened abscess, aloe juice is mixed with olive oil in equal parts, moistened with gauze and put on it, secured with parchment and bandage. They hold such a compress for 12 hours, then make a new one.
- Buckwheat porridge on the water. Boiled buckwheat is also used to treat boils. A spoonful of very thick porridge is spread on cheesecloth, applied to an inflamed place, changing to a fresh mixture after 4 hours.
Treatment of furunculosis in children
Furunculosis is an abnormal infectious condition in which a large number of skin abscesses appear on the skin at different stages of development. Furunculosis can be limited, manifesting in separate areas or general (common, disseminated), in acute and chronic form.
The development of multiple foci occurs after the spread of infection from the primary focus. This often happens in the absence of antiseptic treatment and improper opening of boils.
Adolescence is the period in which furunculosis often occurs for reasons such as:
- underdevelopment of the immune system and skin structure (especially in babies younger than 5 years old);
- hormonal imbalance;
- activity of sebaceous, sweat glands;
- digestive tract diseases, dysbiosis, dermatitis;
- frequent microtrauma, contact with contaminated objects during games;
- poor hygiene, poor nutrition.
Furunculosis in infancy is treated only stationary.
In pediatrics, in the treatment of furunculosis, they resort to surgical treatment, and to the appointment of the same drugs as for adults, but at age dosages.
Apply:
- Antibiotic drugs, including cephalexin powder for suspension and fusidin sodium, which can be used in the treatment of infants.
- Without fail, the child is given vitamins of group B, nicotinic acid, vitamin A and C. In severe cases, vitamins are prescribed in ampoules.
- A simple way to saturate the body with vitamin B is to take brewer's yeast in tablets, which is very often used for furunculosis.
- In order to strengthen local and general immunity at an age-specific dose and taking into account possible allergic reactions, mummies, tincture of Eleutherococcus, Aralia, Pantocrine are used.
- Pharmacy preparations for the stimulation of protective forces are used only after the permission of the pediatrician. These include Seramil, Derinat, Myelopid, Lycopid, Polyoxidonium, Octagam, Intraglobin.
Nutrition for furunculosis
The diet provides for the restriction of carbohydrate and fatty foods, hot spices. The diet includes more products such as sea and river fish, brown bread, yeast, cereals with a high content of vitamin B (buckwheat, oatmeal), vegetables (especially carrots), berries, fruits. Fiber products cleanse the intestines, preventing intoxication of the body with poisons and decay products. You need boiled meat, liver, an abundance of sour-milk dishes that inhibit putrefactive processes.

Do not forget about a small amount of natural butter (without processing) and any kind of vegetable oil.












