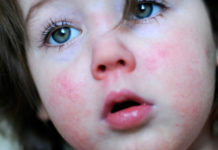
Our skin, like a mirror, reflects the processes taking place in the body. Peeling, pigmentation, itching, pustules and pimples eloquently indicate some pathologies. Because young mothers are so worried when the velvet skin of a child suddenly changes its quality. Follicular keratosis is one of the most harmless dermatological diseases that parents face. But, despite the relative harmlessness, treatment of follicular keratosis is necessary and requires medical supervision. Having heard such a diagnosis, do not panic, but do not start the process, in the hope that "it will pass by itself." After all, the health of a child is a fragile system in which nothing happens just like that.
Material Content:
What is a disease?
We hear the heart beating, the stomach growling and the lungs breathing. We see the result of the bladder and intestines. Everything seems to work in the body and only the skin does nothing. But this, of course, is not so. Waking up in the morning with one skin, in the evening we go to bed with the other, although we do not notice the process of its change. But only until problems arise. One of them is keratosis.
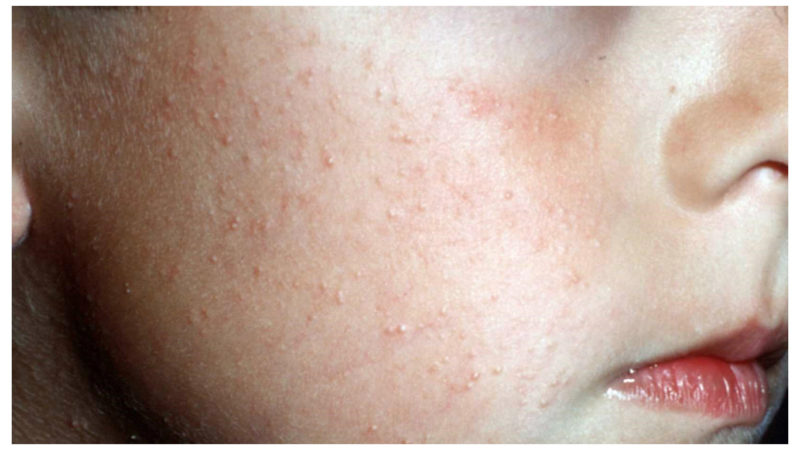
The epidermis is constantly and continuously updated. In its thickness, new, young cells are produced, and the upper ones die off and exfoliate. But sometimes this process is disrupted.Then the old cells do not have time to make room for new ones, clog pores and hair follicles. As a result, the skin is covered with small white tubercles - papules and becomes like a goose cover. Actually, that's what the people call keratosis - goose bumps.
Types and classification
Depending on the severity, causes, and other factors, follicular keratosis is different. It is impossible to independently determine its type, and there is no reason to. Let the dermatologist tackle this issue.
Hair deprive
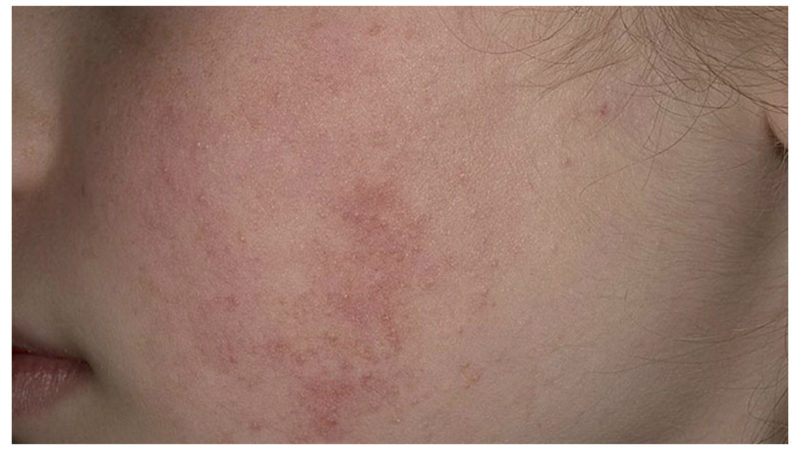
Classical follicular keratosis. It manifests itself as nodules on the skin, which can sometimes become inflamed. Do not itch, do not form plaques. Usually, the disease manifests itself in early childhood and independently disappears after the end of the puberty period.
Persistent lenticular hyperkeratosis of Flegel
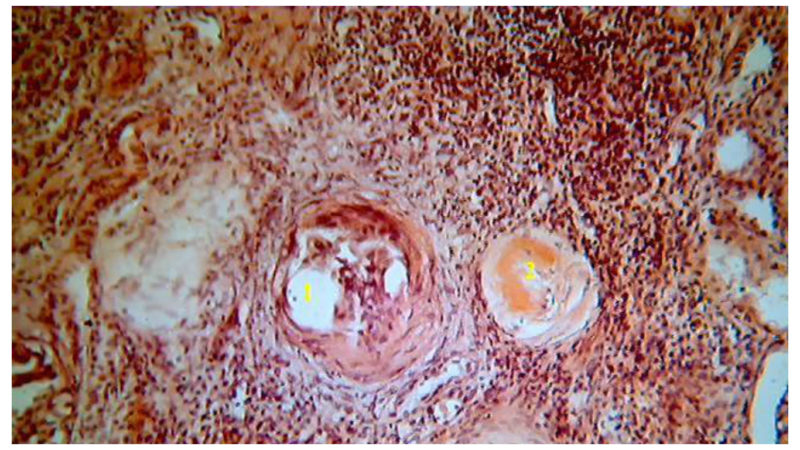
The disease is presumably hereditary and usually first manifests itself already in adulthood. Small reddish papules are localized on the feet and palms. When the formation is removed, a bleeding funnel is detected under it.
Devergy's disease
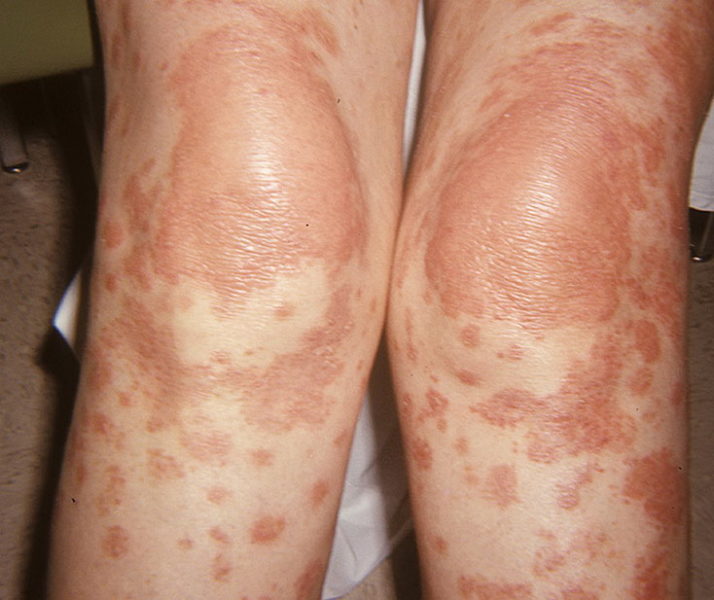
It can manifest at any age. The etiology is unknown. Usually it begins to spread from the head, where it appears with thick scales, as with seborrhea. It develops for months, or even years. Later, a characteristic sign of the disease appears - spiky red papules with scales on top. They are localized on the extensor sections of the arms and legs. The foci of the rash quickly spread throughout the body.
Superciliary Ularythema
The etiology is unknown, both a hereditary predisposition and the infectious nature of the infection are assumed. It is usually diagnosed in children and adolescents. It is characterized by the appearance of nodules above the eyebrows and on the forehead. Over time, hair loss occurs.
Follicular Keratosis Morrow - Brook
An inherited type of transmission of the disease is suspected. It manifests itself at any age and begins with dry feet and hands. Over time, the already described nodules arise. In the absence of treatment, it affects the nails, the entire surface of the skin. Often this type of keratosis is difficult to distinguish from Darier's disease.
Daria White's disease
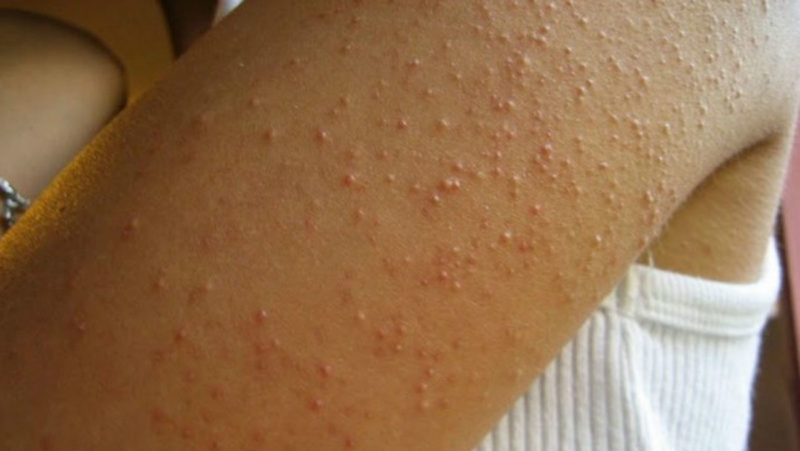
Pathology is hereditary. White nodules on the skin become covered with a yellowish crust over time and may have a specific unpleasant odor. The lesion area increases, plaques are formed, which are usually located symmetrically. This process is accompanied by itching and often leads to infection.
Squamous follicular keratosis Doha
Most often manifested in adolescence among residents of China and Japan. It is characterized by lesions in closed areas of the skin (buttocks, abdomen). Rashes are multiple, but without signs of inflammation.
Read also: seborrheic keratosis of the skin
What does follicular keratosis look like?
Even if mom knows the Soviet medical encyclopedia by heart, and the nearest hospital is 100 km away, it’s dangerous to do home diagnostics. The fact is that many other diseases can resemble follicular keratosis.
In addition, keratosis can be both an independent problem and a symptom of other, very serious pathologies.
Classic follicular keratosis in a child does not look too neat, but also not repulsive. Usually it is manifested by the appearance of single tubercles rising above the surface of the skin. Inside this formation is a dense white or yellowish content. Unlike acne, these tubercles do not occur in the sebaceous glands, but inside the hair follicle. Therefore, the tip of the hair is often visible over the formation, or it can be considered inside.
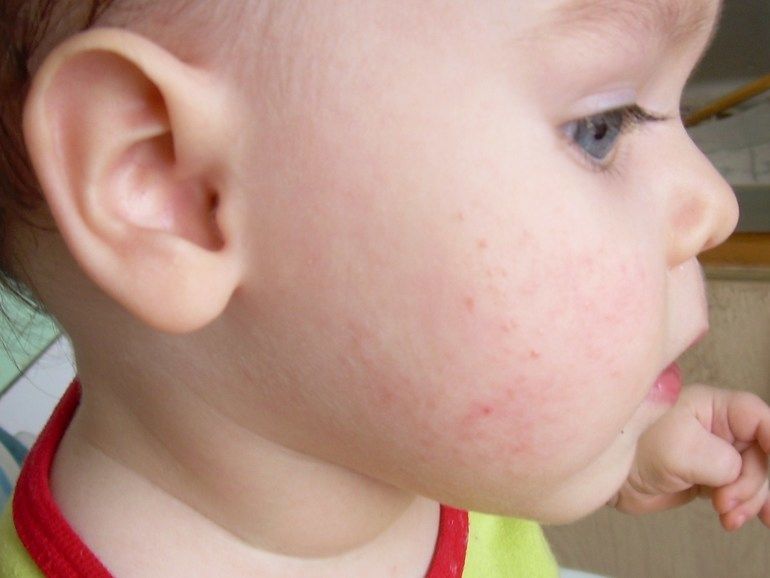
To the touch, such rashes are dense and, unlike acne, non-inflammatory, and therefore do not cause discomfort. “Pimples” can be only a few or a whole scattering. In the latter case, the affected area feels like coarse sandpaper to the touch. Certain types of hair loss can form plaques of various sizes.In neglected forms, they merge with each other and form increasingly extensive lesions.
The epidermis, damaged by follicular keratosis, usually retains its normal color, but may also turn red under adverse conditions. It is possible that the child will rip off the "bumps" that irritate him and then the inflammatory process will probably join. This situation complicates the diagnosis and is fraught with dangerous complications.
Causes of follicular keratosis
The true causes of the pathology have not yet been reliably determined. And this is another argument not in favor of self-treatment. It is known that the disease can be congenital or acquired.
- In children, congenital keratosis is most often manifested. Experts say that the vast majority of cases are caused by heredity. However, this condition can occur suddenly in children whose parents have never encountered it.
- Acquired keratosis is usually characteristic of adults. It can provoke:
- adverse working conditions;
- taking medication;
- more complex pathologies (for example, cancer);
- malfunctions of the endocrine system;
- nervous exhaustion and diseases of the nervous system;
- other factors.
Vitamin A, E and C may cause acquired keratosis in children.
The disease most often proceeds in a mild form, especially if the patient lives in a humid, warm climate. But in winter, as well as in windy or hot weather, the problem can manifest itself with renewed vigor. Exacerbation also provokes nervous tension, an impoverished diet, and insufficient hygiene.
Symptoms and locations
Usually, in addition to "goose bumps", the disease is not accompanied by other symptoms. Unless, of course, itself is one of the signs of other pathologies. Sometimes the affected areas itch, which is caused by dry skin.
Rashes can be localized anywhere. But in children, keratosis prefers to appear on the cheeks, hips, shoulders. If the problem is left unattended, then the lesion area will gradually increase. Then the skin becomes rough on the arms, legs, between the shoulder blades, on the chest.
Which doctor to contact
If you do not like the quality of your child’s skin, do not self-medicate. Many mothers change their diet, daily bathe the baby in a string and chamomile, smear Antoshka cream from head to toe ... Take your child to a dermatologist! Jokes with skin can end sadly, and for the scars and scars remaining after home treatment, the grown child is unlikely to say thanks.
A dermatologist may take a skin scraping to rule out a bacterial infection. It will give a referral for a blood test, which will show the general condition of the body and the pathology search path. In addition, along with keratosis in the child, concomitant dermatological problems can be found that the mother does not see.

Consult a pediatrician, but if you have the opportunity to show your child a specialist in skin diseases, use it.
Treatment of follicular keratosis. Preparations for adults and children
The effectiveness of therapy is largely determined by the cause of the problem. Often, it remains unexplained for a long time if other symptoms are absent. Then it is conditionally considered that the disease is independent and the principles of its treatment are reduced to eliminating a cosmetic defect. Often follicular keratosis, like teenage acne, manages to outgrow.
An important role in the effectiveness of treatment is played by the regularity of the prescribed procedures.
Therapy usually comes down to long courses of treatment of the affected areas:
- salicylic ointment;
- urea-containing preparations;
- water soluble petroleum jelly.
Also, the child is shown regular hygiene procedures. Warm baths, gentle exfoliation of dead epithelial cells, moisturizing with baby milk, folk remedies.In addition, at an older age, adolescents may be given a course of laser or phototherapy.
But the diet practically does not play a role in the treatment of the disease. Of course, it is not advisable to include fried, smoked, spicy and other things in the daily children's menu, but this factor does not affect the course of follicular keratosis. But it is very important to enrich the diet with vitamins A and E, because their content in the menu should be increased.
Traditional medicine methods
Dermatological problems are often treatable with folk remedies, but to completely eliminate follicular keratosis by methods of alternative medicine will not work. Nevertheless, compresses with some products can alleviate the condition, soften the skin and moisturize it.
Propolis

A universal cure for all problems. The benefit of propolis in the case of follicular keratosis is that it helps the skin retain moisture. You can apply it on the entire affected surface at night or for the whole day, if possible. It is advisable to do this after caring procedures and applying therapeutic ointments.
Beet

Peel the root crop and rub it raw or chop it in a blender. Wrap the beets in a bandage and make compresses for the child. Please note that the juice of this vegetable has an insidious ability to color everything it comes into contact with. Therefore, if your child in the morning to school, abandon the idea of leaving the compress for the night.
Potatoes

Grate potatoes on a fine grater, squeeze out excess juice. Wrap the pulp in gauze or a sterile bandage and attach to the area damaged by keratosis. Change compresses every 2-3 hours.
Yeast

A compress can have some effect on live yeast. It is applied if there are no open wounds on the skin. Keep the yeast compress on problem areas for a couple of hours. Please note that the smell of this product is not for everyone, choose a different tool if the child does not tolerate yeast.
Aloe

It nourishes, moisturizes, has an antibacterial and antiseptic effect. After aloe, it certainly won’t be worse, unless of course you decide to replace it with the main treatment. Both aloe and Kalanchoe gain strength with age, so choose older leaves. Cut them thin plates along and apply to the sore areas. Aloe dries quickly enough and after that leaving it on the skin is already pointless.
Onion peel

Compresses prepared in this way are undesirable for young children. Refrain from using them if the child has sensitive skin or damage is present on it.
Grind onion peel to powder. Take 4 tablespoons of the product, transfer to a container of dark glass, pour a glass of vinegar. Tincture should mature for two days. With a filtered solution, moisten a gauze swab and apply to the affected areas. If the child has a burning sensation, immediately remove the compress.
Before treating follicular keratosis in children with any of the methods described, make sure that there are no “live” wounds, inflammations, burns on the skin. Before starting such therapy, attach the product to a healthy area of the skin and check for an allergic reaction.
Keep in mind that treatment can only be concomitant, but not at all basic, therefore a visit to a doctor is strictly necessary.
Disease prevention
Due to the fact that the causes of keratosis are reliably unknown, it is not yet clear how to prevent it. And in the case of a genetic defect, the question is not at all worth it. If the child has already been diagnosed with this, then you can try to avoid exacerbation, to keep the disease under control.
- As a preventative measure, daily, thorough, but gentle skin hygiene is mandatory. Babies are shown baby soap, a soft washcloth and a short stay in water at a comfortable temperature.
- Explain to older children that it is impossible to solve the problem by “peeling off” the skin with a scrub and a hard washcloth.Make sure that the growing child does not squeeze pimples to prevent infection. Ointments with lactic acid or urea will come to the aid of the younger generation.
- Pay attention to diet. The menu must necessarily contain products containing vitamins E and A. These are vegetable oils, rose hips, nuts, carrots, table greens. It is enough to season the daily salad not with mayonnaise, but with vegetable oil and sprinkle it with herbs and crushed nuts, providing a daily norm of vitamins.
- In the cold season and in the heat it is important to treat the skin with petroleum jelly, moisturizers, in order to avoid critical moisture loss.
- Revise your favorite child’s wardrobe. Take away products from artificial material. Pay special attention to winter clothing. To avoid contact with rough skin irritating skin, choose a child's high-quality natural linen.
Follicular keratosis is not considered a dangerous or complex disease, but do not ignore it. Be sure to go through a full examination with the child, exclude all possible concomitant diseases, and only then proceed with a clear conscience to eliminate the cosmetic defect.