Epilepsy is a neurological pathology. The disease, as a rule, manifests itself in infants at an early age (3 - 5 years). In today's article, we will analyze what constitutes a disease, find out the causes of epilepsy in children, treatment methods and first aid for an attack.
Material Content:
Causes and symptoms of epilepsy in children
Epilepsy is a serious disease that is chronic in nature. During the illness, the child develops convulsions, seizures, and the baby may lose consciousness. All these processes arise due to malfunctioning of the brain centers.
Experts still can not name the exact causes of epilepsy in children.
Among the most common are the following:
- hereditary factor;
- birth injuries that lead to changes in the structure of the brain;
- intrauterine infections;
- other diseases (e.g., Down syndrome);
- brain tumors;
- severe head injuries;
- viral or infectious diseases that affect the brain (e.g., meningitis).
As a rule, the disease begins to appear when the child is 3 to 5 years old. For parents, this becomes a real shock.
Symptoms of epilepsy in infants and older children vary.
Signs of the disease in babies up to a year:
- During feeding, the skin around the nasolabial triangle changes color. It turns blue.
- An involuntary twitching of the limbs occurs (do not confuse with tremor). The twitches are sharp, resembling a cramp.
- Focusing your gaze at one point. In this case, the child does not respond to external stimuli.
- The muscles on the face go numb, after relaxation an eye tic is noticeable.
- After the attack, the baby begins to cry a lot.
In children under one year old, epilepsy is extremely rare. But if such symptoms are present, parents should immediately consult a doctor. Pathology at this age is insidious in that irreversible processes can occur in the brain that will lead to a child’s disability.
In older children, epilepsy in most cases manifests itself as follows:
- The child loses consciousness.
- Beats in a fit.
- Arms and legs cramp.
- Foam can come out of your mouth.
- After the attack, the child does not remember anything.
But it is not always these symptoms that may indicate epilepsy. With sleepwalking, frequent nightmares, sensory hallucinations in children, you also need to be wary. All of these signs may indicate changes in the structure of the brain.
Types and forms of seizures
Epilepsy may differ in the form of seizures in children:
- Generalized (convulsive) seizures. They are considered one of the most difficult and dangerous. It all starts with an aura. Goosebumps can run through the child’s body, chills are often felt. After this, the muscles become very tense, breathing is delayed, the child screams and falls to the floor unconscious. Convulsions and convulsions are observed throughout the body, foam comes out of the mouth, eyes roll up. At this point, the child does not control the body, there may be spontaneous bowel movements or urination. The attack can last up to 20 minutes. After him, the child does not remember anything.
- Small seizures. Characterized by the fact that there are no cramps. The child abruptly “turns off”, his gaze is absent, his head is thrown back. The kid does not respond to extraneous sounds, light. After 15-30 seconds, he returns to normal, not remembering anything about the stupor. Many might think that the baby just thought about something. This type of seizure is called absences.
- Children's spasm. It occurs in children under 4 to 5 years. It occurs, as a rule, after waking up. The muscles tighten, the head and body involuntarily leans forward, hands are pressed to the chest. The spasm lasts 5 to 10 seconds.
- Atonic seizures. The child suddenly loses consciousness, the muscles relax. There are no convulsions or convulsions. Many confuse this phenomenon with fainting. In fact, this is also a form of epilepsy.
With any form of epilepsy, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo a series of studies.
Diagnosis of the disease
Epilepsy is a neurological disease that requires extensive diagnosis and thorough treatment. At the first sign, you need to contact a pediatrician. He, in turn, will give direction to a neurologist or epileptologist.
After a visual examination, the specialist should prescribe a series of examinations:
- MRI
- CT
- deprivation;
- detailed blood test.
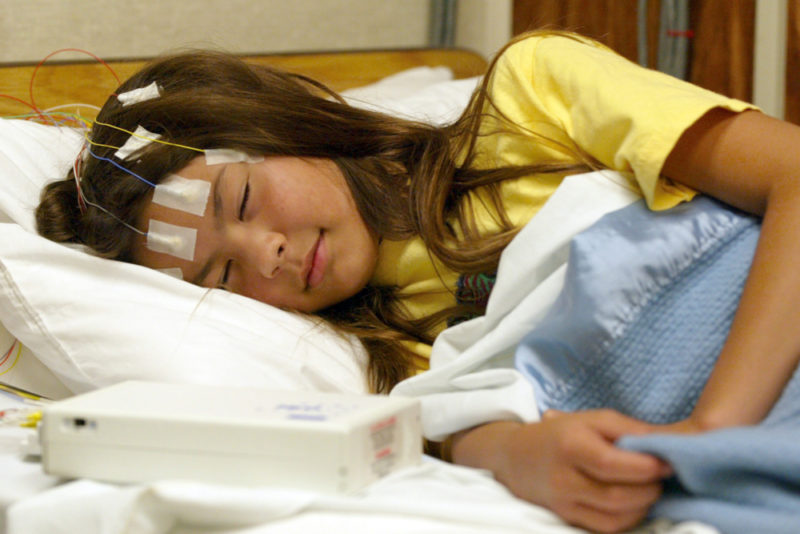
An electroencephalographic study is also prescribed, which is carried out in a dream and while the child is awake. Such an analysis is best done with video recordings in order to get an accurate picture of brain activity and changes that occur in its structure.
It is worth noting that in some cases, studies need to be carried out several times. Not always a neurologist from the first time can make an accurate diagnosis. This is due to developmental features and brain activity in children.
Treatment methods
The treatment of epilepsy in children should be prescribed by a doctor individually, based on the shape of the seizures and the general state of the structure of the brain.
The specialist can offer the following treatment regimen:
- poly / monotherapy;
- surgical intervention (in advanced cases);
- non-drug treatment (with a mild form of the pathological process).
Epilepsy is treatable. This process is quite lengthy, it takes from 4 to 7 years. In some cases, you need to take drugs throughout your life.
In addition, the child must provide the following conditions:
- The correct daily routine.
- Refusal of computer games, minimal use of gadgets.
- Special gentle diet.
- Walks in the open air.
- Avoidance of stressful situations.
- Safe sports: tennis, skiing, badminton.
Children over 5 - 6 years old are recommended to visit a psychologist.
First aid during an attack
An epileptic seizure in a child can begin anywhere and anytime.
That is why adults should know how to behave correctly and provide first aid:
- Put the child on a flat surface.
- Torso and head are better to tilt to one side. Foam or vomiting may start from the mouth during an attack. The turned head will not allow the child to choke.
- It is important to provide the patient with fresh air. If the child is indoors, you need to open a window or balcony.
- If the attack lasts more than 5 minutes, you need to call an ambulance team.
You can’t try to stop the attack, drink the child, or put a spoon (or other hard object) in your mouth. Thus, you can worsen the condition of the crumbs.
Prevention and prognosis of the disease
Doctors give a favorable prognosis for the treatment of epilepsy. According to statistics, if the disease is detected in children under one year of age, and proper treatment begins, then in 90% of cases the problem can be completely eliminated - the child develops normally, but is registered with a neurologist.
In older children, full recovery occurs in 70% of cases. It is important to adhere to and follow all doctor's prescriptions.
Disease prevention - parental control over the condition and behavior of the child, as well as routine examinations (by age) among specialists.
Epilepsy is an insidious disease that can lead to death. That is why when a child is found to have its first signs, you should immediately consult a specialist, undergo a diagnosis and start treatment.